* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 20
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
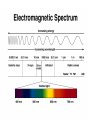
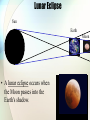
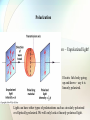
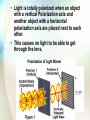
Chapter 27 Properties of Light Electromagnetic Radiation Photons Light These three are the same… • Light * pure energy • Electromagnetic Waves * energy-carrying waves emitted by vibrating electrons • Photons * particles of light Electromagnetic Wave Velocity • The speed of light is the same for all seven forms of light. • It is 300,000,000 meters per second or 186,000 miles per second. Michelson’s 1878 Rotating Mirror Experiment • German American physicist A.A. Michelson • Using this method, Michelson was able to calculate c = 299,792 km/s Picture credit The Electromagnetic Spectrum • A range of light waves extending in wavelength from radio waves to gamma rays The Electromagnetic Spectrum • • • • • • • Radio Waves - communication Microwaves - used to cook Infrared - “heat waves” Visible Light - detected by your eyes Ultraviolet - causes sunburns X-rays - penetrates tissue Gamma Rays - most energetic The Visible Spectrum •A range of light waves extending in wavelength from about 400 to 700 namometers. Questions • Is it correct to say that radio wave is a low-frequency light wave? • Is a radio wave also a sound wave? • See question on page 455. * Transparent Materials • Transparent - the term applied to materials through which light can pass in straight lines Opaque Materials • Opaque - the term applied to materials that absorb light Example Questions • Are clouds transparent or opaque to visible light? • Answer: opaque • Are clouds transparent or opaque to ultraviolet light? • Answer: transparent Shadows • Umbra - the darker part of a shadow where all the light is blocked • Penumbra - a partial shadow • These terms also apply to Solar Eclipses and Lunar Eclipses. Solar Eclipse Sun Umbra Full Shadow Earth Moon Partial Shadow • A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes in front of the Sun. Penumbra Lunar Eclipse Sun Earth Moon • A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes into the Earth's shadow. Polarization Net electric field is zero – Unpolarized light! Electric field only going up and down – say it is linearly polarized. Light can have other types of polarizations such as circularly polarized or elliptically polarized. We will only look at linearly polarized light. How do we make Polarized Light? I. Polarizers- Polarizers are made of long chained molecules which absorb light with electric fields perpendicular to the axis. • Light is totally polarized when an object with a vertical Polarization axis and another object with a horizontal polarization axis are placed next to each other. • This causes no light to be able to get through the lens. Questions • Which type of eclipse is dangerous to view with the unprotected eye? • Why are lunar eclipses more commonly seen than solar eclipses? • See question on page 460. * Chapter 27 Review Questions You will observe a total eclipse of the sun when... (a) you stand in the penumbra of the moon’s (b) shadow you stand in the umbra of the moon’s shad (b) you stand in the umbra of the moon’s shadow (c) sunlight diffracts around the moon (d) sunlight reflects from the moon to the earth The speed of light... (a) has never been measured (b) is about the same as that of sound (c) is infinitely fast (d) is very fast, but not infinite (d) is very fast, but not infinite In the dark at late evening, no color is seen because of lack of stimulation of a. rods. b. cones. b. cones. c. cornea. d. crystalline lens. End of Chapter 25