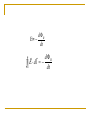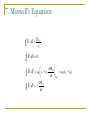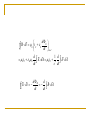* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download di/dt - s3.amazonaws.com
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
Computational electromagnetics wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic nanoparticles wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Induction heater wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
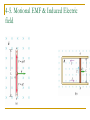
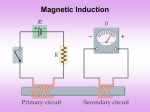
29. Electromagnetic Induction 1. Induction Experiments When there is a change in magnetic field, there will be a momentary current. Induced emf Induced current 2-3.Faraday’s Law & Lenz’s Law Magnetic Flux B B dA Faraday’s law of induction dB E= dt The induced emf in a closed loop equals the negative of the time rate of change of magnetic flux through the loop With N turns of wire, dB E= N dt Example 29.1) (a) Find the induced emf and the induced current in the circuit if the loop is a conductor. (b) If the loop is replaced by one made of an insulator, what effect does this have on the induces emf and induced current? Example 29.4) A simple alternator Example 29.5) A DC generator Example 29.6) The slidewire generator Example 29.7) Work and Power in the slidewire generator. Show that Pdissipated in the circuit is exactly equal to the rate at which work must be done to move the rod through the magnetic filed. Resistance of circuit is R. Lenz’s law The direction of any magnetic induction effect is such as to oppose the cause of the effect. 4-5. Motional EMF & Induced Electric field dB E= dt dB E dl dt Problem 29.54) The current in the long, straight wire AB is upward and increasing steadily at a rate di/dt. a) At an instant when the current is i, what are the magnitude and direction of the field at a distance r to the right of the wire? b) What is the flux through the loop? c) What is the total flux through the loop? d) What is the induced emf in the loop? e) Evaluate the numerical value of the induced emf if a=12.0 cm, b=36.0 cm, L=24.0 cm, and di/dt=9.6A/s. Displacement Current q Cv 0 A ( Ed ) 0 EA 0 B d dE B dl 0 iC 0 dt encl 0 (iC iD ) 7. Maxwell’s Equations E dA Qencl 0 B dA 0 dE B dl i 0 C 0 0 (iC iD ) dt encl dB E dl dt dE B dl i 0 C 0 dt encl d 1 d 0iC 0 0 E dA 0iC 2 E dA dt c dt dB d E dl dt dt B dA Problem 29.2) A coil with 200 turns enclosing an area of 12 cm2 is rotated in 0.040 s from a position where its plane is perpendicular to the earth’s magnetic field to one where its plane is parallel to the field. a) What is the total magnetic flux for parallel and perpendicular position? b) What is the average induced emf? Problem 29.10) A circular loop of wire with a radius of 12.0 cm and oriented in the horizontal xy-plane is located in a region of uniform magnetic field. A magnetic field with a magnitude of 1.5 T is directed along the positive z-direction, which is upward. a) If the loop is removed from the field region in a time interval of 2.010-3 s, find the average emf that will be induced in the wire loop during the extraction process. b) If the coil is viewed looking down on it from above, is the induced current in the loop clockwise or counterclockwise?