* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Social Studies Chapter 6 Review
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Port Royal wikipedia , lookup
Texas in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Roanoke Island wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Sailor's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Malvern Hill wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Antietam wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Island Number Ten wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Second Battle of Corinth wikipedia , lookup
Ulysses S. Grant and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Appomattox Station wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Cedar Creek wikipedia , lookup
Western Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
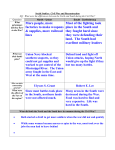
SOCIAL STUDIES CHAPTER 6 REVIEW WHAT ADVANTAGES DID THE NORTH HAVE IN THE WAR? • More people, more factories to make weapons & supplies, more railroad lines WHAT ADVANTAGES DID THE SOUTH HAVE IN THE WAR? • Most of the fighting took place in the South and they fought hard since they were defending their land. The South had excellent military leaders WHAT WAS THE NORTH’S BATTLE PLAN? • Union Navy blocked southern seaports, so they could not get supplies. They also worked to get control of the Mississippi River. The Union army fought in the East and West at the same time. WHAT WAS THE SOUTH’S BATTLE PLAN? • To defend their land and fight off Union attacks. They hoped the North would give up the fight if they lost too many battles. WHO WAS THE COMMANDING GENERAL IN THE NORTH? •Ulysses S. Grant WHO WAS THE COMMANDING GENERAL IN THE SOUTH? •Robert E. Lee WHAT WERE THE EFFECT OF THE WAR ON THE NORTH? • Since most battles took place in the South, northern lands were not affected much. WHAT WERE THE EFFECTS OF THE WAR ON THE SOUTH? • Many areas in the South were destroyed during the War. Food was hard to find and very expensive. Life was hard in the South. WHAT DID BOTH THE NORTH AND THE SOUTH HAVE IN COMMON DURING THE CIVIL WAR? • Both started a draft to get more soldiers when the war did not end quickly • While some women became nurses or spies in the war, most took over the jobs the men had to leave behind WHAT WERE THE BORDER STATES? • Missouri, Kentucky, Delaware & Maryland. West Virginia also became a border state when it separated from Virginia after disagreements WHY WERE THEY CALLED BORDER STATES? • Slavery was allowed in these states, although they remained part of the Union and continued to be U.S. citizens. • Some people in these states fought for the Union army, some fought for the Confederate Army. WHO WERE THE MAIN LEADERS IN THE NORTH? • Abraham Lincoln President of the United States during the Civil War. • Ulysses S. Grant: Grant went to West Point Military Academy. After showing his leadership skills at the Battle of Vicksburg, Grant was made commander of the Union (northern) troops • William Tecumseh Sherman: Union General whose March to the Sea destroyed Confederate supplies. • Andrew Johnson: President of the U.S. after the war when Lincoln was assassinated. WHO WERE THE MAIN LEADERS IN THE SOUTH? • Jefferson Davis: President of the Confederacy (South) during the Civil War. • Robert E. Lee: Lee also went to the West Point Military Academy. Lincoln asked him to lead the Union troops, but when Virginia seceded, he did not want to fight against his state. • Thomas “Stonewall” Jackson: Confederate general, won many battles until accidentally shot. Got his nickname because he stood his ground like a “stone wall” in the First Battle of Bull Run. VOCABULARY • Draft -the government selection of people to serve in the military • Assassination -the murder of an important leader • Impeach -to charge a government official of a crime • Segregation - the forced separation of the races • Primary Source -firsthand information about an event, a place, or a time period • Secondary Source -information from someone who did not witness an event. Secondary information often comes from primary sources. WHAT BATTLES AND EVENTS AFFECTED THE OUTCOME OF THE CIVIL WAR? • Fort Sumter -The Civil War started when Confederate troops attacked Fort Sumter • First Battle of Bull Run -First battle of the Civil War. Both sides thought they’d win the battle and the war quickly. The Confederate army won this battle, but it was worse than both sides expected. • Emancipation Proclamation -Presidential order signed January 1, 1863, by Abraham Lincoln, that freed enslaved people in the Confederate states. It did not free slaves in the border states. The Emancipation Proclamation made the war about ending slavery in the South and took away the chance that Great Britain and France might help the South, since they were against slavery. BATTLES AND EVENTS CONTINUED • Vicksburg -Union Army won this battle and control of the Mississippi River, which cut off Texas and Arkansas from the other Confederate States. • Gettysburg -Union won this battle in the East (Pennsylvania) at the same time Grant was winning the Battle of Vicksburg in the West. After three days of fighting, the Confederate Army was forced to retreat from their attack. The Union victories at Gettysburg and Vicksburg were a turning point in the war. • Atlanta Campaign and Sherman’s March to the Sea -In 1864, Union General William Tecumseh Sherman led his army through Georgia. He burned down most of Atlanta and from there headed to Savannah on the Atlantic coast in what is known as “the March to the Sea.” The goal of this march was to burn anything and everything that could help the South win the war. BATTLES AND EVENTS CONTINUED • Appomattox Courthouse - In April of 1865, Grant’s army, which was well-fed, and armed with supplies met up with Lee’s starving soldiers who had few supplies. Lee and his army were surrounded and Lee surrendered at Appomattox Courthouse, Virginia, ending the War. • President Lincoln Assassinated -Just five days after the Civil War ended, President Lincoln was assassinated while watching a play at Ford’s Theater in Washington D.C. Many people, even Southerners were saddened by Lincoln’s death, since he promised to bring the country together being fair to all. WHAT WAS LIFE LIKE IN THE SOUTH AFTER THE WAR? • Since most of the battles took place there, the South was devastated by the War. Many homes, farms, and businesses were ruined and had to be rebuilt. While former slaves were now free, they had no homes or jobs. WHAT WAS LIFE LIKE IN THE NORTH AFTER THE WAR? • There was very little damage to cities in the North. Northern businesses and railroads grew quickly during and after the war. WHAT WAS RECONSTRUCTION? • The period following the Civil War during which the South rejoined the Union. Before they could rejoin, they had to ratify (approve) the 13th, 14th, and 15th amendments. WHAT DID CONGRESS DO DURING RECONSTRUCTION? • After Southerners passed Black Codes that limited the rights of former slaves to travel, vote, and hold certain jobs and voted for former Confederate leaders, Congress put the South under military control. Congress impeached President Andrew Johnson, but were not able to force him out of office. HOW WERE FORMER SLAVES HELPED DURING RECONSTRUCTION? • Freedmen’s Bureau -Provided food, clothing, medical care, schools and found jobs for many former slaves. • George Washington Carver -Scientist and teacher at African-American Tuskegee Institute. Discovered over 300 products that could be made with peanuts. WHAT WERE THE 13TH, 14TH, AND 15TH AMENDMENTS? • 13th Amendment -Ended slavery in the entire United States • 14th Amendment -Gave citizenship to all people born in U.S., including former slaves and said all citizens must be treated equally under the law • 15th Amendment -Gave all men the right to vote, including African American men. WHAT DIFFICULTIES DID FREED SLAVES FACE IN THE SOUTH? • Sharecropping -A system in which landowners let poor farmers use small areas of their land, and in return, the farmers gave the landowner a share of the crop. The poor farmers, often former slaves, often went in debt borrowing to buy seeds and tools. If they could not sell enough crops, the debt would get worse. • Ku Klux Klan -Used violence to stop African Americans from voting • Jim Crow Laws -Laws that kept African-Americans separate from other Americans. Schools, hospitals and even cemeteries were segregated. Less money was spent on schools and hospitals for African Americans.