* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download U - Net Start Class
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
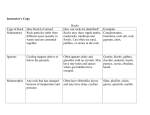
Week 22 Review Weathering-the breaking or wearing away of rocks and mountains Notice the difference in the height of the mountains. Weathering-the breaking or wearing away of rocks and mountains Notice the difference in the height of the mountains. Weathering-the breaking or wearing away of rocks and mountains Notice the difference in the height of the mountains. Weathering-the breaking or wearing away of rocks and mountains The roots of plants grow into cracks in rocks and as they grow the crack becomes bigger until the rock breaks. Weathering-the breaking or wearing away of rocks and mountains The roots of plants grow into cracks in rocks and as they grow the crack becomes bigger until the rock breaks. Weathering-the breaking or wearing away of rocks and mountains The roots of plants grow into cracks in rocks and as they grow the crack becomes bigger until the rock breaks. Erosion-the taking away of small pieces of rock, soil, or sand by wind, water, or ice Rivers erode their banks and beds by taking small pieces of the soil and rock as it flows. EROSION of a river bank over MANY YEARS Erosion-the taking away of small pieces of rock, soil, or sand by wind, water, or ice Example of EROSION by a river and ways to prevent the erosion EROSION over MANY YEARS New plants Rocks used to hold the soil in place The plants grow and their roots help hold the soil in place. Erosion-the taking away of small pieces of rock, soil, or sand by wind, water, or ice A V-shaped valley is made by a fast moving riVer. Erosion-the taking away of small pieces of rock, soil, or sand by wind, water, or ice U A U-shaped valley is formed by a slow moving glaCier. Erosion-the taking away of small pieces of rock by wind, water, or ice U A U-shaped valley is formed by a slow moving glaCier. Weathering and erosion can cause the formation of caves or caverns, arches, and rock stacks. Weathering and erosion wear away rock over time to form caverns. Weathering and erosion wear away rock over time to form arches. Weathering and erosion wear away rock over time to form rock stacks. Deposition-the dropping of sediment to create a new landform The Mississippi Delta is formed when the Mississippi River flows into the Gulf of Mexico. The river slows down as it meets the gulf and the sediment it carries is deposited in a new place making a new landform-a delta. The Mississippi River Delta is shaped like a bird’s foot. bird’s foot shape Deposition-the dropping of sediment to create a new landform The Nile Delta is formed when the Nile River flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The river slows down as it meets the sea. The sediment it carries is deposited in a new place making a new landform-a delta. The Nile Delta is shaped like a triangle or a fan. Erosion and deposition can move sand and create sand dunes in a new place. Wind blows sand and deposits it in a new area. Formation of Fossil Fuels-Petroleum (Oil) and Natural Gas Formation of Fossil Fuels-Coal When the plants decompose a soft, spongy substance called peat is formed. Sun, Earth, and Moon The sun is a medium-size star made of glowing gases. It has an atmosphere but not like the atmosphere of Earth. It is the center of our solar system with 8 planets held in orbit by tremendous gravity. Sunspots are cooler than the rest of the sun. Sun, Earth, and Moon Sunspots-areas on the sun that are cooler than the rest of the sun. Sun, Earth, and Moon Earth is the third planet from the sun. It is made of rock. The Earth is the only planet that has liquid water. Water covers ¾ of the Earth’s surface. The atmosphere of the Earth has the perfect combination of gases to support life. The Earth revolves around the sun in an elliptical, or oval, orbit every 365 ¼ days. The Earth rotates every 24 hours, causing night and day. The tilt of the Earth on its axis, the imaginary line which goes through the center of the Earth from north pole to south pole, causes the four seasons. Sun, Earth, and Moon Sun, Earth, and Moon The Earth revolves around the sun, the moon revolves around the Earth, forming a system. Sun, Earth, and Moon The sun appears to rise in the east and set in the west because of the Earth’s rotation. Sun, Earth, and Moon The moon revolves around the Earth every 29 days (approximately). This revolution causes the phases of the moon to be seen on Earth. Because the moon rotates and revolves at the same rate, we only see one side of the moon. A full moon will be seen every 29th day. Sun, Earth, and Moon SUN EARTH MOON Made of glowing gases Made of rock-does not make light; only reflects sunlight Made of rock-does not make light; only reflects sunlight Has an atmosphere Has an atmosphere that supports life No atmosphere Has gravity Has gravity Has gravity but much less than Earth Center of the solar system Orbits the Sun Orbits the Earth No liquid water Has liquid water No liquid water Has sunspots-areas that are cooler than the rest of the sun Has craters created by asteroids hitting the surface but not as many as the moon due to atmosphere Has many craters created by asteroids hitting the surface