* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Motivation behind botnets
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
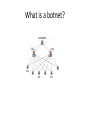
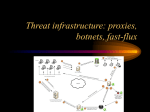
BOTNETS Pius Ndebele Yermek Sakiyev How big is the problem? • • • “The Storm worm botnet has grown so massive and far-reaching that it easily overpowers the world's top supercomputers…If you add up all 500 of the top supercomputers, it blows them all away with just 2 million of its machines. It's very frightening that criminals have access to that much computing power, but there's not much we can do about it." “An industrial control security researcher in Germany who has analyzed the Stuxnet computer worm is speculating that it may have been created to sabotage a nuclear plant in Iran.” “Shockingly, botnets produce 95% of the world's spam and have infected around 100 million systems. It makes defending against botnets tough.” What is a botnet? Life cycle • • • • Exploitation Securing the botnet Waiting for orders and getting the payload Reporting the results Types of botnets • IRC • HTTP • P2P Fast flux networks • Innovative technique built in DNS • Use for load balancing • Abused by criminals in a way that they can register thousands of IP addresses assigned to one hostname and change TTL to very short time • This way it will be very hard to detect the real IP addresses of C&C What can a botnet do? • • • • Recruit others DDoS Spam Phishing and identity theft Motivation behind botnets First Generation Distribution/Platform: IRC / Chat rooms and warez DDoS: fun, demonstration elite skill [l33t sk1llz, p0wnag3], political activism. Examples: AOHell [1] Punter (IM-bomber), which would send an Instant Message containing HTML code to another user that would sign them off. Mail bomb - script which would rapidly send e-mails to a user's inbox until it was full. Flooding script that would flood a chat room with ASCII art of an offensive nature. An 'artificial intelligence bot', which did not really contain artificial intelligence, but had the ability to automatically respond to a message in a chatroom upon identification of keywords. (For example, a 'profane language' autoresponse was built-in to the program.) ------------------------------------[1] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/AOHell Motivation behind botnets Second Generation Distribution/Platform: Worm/trojan with malicious payloads Motive: Money highly organized criminal organization botnet avoiding Ukraine.[6] Why? Avoiding local law enforcement Conficker used latest encryption algorithm MD6 [submitted to NIST/FIPS]. Flaw discovered and fixed in 16 days [2] Examples: Storm harvesting Personal Identifiable Information, racking a suspected profit $2m in 1 year [3] DDoS researchers investigating it [4] Koobface [5] targeting social networks. Which one? --------------------------------------[2] http://www.confickerworkinggroup.org/wiki/pmwiki.php/ANY/Timeline [3] http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/technology/7719281.stm [4] http://boingboing.net/2007/10/24/stormworm-botnet-las.html [5] http://www.infowar-monitor.net/reports/iwm-koobface.pdf [6] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conficker Motivation behind botnets Third Generation Distribution/Platform: Industrial systems Hardware and firmware based botnets Potential political/economic ‘cyberwar’ or espionage Counterfeit networking gear (Cisco) sold to DoE, US AirForce, Federal Aviation Administration and several universities [6] To counteract NSA has its own chip fabrication plant [7] and a hardware/software certification program [8] Example: Stuxnet [9] Targeting Programmable Logic Circuits (PLC) in control system sold to vendors in Finland and Iran. Specifically targeted were nuclear high-speed centrifugal motors. --------------------------------------------------------[6] http://www.popularmechanics.com/technology/gadgets/news/4253628 [7] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/National_Security_Agency [8] http://www.nsa.gov/business/programs/tapo.shtml [9] http://www.symantec.com/connect/blogs/stuxnet-breakthrough Detection & Prevention Techniques Detection techniques Reactive (N)(H) IDS external notifications (eg spamming friends, spam-blacklist) Proactive honeypots/honeynets (understanding internal workings; Torpig, Conficker) Note: Honeypot used to lure researcher to a fake C&C to study their techniques and provide fake statistics (exploitation rates for IE, PDF, Java vulnerabilities) [10] Prevention techniques Depth-in-defense [Protection in layers] Anti-Malware [anti-virus, rootkit detectors] (N)(H) IPS proxies; network and application [layer 3-7] firewalls (egress filtering) policies (security, patching policy, computer use – ex. use of usb media) local legislature and international laws: used as severe punitive deterrents New research points to using new approaches like economics (incentives), psychology ( ---------------------------------[10] http://blog.tllod.com/2010/11/03/statistics-dont-lie-or-do-they/