* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Basics of Geography
Environmental determinism wikipedia , lookup
Department of Geography, University of Kentucky wikipedia , lookup
Early world maps wikipedia , lookup
Counter-mapping wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of cartography wikipedia , lookup
Cartography wikipedia , lookup
Cartographic propaganda wikipedia , lookup
Mercator 1569 world map wikipedia , lookup
Map projection wikipedia , lookup
Iberian cartography, 1400–1600 wikipedia , lookup
Military geography wikipedia , lookup
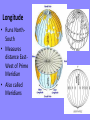
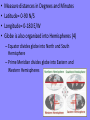
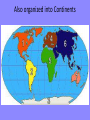
Do Now • Make a map of your house and its surrounding area – Including landscape, landmarks, businesses, etc…. The Basics of Geography The Basics of Geography • Geography- the study of everything on Earth – From rocks and rainfall to people and places • Geographers-people who study geography – How natural environment influences people, how people affect the Earth, and how the world changes Two Main Branches: Human and Physical • Human Geography: people study the distribution and characteristics of the world’s people – Where they live, work, and ways of life • Physical Geography: focuses on Earth’s natural environment – Landforms, water features, atmosphere, animals, plants, etc….. • These two branches link together by how people interact with their environment Who uses geography?? YOU DO!! •How you choose to get to and from school, hear about other countries, watch the news, use your phone… •Most jobs require the use of geography: – Restaurant owner? – Politician? – Clerk at gas station? The Five Themes of Geography • Help geographers describe the use of space on Earth. • The Five themes of Geography: – – – – Location: Where is it? Place: What is it like? Region: How are places similar or different? Movement: How do people, goods, and ideas from one location to another? – Human-Environment Interaction: How do people relate to the physical world Location • Described in two ways: – Absolute: the exact place on earth where its found – Relative: describes a place in comparison to other places around it • Absolute Location: – Geographers use a grid system of imaginary lines for locating places on earth – The earth is then organized! Organizing the Globe • • • • • • Latitude Longitude Meridians Parallels Hemispheres Continents Latitude • Runs East-West • Measures distance NorthSouth of equator • Also called parallels Longitude • Runs NorthSouth • Measures distance EastWest of Prime Meridian • Also called Meridians • • • • Measure distances in Degrees and Minutes Latitude= 0-90 N/S Longitude= 0-180 E/W Globe is also organized into Hemispheres (4) – Equator divides globe into North and South Hemisphere – Prime Meridian divides globe into Eastern and Western Hemispheres Also organized into Continents Place • Includes the physical features and cultural characteristics of a location – Physical features: climate, landforms, vegetation – Cultural (human) features: highways, houses, buildings, etc… Region • A region is an area of the earth’s surface with similar characteristics • Usually have more than one characteristic that unifies them • Geographers categorize regions in three ways – Formal – Functional – Perceptual Types of Regions • Formal- Based on any feature or combination of features – Physical, economical, etc…. – Examples: United States, The South, the Rocky Mountains, Europe, South Asia • Functional- Different places that are linked together and function as a unit – Example: City with its suburbs, Shopping Mall • Perceptual-reflect human feelings and attitudes – “Back home” easy to know but hard to define exactly – Dixie: seen in different ways Human-Environment Interaction • The relationship between humans and their environment • People may view the environment as recreation: the beach, or they may view the same environment as an opportunity: grow citrus, grapes, olives • People may alter the environment to fit their life – May drain swamps or dig ditches or cut down trees Movement • How goods, people, and ideas move from one place to another • Linear distance: how far across the earth a person, idea, or product travels • Time distance: amount of time it takes for person, idea, or product travels • Psychological distance: the way people view distance – As we become familiar with a place we think it is closer than it actually is A Geographers Tools • Maps and Globes • Oldest known map is a Babylonian clay tablet created 2,500 years ago • Maps function: show locations of places, landforms, and bodies of water • Globes: three dimensional representation of earth • Maps: two dimensional graphic representation Types of Maps • Reference Maps: topographic map- a representation of natural and man-made features on earth • Thematic Maps: Emphasize specific kinds of information such as climate map or population map • Navigation Maps: mostly used by sailors and pilots Understanding Maps • • • • • Atlas- collection of maps in one book Scale Directional Indicators Legends Other Elements