* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download presentation
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
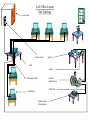
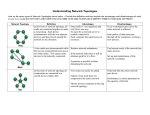
“Getting to Know Networks” What Is a Network? A network is a collection of computers hooked up together, usually by cables or telephone wires, for the purpose of sharing information and resources. Commonly connected devices include personal computers (PCs), minicomputers, mainframe computers, terminals, workstations, printers, fax machines, smartphones, and various data-storage devices. Advantages of Networks The most obvious benefit is that you can store virtually any kind of information at a central location on the network as well as access it from any connected computer. Other advantages are: 1. Cost-effective Resource Sharing—peripherals can be shared. 2. Streamlined Business Processes—tasks such as employee collaboration on projects and holding meetings can take less time and cost less. 3. Cheaper Sales Process—networks connect businesses to customers through the electronic storefront: a Web site allows customers to search for and order products and services. Advantages 4. Secure Management of Sensitive Information— the ability to protect network resources and files. Proper security features will control who will have access to sensitive data, equipment, and other resources. 5. Worldwide, Instantaneous Access to Information—you will be able to distribute critical information to many locations anywhere in the world, almost instantaneously. Recent Networked Peripherals Recently, other types of devices have become network-connectable, including interactive televisions, smartphones, tablets, ebooks, GPS, and environmental control systems. Networked devices everywhere provide two-way access to a vast array of resources on a global computer network through the largest network of all—the Internet. Types of Network Stations LAN—Local area networks operate primarily over a small area, such as an office building. The cables that hook parts of the network up together are owned by the user. WAN—Wide area networks covers a large area, such as all the branches of a bank. It is usually connected through leased telephone lines and satellite hookups. Hardware Needed 1. Network Interface Cards—an expansion board inserted into a computer so the computer can be connected to a network. 2. Networking Software—directs the communication functions, security protection, and data and peripheral sharing within a group of computers. Examples include Novell and Windows NT. 3. Networking Security—The authorization of access to data in a network. How Does Fiber Optics Work? Instead of sending electrical signals through metal, light pulses are transmitted. While plastic cables are easier to install, glass allows you to transmit network signals over a much longer distance. Fiber optics is faster than standard electronics because transmission travels at the speed of light. What’s Network Physical Topology? “Network topology” refers to the layout of a network. Due to the specific nature of computer network technology, networks must be arranged in a particular way in order to work properly. Some of them include: – Ring – Bus – Star – Tree What Is a Ring Topology? The most common topology today is a collapsed ring. This is due to the success of a network protocol called the Ethernet. This protocol, or a network language, supports the Internet, Local Area Networks, and Wide Area Networks. In this design, computers are connected via a single cable, but the end nodes also are connected to each other. In this design, the signal circulates through the network until it finds the intended recipient. If a network node is not configured properly, or it is down temporarily for another reason, the signal will make a number of attempts to find its destination. A collapsed ring is a topology where the central node is a network device called a hub, a router, or a switch. This device runs a ring topology internally and features plugins for cables. Next, each computer has an independent cable, which plugs into the device. Most modern offices have a cabling closet, or a space containing a switch device that connects the network. All computers in the office connect to the cabling closet and the switch. Even if a network plug is near a desk, the plug is connected via a cable to the cabling closet. What Is a Bus Topology? A bus topology is another type of design where a single cable connects all computers and the information intended for the last node on the network must run through each connected computer. If a cable is broken, all computers connected down the line cannot reach the network. The benefit of a bus topology is a minimal use of cabling. What Is Star Topology? A star topology is a design of a network where a central node extends a cable to each computer on the network. On a star network, computers are connected independently to the center of the network. If a cable is broken, the other computers can operate without problems. A star topology requires a lot of cabling LAN Office Layout Star Topology secure room network server printer Hub scanner twisted-pair cable network administrator USB cable workstation digital camera Smart phones The Future of Wireless Technology? Wireless topologies differ greatly from wired topologies, because the medium (radio frequencies) has different properties than wires. The principles used in creating wireless networking solutions are based on the technology currently in use with cellular telephone systems. So far, there have been three generations of mobile technologies. The first generation is the analog cellular system, the second is digital wireless, and the third generation (3G). This system is designed to be an always-on service for everything from voice to video to data transfer. Thank you for viewing “Getting to Know Networks”!