* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geography - Bingham`s Place
Environmental determinism wikipedia , lookup
Iberian cartography, 1400–1600 wikipedia , lookup
Mercator 1569 world map wikipedia , lookup
Department of Geography, University of Kentucky wikipedia , lookup
Location-based service wikipedia , lookup
History of longitude wikipedia , lookup
Map database management wikipedia , lookup
History of navigation wikipedia , lookup
Military geography wikipedia , lookup
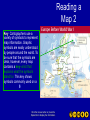
Geography Essential Knowledge Latitude Lines of latitude, or parallels, circle the earth parallel to the Equator and measure the distance north or south of the Equator in degrees. The Equator is measured at 0° latitude, while the Poles lie at latitudes 90° N (north) and 90° S (south). Parallels north of the Equator are called north latitude, and parallels south of the Equator are called south latitude. Longitude Lines of longitude, or meridians, circle the earth from Pole to Pole. These lines measure distances east or west of the starting line, which lies at 0° longitude and is called the Prime Meridian. By international agreement, the Prime Meridian is the line of longitude that runs through the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, England. Places east of the Prime Meridian are known as east longitude, and places west of the Prime Meridian are known as west longitude. The Global Grid Every place has a global address, also called its absolute location (see page 9 of your textbook). You can identify the absolute location of a place by naming the longitude and latitude lines that cross exactly at that place. For example, the city of Tokyo, Japan, is located at 36ºN latitude and 140ºE longitude. For more precise readings, each degree of latitude and longitude is subdivided into 60 units called minutes. Common Map Projections Geographic Information Systems A cartographer uses GIS to make a map. Reading a Map 2 Key Cartographers use a variety of symbols to represent map information. Graphic symbols are easily understood by people around the world. To be sure that the symbols are clear, however, every map contains a key–a list that explains what the symbols stand for. This key shows symbols commonly used on a political map. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information. Compass Rose Most maps feature a compass rose, a marker that indicates directions. The four cardinal directions–north, south, east, and west–are usually indicated with arrows or points of a star. The intermediate directions northeast, northwest, southeast, southwest–may also be shown, usually with smaller arrows or star points. Sometimes a compass rose may point in only one direction because the other directions can be determined in relation to the given direction. The compass rose on this map indicates north only. Reading a Map 4 Reading a Map 6 Scale Bar The scale bar shows the relationship between map measurements and actual distances. By laying a ruler along the scale bar, you can calculate how many miles or kilometers are represented per inch or centimeter. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information. Graphs, Charts, and Diagrams Graphs •A graph is a visual presentation of information. •There are many kinds of graphs, each suitable for certain purposes. •Most graphs show two sets of data, one displayed along the vertical axis and the other displayed along the horizontal axis. •Labels on these axes identify the data being displayed. Line Graphs A line graph shows changes in two variables, or changing sets of circumstances over periods of time. To analyze data on a line graph, study the changes and trends as shown by the line. Then draw conclusions based on the information. This line graph shows U.S. population growth between 1900 and 2000. The vertical axis lists population, and the horizontal axis indicates the passage of time. Bar Graphs A bar graph shows comparisons. To analyze a bar graph, note the differences in quantities. Then make generalizations or draw conclusions based on the data. This bar graph shows lumber production among the top five lumber-producing countries in the world. The vertical axis shows the amount of lumber produced. Circle Graphs A circle graph, or pie graph, shows the relationship of parts to a whole. Percentages are indicated by relative size and sometimes by color. To analyze a circle graph, study the relationships of areas to one another and to the whole. This circle graph shows the land areas of the world’s continents and other landmasses, such as islands, expressed as percentages of Earth’s total landmass. Graphs, Charts, and Diagrams Charts and Tables Data are arranged in columns and rows in a chart or table. Charts and tables display facts in an organized manner and make comparisons easy. To find key information in a chart or table, look for the intersections of columns and rows. The table on the following slide displays information about the population and land area of the world’s continents. