* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download obstetric anatomy midw 201
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
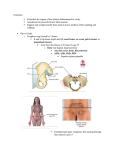
OBSTETRIC ANATOMY MIDW 201 BY ESTHER A. M. ANYIDOHO 17TH NOV., 2014 COURSE OBJECTIVES By the end of the course students should be able to: 1. Describe the female and male reproductive systems 2. Describe the physiology of ovulation and fertilization 3. Describe the placenta and its functions 4. Describe the various types of female pelvis and their relationship in labour and delivery THE FEMALE PELVIS • Objectives: By the end of the session, students should be able to: a. List the parts of the female bony pelvis b. Describe each component part of the bony pelvis c. List the types of the female bony pelvis d. List 2 effects of each type of the female bony pelvis on labour and delivery Female Bony Pelvis cont’d • General description: The bony pelvis is located between the trunk and the lower limbs of the body. It articulates superiorly with the 5th Lumbar vertebra It articulates inferiorly with the coccygeal vertebrae which form part of it It articulates laterally with the left and right femoral heads in a depression called the Acetabulum The Female Bony Pelvis cont’d The anterior border is the Symphysis Pubis. Bones of the Bony Pelvis is made up of 4 bones: 1. The Sacrum 2. The Cocyx 3. Two Innominate bones These bones together make the bony pelvis the largest bone formation in the human body The Female bony Pelvis cont’d The Sacrum: It is made up of 5 fused vertebrae. It is triangular in shape with the apex pointing downwards. It lies between the right and left innominate bones It articulates with the 2 innominate bones It has 4 pairs of foraminae (windows or holes). These communicate with the sacral canal. The foraminae serve as exit for nerves from the spinal cord at the level, blood vessels and lymphatic channels as well. The Female Bony Pelvis cont’d The Sacrum has a hollow which is the anterior concave surface. The concavity of the hollow increases the capacity of the pelvis. It has a widened portion on each of the first sacral vertebra which are referred to as alae (wings). The Promontory is the centre point of the upper border of the first sacral vertebra. This protrudes over the hollow with the fifth lumbar vertebra. The Female bony Pelvis cont’d • The Sacral canal runs longitudinally through the sacrum and opens at the level of the fifth lumbar vertebra. The spinal nerves fan out through the canal at the level of the 2nd and 3rd sacral vertebrae to form the Cauda equina • Obstetric Importance: Anaesthetic agent is introduced through the caudal canal to relieve pain from uterine contractions during labour. This causes temporal paralysis of the nerves leading to the relief of the pains. The Female Bony Pelvis cont’d • The Cocyx (Tail): This is four tiny fused vertebrae. It is also triangular in shape. The base articulates superiorly with the inferior aspect of the 5th sacral vertebra. It serves as an attachment for muscles and ligaments. • Obstetric importance: In the female, during the second stage of labour, the cocyx tips backwards to widen the exit of the birth canal for the head of the baby to pass through. The Female Bony Pelvis cont’d The Innominate Bones: These bones form the lateral aspects of the bony pelvis. Each bone developed from 3 primary centres of ossification. This formed three bones thus – Ilium, Ischium and Pubis. The 3 bones meet in cup-shaped depression called Acetabulum The Female Bony Pelvis cont’d • The ILIUM is the biggest and the uppermost of the innominate bones. The uppermost end is called the Iliac crest which is easily palpable (the waist) by the hands resting on the hips. It has four projections, two anterior and two posterior called spines. • The ilium articulates anteriorly with the antero-superior iliac spine and posteriolry, with the postero-superior iliac spine. The Female Bony Pelvis cont’d • The Antero-inferior lies approximately 2.5cm below the antero-superior iliac spine. The postero-superior iliac spines are located in the dimples at the lower back of the individual. The postero-inferior iliac spines mark the upper border of the Greater Sciatic Notch through which the Sciatic Nerves pass. • The ilium forms the upper two-fifth of the Acetabulum. The Female Bony Pelvis cont’d • The inner concave surface is smooth and the outer surface is rough for attachment of the gluteal muscles forming the buttocks. • The ISCHIUM is the lowest portion of the innominate bone. It forms the lower two-fifth of the acetabulum. It has two projections called the Ischial spine and the Ischial Tuberosity respectively. The Ischial spine terminates into the Lesser Sciatic Notch. The Female Bony Pelvis cont’d • The Ischial Tuberosity is the thickened portion of the Ischium on which the weight of the body rests in a sitting position. • The Ischial spine separates the Lesser Sciatic Notch from the Greater Sciatic Notch. • The PUBIS is the smallest bone of the innominate bone. It forms the lowest one-fifth of the Acetabulum. The Female Bony Pelvis cont’d • There are two Pubic bones which are united anteriorly to form the a square-shaped pubic bones. The two bones are fused together by a pad of cartilage in the middle, called the Symphysis Pubis. • The Superior Pubic Ramus forms the upper portion. It unites with the ilium to form the Iliopectineal eminence. The Female Bony Pelvis cont’d • The right and left descending Rami form the Pubic Arch. Its importance is during the birth of the baby, it widens out. • The Ischium and the Pubis surround a foramen called the Obturator Foramen