* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Social Networks and Peer to Peer
Survey
Document related concepts
Backpressure routing wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Dijkstra's algorithm wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
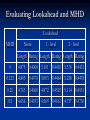
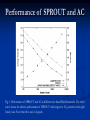
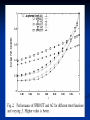
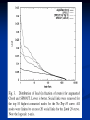
Social Networks and Peer to Peer As Presented by Jeremy Robinson 3/22/2007 What is a social network? A social network is a social structure of nodes tied together by one or more specific types of relations. Examples: Classmates.com Friendster Myspace Facebook SPROUT Introduction Why do we need it? P2P vulnerable to routing Denial of Service Attacks Misrouting attacks What is misrouting? Any failure by a node to forward a message to the appropriate peer according to the correct routing algorithm. SPROUT Introduction Malicious users Masquerade as index owner of keys Can acquire several valid network identifiers to control multiple nodes – Sybil attack. Can avoid this by sending messages only to “trusted” nodes like people we know personally perhaps in a real life social context. They propose to use existing social network services to build P2P Networks to add highly trusted links at little additional cost. SPROUT Trust Model Big Assumption Friends are not likely to be selfish or malicious. Also, friends of friends are also unlikely to be malicious. Also assume that likelihood that B purposefully misroutes A’s message is proportional to distance between A’s owner and B’s owner. SPROUT Trust Function T ( A, B) is the trust A has in B Probability f = 0.95 that friends will route correctly, 0.90 that friends’ friends route correctly, 0.85 that friends’ friends’ friends route correctly and so on. Probability r = 0.6 that any random node will route correctly. This means 40% of randoms are malicious SPROUT Path Rating Path trust rating, P, found by multiplying separate node trust ratings for each node. Source node = S, Destination = D P = T(S,A) * T(S,B) * T(S,C) * T(S,D) SPROUT Social Path Routing Algorithm Build a DHT routing algorithm built on basic Chord algorithm. Can be applied to other DHT designs like CAN or Pastry. Like in Chord, user joins, gets randomly assigned a network identifier. Establishes links to sequential neighbors, but THEN add additional links to any friends that are online. Most popular instant messenger services keep user aware of when friends enter or leave network. SPROUT Social Path Routing Algorithm SPROUT Optimization Lookahead Can see friends’ friends Minimum Hop Distance MHD May have friend at each sequential neighbor, gives worst case routing O(n). Use MHD of 0.25 then next friend must be at least a quarter away, or we use Chord. SPROUT Simulations Used data from Club Nexus community website at Stanford University. About 2200 users, on average each node had about 8 links. Also ran experiments on 130,000 AOL Instant Messenger users. Used f = 0.95 and r = 0.6. SPROUT VS. CHORD Avg. Path Length Avg. Reliability Regular Chord 5.343 0.3080 Augmented Chord 4.532 0.3649 SPROUT(1,0.5) 4.569 0.4661 Evaluating Lookahead and MHD Lookahead MHD None 1 - level 2 - level Length Rating Length Rating Length Rating 0 4.875 0.4068 5.101 0.4420 5.378 0.4421 0.125 4.805 0.4070 5.003 0.4464 5.258 0.4478 0.25 4.765 0.4068 4.872 0.4525 5.114 0.4551 0.5 4.656 0.4033 4.569 0.4661 4.757 0.4730 Performance of SPROUT and AC Fig. 1. Performance of SPROUT and AC in different size Small World networks. The third curve shows the relative performance of SPROUT with respect to AC, plotted on the righthand y-axis. Note that the x-axis is logscale. SPROUT Calculating Trust SPROUT Message Load Biggest problem for SPROUT Uneven distribution. Load bigger than AC. Can use as advantage, One highly connected large capacity node increases reliability and decreases load on other nodes. Searching Social Networks Only small bit pertains to P2P P2P uses brute force to find things, they propose a referral agent system. Most P2P algorithms don’t fit social networks because they cannot be partitioned by IP address. Also P2P have fixed routing tables for each node so network is not reconfigurable. The End Questions??