* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1. Higher Electricity Questions [pps 1MB]
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
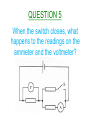
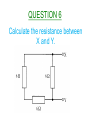
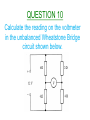
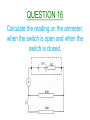
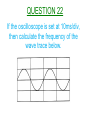
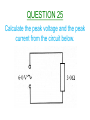
Higher Electricity QUESTION 1 What is the definition of electrical current? QUESTION 2 What is the definition of potential difference? QUESTION 3 What is the definition of electrical power? QUESTION 4 Calculate the resistance between X and Y. QUESTION 5 When the switch closes, what happens to the readings on the ammeter and the voltmeter? QUESTION 6 Calculate the resistance between X and Y. QUESTION 7 What is the purpose of Wheatstone Bridge Circuits? QUESTION 8 State two things about a Wheatstone Bridge Circuit which will indicate that it is balanced. QUESTION 9 When Rv is increased from 10kΩ, what will the graph look like of V against ΔR? QUESTION 10 Calculate the reading on the voltmeter in the unbalanced Wheatstone Bridge circuit shown below. QUESTION 11 State the definition of EMF. QUESTION 12 What is meant by a terminal potential difference of 5V? QUESTION 13 State the three variations of the EMF equation. QUESTION 14 Which two pieces of information can be taken from the graph below when it cuts the y-axis and the x-axis? QUESTION 15 Find the internal resistance of the battery from the graph below. QUESTION 16 Calculate the reading on the ammeter, when the switch is open and when the switch is closed. QUESTION 17 What is meant by the term ‘short circuit current’? QUESTION 18 Under what conditions do you have maximum power transfer in a circuit from a battery with an internal resistance r? QUESTION 19 State the mains voltage and mains frequency of the supply in the UK. QUESTION 20 State the names of the controls on an oscilloscope used to measure a)Peak Voltage b)Frequency. QUESTION 21 If the oscilloscope is set at 5V/div, then calculate the peak voltage and the rms voltage from the wave trace below. QUESTION 22 If the oscilloscope is set at 10ms/div, then calculate the frequency of the wave trace below. QUESTION 23 State two observations of the wave trace below if the oscilloscope setting is changed from 5ms/div to 20ms/div. QUESTION 24 A peak current of 0.37A flows through a lamp of resistance 885 Ω. Calculate the power of the lamp. QUESTION 25 Calculate the peak voltage and the peak current from the circuit below. QUESTION 26 What do capacitors store and what type of circuits would you find them in? QUESTION 27 State the unit for Capacitance and give another unit which is equivalent to it. QUESTION 28 State what is meant by a capacitor having a capacitance of 3000µF. QUESTION 29 A capacitor is marked 6V,120µF. Calculate the maximum charge and the maximum energy that it can store. QUESTION 30 If the capacitance and resistance are both increased in the diagram below, then sketch the new waveform produced. QUESTION 31 Calculate the energy stored in the capacitor below, when the voltage across it is 8V. QUESTION 32 QUESTION 33 What will happen to the readings on each ammeter when the frequency of both supplies are increased? QUESTION 34 Name the process involved when impurity atoms are added to form a p-type or an n-type semiconductor material. QUESTION 35 Name the two types of bias that a p-n material can be connected up in with a battery. QUESTION 36 State the charge present in p-type and n-type semiconductor materials and what type of charge carriers do they both prefer? QUESTION 37 Name component X, state the mode it is operating in and describe how it will turn the electric motor. QUESTION 38 What difference is noticeable between the conduction and valence bands in semiconductors and insulators when comparing them? QUESTION 39 What happens to the band gap in a semiconductor material when the temperature increases? QUESTION 40 Explain using Band Theory how LED’s emit photons of light. The End