* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CN-0022 利用AD5546/AD5556 DAC实现精密、单极性、反相转换 .
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
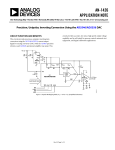
matching and temperature tracking that minimize the number of components needed for multiquadrant applications. CIRCUIT FUNCTION AND BENEFITS This circuit provides precision, unipolar, inverting data conversion using the AD5546/AD5556 current output DAC with the ADR03 precision reference and AD8628 operational amplifier (op amp). This circuit provides accurate, low noise, high speed output voltage capability and is well suited for process control, automatic test equipment, and digital calibration applications. This circuit uses the ADR03, which is a highly accuracy, high stability, 2.5 V precision voltage reference. As voltage reference temperature coefficient and long-term drift are primary considerations for applications requiring high precision conversion, this device is an ideal candidate. An op amp is used in the current-to-voltage (I-V) stage of this circuit. An op amp’s bias current and offset voltage are both important selection criteria for use with precision current output DACs. Therefore, this circuit employs the AD8628 autozero op amp, which has ultralow offset voltage (1 µV typical) and bias current (30 pA typical). The value of C7 for this circuit is 2.2 pF, which is optimized to compensate for the external output capacitance of the DAC. CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION The AD5546 and AD5556 are 16-bit and 14-bit, precision, multiplying, low power, current output, parallel input digital-toanalog converters. They operate from a single 2.7 V to 5.5 V supply with ±15 V multiplying references for 4-quadrant outputs. Built-in 4-quadrant resistors facilitate the resistance +5V 2 C2 0.1µF VIN TRIM VOUT U3 ADR03 5 +2.5V C4 0.1µF GND 4 R1 RCOM R1 R2 REF ROFS ROFS RFB C7 2.2pF RFB VDD C3 0.1µF IOUT 16-BIT/ 14-BIT U1 AD5546/AD5556 – V+ U2 AD8628 GND + 16-BIT/14-BIT DATA WR LDAC RS VOUT –2.5V TO 0V V– C5 0.1µF MSB WR LDAC RS MSB –5V Figure 1. Unipolar Multiplying Mode, VOUT = 0 V to –VREF (Simplified Schematic) www.BDTIC.com/ADI C6 1µF 08244-001 C1 1µF Note that the AD8628 has rail-to-rail input and output stages, but the output can only come within a few millivolts of either rail depending on load current. For the circuit shown, the output can swing from –2.5 V to approximately –1 mV. The input offset voltage of the op amp is multiplied by the variable noise gain (due to the code-dependent output resistance of the DAC) of the circuit. A change in this noise gain between two adjacent digital codes produces a step change in the output voltage due to the amplifier’s input offset voltage. This output voltage change is superimposed on the desired change in output between the two codes and gives rise to a differential linearity error, which, if large enough, could cause the DAC to be nonmonotonic. In general, the input offset voltage should be a fraction of an LSB to ensure monotonic behavior when stepping through codes. For the ADR03 and the AD5546, the LSB size is 2. 5 V (1) = 38 µV 216 references available from the same reference family as the ADR03. Other low noise references that would be suitable are the ADR441 and ADR445 products. The size of the reference input voltage is restricted by the rail-to-rail voltage of the op amp selected. These circuits can also be used as a variable gain element by utilizing the multiplying bandwidth nature of the R-2R structure of the AD5546/AD5556 DAC. In this configuration, remove the external precision reference and apply the signal to be multiplied to the reference input pins of the DAC. LEARN MORE ADIsimPower Design Tool. Kester, Walt. 2005. The Data Conversion Handbook. Analog Devices. See chapters 3 and 7. MT-015 Tutorial, Basic DAC Architectures II: Binary DACs. Analog Devices. The input offset voltage of the AD8628 auto-zero op amp is typically 1 µV, which is negligible compared to the LSB size. MT-031 Tutorial, Grounding Data Converters and Solving the Mystery of AGND and DGND. Analog Devices. The input bias current of an op amp also generates an offset at the voltage output as a result of the bias current flowing through the feedback resistor, RFB. In the case of the AD8628, the input bias current is only 30 pA typical, which flowing through the RFB resistor (10 kΩ typical), produces an error of only 0.3 µV. MT-033 Tutorial, Voltage Feedback Op Amp Gain and Bandwidth. Analog Devices. The AD5546/AD5556 DAC architecture uses a current-steering R-2R ladder design that requires an external reference and op amp to generate the output voltage. VOUT can be calculated for the AD5546 using the equation −VREF × D (2) VOUT = 216 where D is the decimal equivalent of the input code. VOUT can be calculated for the AD5556 using the equation VOUT = −VREF × D (3) 214 MT-035 Tutorial, Op Amp Inputs, Outputs, Single-Supply, and Rail-to-Rail Issues. Analog Devices. MT-055 Tutorial, Chopper Stabilized (Auto-Zero) Precision Op Amps. Analog Devices. MT-101 Tutorial, Decoupling Techniques. Analog Devices. Data Sheets AD5546 Data Sheet. AD8628 Data Sheet. ADR03 Data Sheet. REVISION HISTORY where D is the decimal equivalent of the input code. 5/09—Rev. 0 to Rev. A COMMON VARIATIONS Updated Format .................................................................. Universal For multichannel applications, the AD8629 is a dual version of the AD8628. The ADR01 and ADR02 are other low noise 10/08—Revision 0: Initial Version (Continued from first page) "Circuits from the Lab" are intended only for use with Analog Devices products and are the intellectual property of Analog Devices or its licensors. While you may use the "Circuits from the Lab" in the design of your product, no other license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patents or other intellectual property by application or use of the "Circuits from the Lab". Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, "Circuits from the Lab" are supplied "as is" and without warranties of any kind, express, implied, or statutory including, but not limited to, any implied warranty of merchantability, noninfringement or fitness for a particular purpose and no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for their use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from their use. Analog Devices reserves the right to change any "Circuits from the Lab" at any time without notice, but is under no obligation to do so. Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners. ©2008–2009 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners. CN08244-0-5/09(A) www.BDTIC.com/ADI