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information. Graphs, Charts, and Diagrams Charts and Tables Checking for Understanding Define Match each definition in the left column with the appropriate term in the right column. __ M 1. the study of human activities and their relationship to the cultural and physical environments __ F 2. a particular space with physical and human meaning __ B 3. the exact position of a place on the earth’s surface __ K 4. the complex community of interdependent living things in a given environment __ L 5. ongoing movement of people, goods, and ideas A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. K. L. M. location absolute location hemisphere grid system relative location place region formal region functional region perceptual region ecosystem movement human environment interaction Checking for Understanding Define Match each definition in the left column with the appropriate term in the right column. __ C 6. half of a sphere or globe, as in the earth’s Northern and Southern Hemispheres __ J 7. a region defined by popular feelings and images rather than by objective data __ I 8. a central point and the surrounding territory linked to it __ A 9. a specific place on the earth __ H 10. a region defined by a common characteristic, such as production of a product A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. K. L. M. location absolute location hemisphere grid system relative location place region formal region functional region perceptual region ecosystem movement human environment interaction Checking for Understanding Define Match each definition in the left column with the appropriate term in the right column. __ D 11. pattern formed as the lines of latitude and longitude cross one another __ G 12. place united by specific characteristics __ E 13. location in relation to other places A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. K. L. M. location absolute location hemisphere grid system relative location place region formal region functional region perceptual region ecosystem movement human environment interaction The Geographer’s Craft Terms to Know • • • • • physical geography human geography meteorology cartography geographic information systems (GIS) Branches of Geography • Physical geography focuses on the study of Earth’s physical features. • Human geography, or cultural geography, studies human activities and their relationship to the environment. Geographers at Work • Direct Observation Going to a geographic location to see what it is like is direct observation • Mapping Cartographers are people who design and make maps–graphic representations of places and regions and more complicated information about the relationships of people, places, and things. Geographers at Work (cont.) • Interviewing Cultural geographers often interview the people whose activities they study. • Interviewing Cultural geographers often interview the people whose activities they study. • Technology Geographers use advanced technology–satellite photos, radar, and geographic information systems (GIS)–to study the environment, the weather, and human settlement patterns. Checking for Understanding Define Match each definition in the left column with the appropriate term in the right column. __ D 1. the science of mapmaking __ B 2. the study of human activities and their relationship to the cultural and physical environments __ E 3. computer tools for processing and organizing details and satellite images with other pieces of information __ C 4. the study of weather and weather forecasting __ A 5. the study of Earth’s physical features A. physical geography B. human geography C. meteorology D. cartography E. geographic information systems (GIS) Reviewing Key Terms Insert the key term that best completes each of the following sentences. absolute location cartography ecosystem formal region grid system human geography physical geography relative location geographic information systems (GIS) 1. Plants and animals depend on one another in a(n) ___________________. ecosystem grid system 2. Geographers use a(n) ___________________ formed by lines of latitude and longitude to determine ___________________ . absolute location Reviewing Key Terms Insert the key term that best completes each of the following sentences. absolute location cartography ecosystem formal region grid system human geography physical geography relative location geographic information systems (GIS) 3. ___________________ is the study of the human Human geography aspects of geography. 4. A(n) ___________________ has boundaries formal region determined by a common characteristic. 5. Another name for mapmaking is _____________. cartography Reviewing Key Terms Insert the key term that best completes each of the following sentences. absolute location cartography ecosystem formal region grid system human geography physical geography relative location geographic information systems (GIS) 6. ________________ Relative location is expressed in relation to other places. 7. Computer tools that process data and satellite images with other pieces of geographic information geographic information systems (GIS) are called ________________________________. Reviewing Key Terms Insert the key term that best completes each of the following sentences. absolute location cartography ecosystem formal region grid system human geography physical geography relative location geographic information systems (GIS) 8. _________________ Physical geography focuses on the study of the earth’s physical features. Locating Places Match the letters on the map with the places and physical features of the earth. __1. B North America __2. A South America __3. D Africa __4. E Asia __5. C Europe __6. G Antarctica __7. F Australia __8. I Atlantic Ocean __9. H Indian Ocean __10. J Pacific Ocean Use the circle graph below and your knowledge of geography to answer the following questions. 1. Which ocean covers the smallest area of the earth’s surface? A Atlantic B Indian C Pacific D Arctic Test–Taking Tip Study the information shown on the circle graph for the areas of the earth covered by land and by oceans. Then compare the relative sizes of the different graph segments. By comparing the segments you will be able to determine the correct answers. 2. Which ocean covers about as much of the earth’s surface as land does? F Indian H Arctic G Pacific J Atlantic Test–Taking Tip Study the information shown on the circle graph for the areas of the earth covered by land and by oceans. Then compare the relative sizes of the different graph segments. By comparing the segments you will be able to determine the correct answers.