* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Spanning Tree
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Spanning Tree Protocol wikipedia , lookup
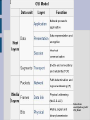
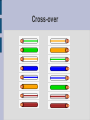
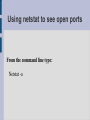
Sysops Network Training by Brett Haffener Introductions - Name - School - What are you most interested in learning about? Where do we start? OSI Model - Breaks up networking into smaller parts OSI stands for (Open Systems Interconnection) Taken from: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ OSI_Model Layer 1 (Physical layer) Media & Signalling Devices include hubs repeaters transceivers cabling Ethernet Cabling Standards Categories of copper cabling: Category 5: Limited to 100Mbps Category 5e: Up to 1000Mbps (Gigabit) Category 6: Up to 1000 Mbps All three are limited to 100M (328ft) in length from end device to end device Gig vs. 100Mbps Backbone and server connections would be best at Gig What category cabling should you use? I recommend Cat6 Costs 20 - 40% more Prepares you for the future 80-90% of new copper installs are now Cat6 Less interference between cables, so there are fewer errors causing fewer resent packets (slightly faster performance) Types of cables Straight through Crossover Rollover Straight-through Cross-over Rollover Where do I use each cable? Straight through (unlike interfaces) router to switch router to hub PC to switch PC to hub Cross-over (like interfaces) switch to switch hub to hub switch to hub PC to PC Rollover Console into router What happens when you use the wrong cable? ??????? Testing cables Using a cable tester http://www.flukenetworks.com/fnet/enus/products/MicroScanner+2/Overview.htm?categor ycode=CPTT Fiber Multimode fiber – Supports up to 10Gbps (10 Gig) Up to 550Meters Used commonly to interconnect wiring closets or buildings Single mode fiber – Supports up to 10Gbps (10 Gig) Up to 60 Kilometers Used to connect geographically distant locations (not as common in schools) Network Topology Recommend extended star *** many schools daisy chain their switches *** Layer 2 (Data-link layer) Physical addressing Switching Devices switch bridge How do you find the MAC Address? Windows 1. Click Start 2. Run 3. cmd 4. ipconfig/all Mac 1. Open up a terminal 2. Type ifconfig Two parts to the MAC Address XX – XX – XX – XX – XX - XX Matching an OUI with a company http://coffer.com/mac_find/ Tracking down a problem with the MAC Address If you don't know where a machine is located you can use the MAC address to track it down (if you have managed switches) Loops in the network Loops are formed whenever there are redundant links in the network Traffic continues around the loop generating excess traffic Can cause broadcast storms (drastically reducing performance) Spanning Tree Spanning tree protocol prevents loops from occurring by blocking traffic on the extra interface (Enabling spanning tree) Spanning Tree (pros & cons) Pros – If there is a loop in your network it won't take the entire network down Cons – In the past Spanning Tree has slowed Mac logins down - If there is a loop in your network you may not know about it if you don't check your switches *** Recommend using “Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol” if you are going to use this *** Hubs vs. Switches The major difference between hubs and switches is that hubs broadcast traffic out all interfaces whereas switches only sent unicast traffic out the destined interface Speed & Duplex settings Mismatched settings often times causes errors Best to hard set connections between network devices when possible Best to leave connections to workstations and servers in auto-negotiate (in general) Layer 3 Logical addressing (IP addressing) Devices router layer 3 switch How routing works Packet Tracer Firewalls and port openings The main place where you'll have to worry about ports being opened is in your firewall Using netstat to see open ports From the command line type: Netstat -a Wireless testing http://www.netstumbler.com/ http://www.macstumbler.com/ Wireless security Recommend WPA2 Public & Private wireless network Troubleshooting tools Ping Traceroute NSLOOKUP Troubleshooting DNS From a command prompt or terminal you can type nslookup <URL> If you think you are having DNS issues you can try going to the IP address instead