* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EIGRP
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
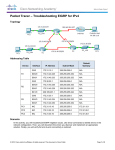
EIGRP Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol What is EIGRP? • Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) is an advanced version of IGRP. • Provides superior convergence, operating efficiency and combines linkstate protocol with distance-vector protocols. Advantages of EIGRP • low usage of network resources during normal operation • when a change occurs, only routing table changes are propagated, not the entire routing table, this reduces the load the routing protocol itself places on the network • rapid convergence times for changes in the network topology Neighbor Discovery • EIGRP uses non-periodic incremental routing updates. • EIGRP only sends routing updates about paths that have changed when those paths change. How EIGRP Works? A typical distance vector protocol saves the following information when computing the best path to a destination: the distance (total metric or distance, such as hop count) and the vector (the next hop). For instance, all the routers in the network in Figure 1 are running Routing Information Protocol (RIP). Router Two chooses the path to Network A by examining the hop count through each available path. How EIGRP Works? Since the path through Router Three is three hops, and the path through Router One is two hops, Router Two chooses the path through One and discards the information it learned through Three. If the path between Router One and Network A goes down, Router Two loses all connectivity with this destination until it times out the route of its routing table (three update periods, or 90 seconds), and Router Three re-advertises the route (which occurs every 30 seconds in RIP). How EIGRP Works? EIGRP, instead of counting on full periodic updates to re-converge, builds a topology table from each of its neighbor's advertisements (rather than discarding the data), and converges by either looking for a likely loop-free route in the topology table, or, if it knows of no other route, by querying its neighbors. Router Two saves the information it received from both Routers One and Three How EIGRP Works? It chooses the path through One as its best path (the successor) and the path through Three as a loop-free path (a feasible successor). When the path through Router One becomes unavailable, Router Two examines its topology table and, finding a feasible successor, begins using the path through Three immediately. Properties of EIGRP • • • EIGRP can route IP, IPX and AppleTalk. Along with IS-IS, which is one of the few multi-protocol routing protocols The Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL) is the heart of EIGRP. In essence, DUAL always keeps a backup route in mind, in case the primary route goes down. DUAL also limits how many routers are affected when a change occurs to the network There is no maximum allowable number of hops. In a EIGRP network, each router multi-casts "hello" packs to discover its adjacent neighbor. This adjacency database is shared with other router to build a topology database. From the topology database the best route (Successor) and the second best route (Feasible Successor) is found Properties of EIGRP • EIGRP is classless, meaning it does include the subnet mask in routing updates. However, by default 'auto-summary' is enable. You must disable if you want subnet information from other major networks • The EIGRP metric is a can be a complex calculation, but by default it only uses bandwidth and delay to determine the best path. EIGRP v.s Other Routing Protocols Feature classful or classless metric periodic advertisement advertising address administrative distance category RIP v1 RIP v2 OSPF IGRP EIGRP classful classless classless classful classless hop count hop count composite (BDRLM) composite (BDRLM) 30 seconds 30 seconds cost (100,000/b w) none 90 seconds 30 seconds 255.255.255. 255 (broadcast) 224.0.0.9 (multi-cast) 255.255.255. 255 (broadcast) 120 120 224.0.0.5 224.0.0.6 (multicast) 110 distance vector distance vector link-state distancevector 224.0.0.1 0 (multicast) Internal 90 External hybrid 170 100 Configurations and Show Commands for EIGRP Router#conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)#router EIGRP 200 Places you in Router EIGRP Config mode, the '200' is the Autonomous system (AS) number. On routers with the same AS number will share information. Router(config-router)#network 10.0.0.0 Enables EIGRP on all interfaces that are part of the Class A 10.0.0.0 Router(config-router)#network 157.89.0.0 Router(config-router)#network 200.1.1.0 Router(config-router)# Router# To debug: debug ip eigrp To view routing table: show ip route To view IP address: show ip int brief To view the EIGRP Topology table: show eigrp topology all-links To view EIGRP key statistics: show eigrp traffic EIGRP Scenario and Router Configurations Based on 3 Routers Meshed Dallas Router Configuration: Singapore#show runningconfig Building configuration... Current configuration: ! version 12.0 service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service passwordencryption ! hostname Dallas ! ! ! ip subnet-zero no ip domain-lookup ! ip audit notify log ip audit po max-events 100 ! ! process-max-time 200 ! interface FastEthernet0/0 Dallas Router interface Serial0/0 ip address 192.168.224.2 255.255.255.2 no ip directed-broadcast no ip mroute-cache no fair-queue clockrate 56000 ! interface BRI0/0 no ip address no ip directed-broadcast shutdown isdn guard-timer 0 on-expiry accept ! interface Serial0/1 ip address 192.168.240.1 255.255.255.2 no ip directed-broadcast clockrate 56000 ! router eigrp 100 network 192.168.224.0 network 192.168.232.0 ! router igrp 100 network 192.168.240.0 ! ip classless no ip http server ! ! line con 0 logging synchronous transport input none line aux 0 line vty 0 4 ! ! no scheduler allocate end Orlando Router Configuration: SanJose3#show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration: ! version 12.0 service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption ! hostname Orlando ! ! ! ! ! ! ip subnet-zero no ip domain-lookup ! ip audit notify log Orlando Router ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 192.168.1.3 255.255.2 no ip directed-broadcast no keepalive ! interface Serial0/1 no ip address no ip directed-broadcast shutdown ! router eigrp 100 network 192.168.0.0 network 192.168.1.0 network 192.168.224.0 ! ip classless no ip http server ! ! line con 0 logging synchronous transport input none line aux 0 line vty 0 4 ! ! no scheduler allocate end New York Router Configuration: NewYork#show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration: ! version 12.0 service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service passwordencryption ! hostname NewYork ! ! ! ! ! ! ip subnet-zero no ip domain-lookup ! ip audit notify log ip audit po max-events 100 ! ! ! process-max-time 200 ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 192.168.248.1 255.255.255.0 no ip directed-broadcast no keepalive ! interface Serial0/0 ip address 192.168.240.2 255.255.255.252 no ip directed-broadcast no ip mroute-cache no fair-queue ! interface Serial0/1 ip address 192.168.228.2 255.255.255.252 no ip directed-broadcast New York Router ! router eigrp 100 network 192.168.240.0 network 192.168.248.0 ! ip classless no ip http server ! ! line con 0logging synchronous transport input none line aux 0 line vty 0 4 ! ! no scheduler allocate end