* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download High-speed digital telecommunications networks that are national or
Universal asynchronous receiver-transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Windows Vista networking technologies wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications in China wikipedia , lookup
Quality of service wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
PSTN network topology wikipedia , lookup
Packet switching wikipedia , lookup
Carriage dispute wikipedia , lookup
History of smart antennas wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
History of telecommunication wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications in Russia wikipedia , lookup
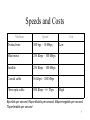
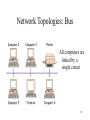
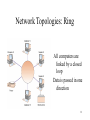
9 TELECOMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKS 1 Telecommunications Communicating information via electronic means over some distance Information SuperHighway High-speed digital telecommunications networks that are national or worldwide in scope and accessible by the general public 2 Components of a Telecommunications System • • • • • • Computers I/O devices Communications channels – cables, telephone lines Communications Processors – modems, multiplexors Communications Software Uses Protocols 3 Types of Signals • Analog signal – Continuous waveform – Voice communications • Digital signal – – – – Discrete waveform Two states: 0 and 1 On-off electrical pulses Data communications • Modem – Translates b/t digital and analog 4 Communications Channels • • • • The links by which data or voice are transmitted Twisted wire Coaxial cable Fiber-optic cable Wireless – – – – – – microwave Satellite and other wireless channels Pagers Cellular phones PCS PDAs 5 Transmission Speed • Transmission – Bits per second (bps) • Bandwidth – Range of frequencies that can be accommodated on a channel – Greater range Greater bandwidth Greater capacity 6 Speeds and Costs Medium Speed Twisted wire 300 bps – 10 Mbps Microwave 256 Kbps – 100 Mbps Satellite 256 Kbps – 100 Mbps Coaxial cable 56 Kbps – 200 Mbps Fibre optic cable 500 Kbps – 6+ Tbps Cost Low High Bps=bits per second; Kbps=kilobits per second; Mbps=megabits per second; Tbps=terabits per second 7 Communications Processors • Front- end processor – Special purpose computer that manages communication for host computer in a network • Concentrator – Computer that collects & temporarily stores messages from terminals for batch transmission to host computer • Multiplexer – allows channel to carry data from multiple sources simultaneously 8 Network Topologies: Star All computers and devices connected to a central host computer 9 Network Topologies: Bus All computers are linked by a single circuit 10 Network Topologies: Ring All computers are linked by a closed loop Data is passed in one direction 11 Local Networks • Private branch exchange (PBX) – Firm’s central switching system – Handles digital and voice • Local area network (LAN) – Dedicated channels – Limited distance (less than 700 metre radius) – Higher capacity than PBX 12 Typical LAN 13 LAN Technology • Gateway – A communications processor that connects dissimilar networks • Router – A device that forwards packets of data between similar networks • Bridge – A device that connects segments of the same or similar networks • Network operating system (NOS) – Coordinates resources 14 Wide Area Networks (WAN) A telecommunications network that spans a large geographical distance • Switched lines – Telephone lines used by a computer to send data • Dedicated lines – Continuously available – Conditioned to transmit data at high speeds • MAN and GAN – Metropolitan and global area networks 15 Network Technologies • Packet Switching – Data broken into small packets – Packets are then routed in the most economical way • Frame Relay – A shared network service technology that packages data into bundles – Does not use error-correction – Cheaper and faster than packet-switching • Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) – Information parceled into 8-byte cells – Data transmitted between computers of any vendor 16 Network Technologies • Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) – Dialup: voice, data, image, video on single line • Digital Subscriber Lines (DSL) – Operate over existing telephone lines – High speed transmissions • Cable Modems – Operates over cable lines to provide access to networks • T1 Line – Dedicated telephone line, rate of 1.544 Mbps 17 Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) Computer-to-computer exchange of standard business transaction documents 18