* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Stego Intrusion Detection System (SIDS)
Survey
Document related concepts
Factorization of polynomials over finite fields wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Information privacy law wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Mobile security wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
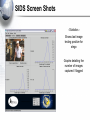
Stego Intrusion Detection System (SIDS) Michael Sieffert Assured Information Security, Inc. Topics Covered • • • • • • • • Steganography Steganalysis Misuse / Motivation SIDS structure Screenshots Demo? Future of SIDS Conclusion Steganography • “Art of covered writing” • Concealing the existence of communication between two parties • Hiding data in common, unstructured areas of media files – Transmitted via computer networks • Many tools available freely that work with: – Image, music files – Text – TCP/IP header fields Stego (continued) (original) (carrier) Steganalysis • Detecting the presence of steganographic data • Does a given file contain stego? – How sure can we be? • Not always a certainty – If so, is it possible to extract its contents? • Many products / algorithms available that attempt to discover stego – Some algorithms are closed source or proprietary – Not organized into any consistent API Potential for Misuse? • Of course! • Transmission/storage of illegal or proprietary data – Child pornography – Company secrets • Terrorist message passing? • Adversaries • Intruders – Data exfiltration/infiltration • Insider threat Motivation • Adversaries can use stego to communicate undetected – Even through our own networks – Manual attacks – Programmatic attacks • A stealthy piece of malicious software is aware of network defenses, and will circumvent them • An intelligent virus/trojan program could be using HTTP to transmit and receive data – Current network defense mechanisms will not stop this • Firewall • Intrusion detection systems • Corporate espionage gets easier! Your network is at risk! HTTP Image Transfer • How many images are pulled into/out of your network daily? – Makes an attractive channel for stego’ed data transfer • An attacker / virus could create (seemingly normal) HTTP traffic that contains important* data – Instructions for the program – Proprietary / sensitive information (secrets, credit card numbers, etc) SIDS • Stego intrusion detection system – Aims to flag all HTTP traffic containing imagery that tests positive for stego content (more protocols later) • Gateway defense mechanism – Placed at a network border – In promiscuous mode, sniffs all HTTP traffic and reconstructs (if necessary) any images transmitted – Tests each image against all known steganalysis algorithms – Alerts user/administrator to presence of stego on their network Not a firewall! High Level View Master Database Internet image1 image2 image3 image4 image5 Scanner Algorithm 1 Algorithm 2 Algorithm 3 Algorithm 4 Algorithm n SIDS Highlights • Plug-in interface for steganalysis algorithms – Allows SIDS to increase its effectiveness as new methods are developed – Proprietary or sensitive algorithms can be used in house • Interface written in Java, making the GUI section of SIDS easily portable to a separate platform in the future • SIDS machine does not even need an IP address, making it undetectable to an attacker SIDS Screen Shots - Statistics - Shows last image testing positive for stego Graphs detailing the number of images captured / flagged Screen Shots (continued) - Recent Finds - Details of individual images captured from the wire Summary of steganalysis information Allows for manual inspection of images Screen Shots (continued) - Histograms - Provide a breakdown of the most frequent offender's IP addresses Limitations • Extremely high traffic can cause packet loss • Only a handful of algorithms ship with SIDS currently – Working to add more algorithms – User can add their own – Attempting to establish a community standard • User interface can be improved, made more lean • Only HTTP, currently – Unable to examine encrypted data Future of SIDS • Always more protocols/places to check for stego – FTP, P2P, NNTP, IRC, ICMP, TCP/IP headers, Timing – Email (attachments), etc. • Host based version of SIDS likely on the way – Continually checking all images found on a system for stego – Help catch use of stego storage (stuff that’s not sent across the wire) • Enterprise Edition • Hardware assisted steganalysis • Neural nets Future of SIDS (continued) • Best detection with newest steganalysis algorithms • Moving towards the anti-virus model – Database of detection ‘signatures’ must be up to date • Development of public database of detection algorithms – Developed as plug-ins for all versions of SIDS – Freely downloadable Conclusion • Stego is being used... and will continue to gain acceptance as a method of hiding in plain sight • Defense is a hard problem • Efficiency issues with loads of scanning / analysis • Steganalysis is improving – Still behind the state of the art in steganography • This trend will likely to continue as new forms of stego emerge Questions.. • SIDS – Created by Dr. Leonard Popyack and Charles Green (Assured Information Security, Inc.) – Code Authors: • Rodney Forbes (daemons, plug-in interface) • Mike Sieffert (Java GUI) – Sponsored by Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL), Air Force Information Warfare Battlelab (AFIWB) • POC: Thomas Blake, AFRL/IFGB ([email protected])

























![[draft 3 – August 26] - Permanent Mission to the United Nations](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002283207_1-9fe48da960ce73311bff9a7b672b902e-150x150.png)

