* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Five Themes of Geography
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
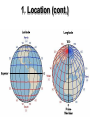
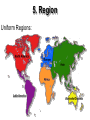
What is geography? the study of the earth and man’s interaction with it The Five Themes of Geography 1. location 2. place 3. human/environment interaction 4. movement 5. region 1. Location • “Where is it?” • absolute location – a place’s position on the globe • relative location – location of a place in relation to something else • hemisphere – half of the earth • latitude – imaginary lines that measure distance north or south of the equator (also called parallels) • longitude – imaginary lines that measure distance east or west of the Prime Meridian (also called meridians) - ends at the International Date Line 180° • grid system – network of lines used to find location 1. Location (cont.) 2. Place • “What is it like there?” • describes landforms, culture, history, language, religion, clothing, education, art, etc. • place is how you would describe an area to someone 3. Human-Environment Interaction • “What is the relationship between people & their environment?” • describes how the environment affects the people & how people affect the environment (pollution, use of resources, settlement patterns, conservation, adapting to the climate, etc.) • people adapting to or changing their environment • people’s activities within their environment 4. Movement • “How are people & places connected?” • describes why people move from one place to another & how they get around • concerned with the movement of three things: people, goods, ideas • interdependent – relying on one another for goods, services, and ideas 4. Movement (cont.) 4. Movement (cont.) 5. Region • “How are places alike?” (What common characteristics?) • a way to group & organize the world • 2 types of regions: 1. uniform region – an area with some common characteristic throughout (religion, language, climate, crops, etc.) Ex: The Middle East, The Sunbelt 5. Region Uniform Regions: 5. Region Uniform Regions: Sunbelt 5. Region 2. functional region – an area that functions together Ex: The Baton Rouge Metropolitan Area Maps & Globes • A map is a flattened out portion of a globe. • The oldest known map is a Babylonian clay tablet created 2,500 years ago. • cartographer – map maker Maps used to be made by manually observing, surveying, and recording information about a place. • By the 1940s, cartographers began to use aerial photography to aid in map making. • Now, we use satellites & computers to render images of the earth. GIS (Geographic Information Systems) –stores geographic information in a digital database –users can select the layers of info they need & GIS creates a composite map GPS (Global Positioning System) • developed for the military • uses 24 satellites, called Navstars, to beam info to the earth Parts of Maps: TODALSIG • • • • • T = title O = orientation D = date A = author L = legend (key) – explains the symbols used on a map • S = scale – the relationship between measurements on a map to actual measurements on earth • I = index • G = grid • compass rose – directional marker on a map • cardinal directions – north, east, south, west • Globes are the most accurate representation of the earth, because all maps are distorted in some way. • great circle path – shortest distance between two places on the earth’s surface Types of maps: • physical – shows physical features like mountains, rivers, deserts, etc • political – shows the boundaries between countries, states, parishes, etc. • special purpose (thematic) – focuses on one aspect like population, religion, climate, land use, languages, etc. Charts, Graphs & Diagrams • graph – a visual way of presenting information • bar graph – uses bars to compare data • line graph – reveals trends and relationships between data (shows changes over time) Charts, Graphs & Diagrams (cont.) • circle graph (pie chart) – uses percentages to compare the parts to the whole • pictograph – uses pictures to present info • chart – shows facts arranged in columns & rows • diagram – shows what something is or how something is done Create the best graph to represent each of the following sets of info: 1. Last week Mrs. Lipscomb gave 2 homework assignments. Mrs. Spence gave 3 homework assignments. Mrs. Devall & Mrs. Chaves each gave 1 homework assignment. 2. Of Mrs. Devall’s 30 students, 15 have brown eyes, 10 have blue eyes, and 5 have green eyes. (show percentages) 3. The number of students earning college scholarships has doubled every year, starting with 10 in 2004 and 160 in 2008. Know the continents & oceans: