* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Network Topology Bus Topology Bus topology uses a common
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
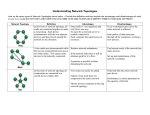
Network Topology Bus Topology Bus topology uses a common backbone to connect all the network devices in a network in a linear shape. A single cable functions as the shared communication medium for all the devices attached with this cable with an interface connector. The device, which wants to communicate send the broadcast message to all the devices attached with the shared cable but only the intended recipient actually accepts and process that message. Advantages -easy to install dont need much cable computers can be detached without effect other computers cheap disadvantages performance issue if more then 15 computers are added to the network if the backbone cable is broken then the network become useless and no communication between the computers is possible its easy to sniff the traffic on the network all the traffic is tranfered over the same cable Examples 10Base5 10Base2 Ring Topology In ring Network, every computer or devices has two adjacent neighbors for communication. In a ring network, all the communication messages travel in the same directory whether clockwise or anti clockwise. Advantages -no kollision in the network -all stations work as repeater disadvantages if one computer or cable fails the network will breakdown hard to install examples Token ring star topology all computer are connected with a point to point connection to a central device advantages if a cable is broken only the computer wich is connected to the cable can no longer communicate with the network if a computer fails then the other computers are not affected easy extensible high transmission rate disadvantages if the central device fails the network whole will brakdown examples telephone network Ethernet Tree Topology advantages if a computer fails then the other computers are not affected disadvantages if a central device fails all computer wich are connected to the central device are no longer reachable Mesh Topology every computer will be connected to one ore more other computers. If every computer is connected to every other computer, the network will be called complete meshed network advantages -the safest network variant -if one computer faill the communication is still possible because the data will be redirected disadvantages -very hard to install(am härtesten zu installierende) -much cable is necessary Network Cable BNC Cable yellow cable 500 METER LONG 10 Mbit speed 10 mm Durchmesser 10Base5 Thinwire (10Base 2) 185Meter 30 stationen Minimalabstand 0.5 milimeter Enden müssen terminiert werden Kabel Beschreibung consist Twisted Pair Kabel 10BaseT 100M 10-10000Mbit Mehrere Categorie CAT-1 für Alarmsysteme und analoge Sprachübertragung CAT-2 für Sprache und RS232-Schnittstellen CAT-3 Datenübertragung bis 10mbit CAT-4 Datenübertragung bis CAT-5 Datenübertragung bis 100 mbit cat 5e gigabit ethernet cat 6 gigabit ethernet cat 7 10Gbit ethernet cat 8 ?? Beschreibung der Kabel //optional LWL Monomode Multimode //optional OSI The OSI model defines internetworking in terms of a vertical stack of seven layers. The upper layers of the OSI model represent software that implements network services like encryption and connection management. The lower layers of the OSI model implement more primitive, hardware-oriented functions like routing, addressing, and flow control. layers 7. Application Network process to application 6.Presentation Data representation and encryption 5. Session Interhost communication 4. Transport End-to-end connections and reliability 3. Network Path determination and logical addressing 2. Data Link Physical addressing (MAC & LLC) Bit 1. Physical Media, signal and binary transmission Network Hardware Hub classify as Layer 1 devices in the OSI model. At the physical layer, hubs can support little in the way of sophisticated networking. Hubs do not read any of the data passing through them and are not aware of their source or destination. Essentially, a hub simply receives incoming packets, possibly amplifies the electrical signal, and broadcasts these packets out to all devices on the network - including the one that originally sent the packet! passive active intelligent Passive hubs do not amplify the electrical signal of incoming packets before broadcasting them out to the network. Active hubs, on the other hand, do perform this amplification, as does a different type of dedicated network device called a repeater. Some people use the terms concentrator when referring to a passive hub and multiport repeater when referring to an active hub. Intelligent hubs add extra features to an active hub that are of particular importance to businesses. An intelligent hub typically is stackable (built in such a way that multiple units can be placed one on top of the other to conserve space). It also typically includes remote management capabilities via SNMP and virtual LAN (VLAN) support. Switch it is network device that connects networksegments and computers. Network switches appear nearly identical to network hubs, but a switch generally contains more intelligence (and a slightly higher price tag) than a hub. Unlike hubs, network switches are capable of inspecting data packets as they are received, determining the source and destination device of each packet, and forwarding them appropriately. By delivering messages only to the connected device intended, a network switch conserves network bandwidth and offers generally better performance than a hub. Unmanaged switches — These switches have no configuration interface or options. They are "plug-and-play." They are typically the least expensive switches, found in home, SOHO, or small businesses. They can be desktop or rack mounted. Managed switches — These switches have one or more ways, or interfaces, to modify the operation of the switch. Common management methods include: a serial console or Command Line Interface accessed via telnet or Secure Shell; an embedded Simple Network Management Protocol SNMP agent allowing management from a remote console or management station; a web interface for management from a web browser. Examples of configuration changes that one can do from a managed switch include: enable features such as Spanning Tree Protocol; set port speed; create or modify VLANs, etc. Two sub-classes of managed switches are marketed today: switch layer (tabelle) layer1 Hub layer2 switch layer3 switch switch with router functionality (descriotion on the next page) layer4 switch with firewall, vpn functions layer7 switch with a proxy Router A router (pronounced /'rautər/ in the USA, pronounced /'ru:tər/ in the UK and Ireland, or either pronunciation in Australia and Canada) is a computer whose software and hardware are usually tailored to the tasks of routing and forwarding information. For example on the internet information gets routed to different places using routers. Routers connect two or more logical subnets, which do not necessarily map one-to-one to the physical interfaces of the router.[1] The term "layer 3 switch" often is used interchangeably with router, but switch is a general term without a rigorous technical definition. In marketing usage, it is generally optimized for Ethernet LAN interfaces and may not have other physical interface types. In comparison a network hub does not do any routing, instead every packet it receives on one network line gets forwarded to the other network lines. Bridge connect networks with a different media for example ehternet wlan repeater ?? firewall ??