* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Airport security wikipedia , lookup
Proxy server wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Unix security wikipedia , lookup
Cyber-security regulation wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Computer and network surveillance wikipedia , lookup
Mobile security wikipedia , lookup
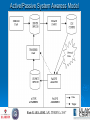
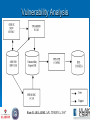
Enterprise-wide Web Security Res. Assistant Enis Karaarslan Ege Univ. Campus Network Manager ULAK-CSIRT http://csirt.ulakbim.gov.tr/eng CONTENT 1. Why web security? 2. Network / web system Awareness 3. Secure Coding 4. Enterprise Web Security Model Standardization Awareness Training/Testing Detection Prevention Coordination Centre CONTENT (cont.) 4. Implementation 5. Conclusion 1. Why need web security? Web information systems, devices ...etc Web (server) usage increases incidents increase Zone-H – 400,000 (%36) increase in 2004 CSI-FBI – “Computer Crime and Security Survey” - %95 of the correspondents experienced more than 10 web site incidents in 2005 Why need web security? (contd.) Incidents can cause Loss of privacy of the customer data Many results of private data loss Damage to the enterprise’s/vendor’s reputation Reaching network devices and ... Etc. Major Problems in Web Security • Not enough importance is given for the web security • Traditional security measures are not sufficient • Insufficient web server security • Lack of secure coding We wouldn’t need so much network security, if we didn’t have such bad software security. Bruce Schneier To win a war, one must know the way Sun Tzu The Art of War 2. Network / Web System Awareness Know your enemy (?) Know yourself, know your assets know what to protect Know your systems more than the attacker Network / Web System Awareness (contd.) Network Awareness the ability of knowing what is happening on the network Web System Awareness specialized form of network awareness Web System Awareness Vulnerability Analysis System Monitoring Web System Awareness Web Infrastructure Awareness Collect and have current system information Vulnerability Testing Know your visible weaknesses Monitoring the system See the current status of the system Web Infrastructure Awareness Web server IP addresses Protocols used (https, http) Site domain names (ex. socrates.ege.edu.tr) Web server ports (80, 8080, etc) Operating system (Linux, Windows, etc) Web server software types and versions (Apache 2.0, IIS 6.0, etc) Web Infrastructure Awareness (contd) Content Management Systems (CMS), Portals, Wikis, Bulletin Boards, discussion forums Web frameworks (PHP, .NET, J2EE, Ruby on Rails, ColdFusion, Perl, etc) and all types of web applications Application file names Path to the applications, the directory structures Application parameters and their types 3.Secure Coding Secure coding and vulnerability testing in Software Devolopment Life Cycle (SDLC) Assurance Models Ex. OWASP Clasp, Microsoft SDL OWASP Tutorials http://www.owasp.org Secure Coding (contd.) Can not be implemented perfectly as Project deadlines Programmer’s lack of security-awareness But should be focused on. Also network based measures must be considered. 4. Enterprise Wide Web Security Model Model consists of sub modules: Standardization Awareness Training/Testing Detection Prevention Coordination Centre Standardization Policy based Define what is permitted, what is not Define the preffered system Supply templates, best practices Secure coding Documentation Training / Testing Workshop Show secure coding examples, attack scenarios Training Portal Related secure coding best practices Guidelines, standards Test Server Black box testing Source code analysis Intrusion Detection Intrusion Detection Systems Ex. Snort, Mod Security Log Control Honeypot, honeynet Prevention Access Control Ex. Network firewall, router ACL Server Local Security Ex. Mod Security Reverse Proxy - Web Application Firewall Ex. Mod Security – Mod Rewrite 5. Implementation Web Security model on process in Ege University –Turkey Web Security Group in Ulak-Csirt Focus on Web System awareness and training Open source tools Results will be given 5.1. Active/Passive System Awaress Aim is to collect and have the current view of the web system Active Scan NMAP – AMAP Perl Code for the analysis Open Source Search Engine (future work) Passive Scan Snort Mod Security Active/Passive System Awaress Model Test Deployment Schema • IDS configured for web security – WEBIDS – TWEBIDS- knows web system infrastructure Statistical Results WEBIDS Total Number of Alerts Source IP Address Destination IP Address Unique IP Links Unique Alerts TWEBIDS 902,151 92,046 79,419 17,010 106 106 87,062 10,657 112 99 • Alerts collected in one month duration • TWEBIDS which knows the system, has more specific alerts and less false alarms • More statistics in the paper Vulnerability Analysis Awareness Portal A web portal for web server administrators and security proffessionals: Detailed reports about their web systems Summarized information about the vulnerabilities Recommend actions to solve the problems. Track the changes on the systems. Plan to expand this implementation to control the critical web servers of the universities in the Turkish Acedemic Network ULAKNET. System Database Schema 5.2. Training Workshops, meetings, live demos Web server administrators, web application developers Habits can’t change easily Education is a must! Documentations Turkish documents - translations http://websecurity.ege.edu.tr http://csirt.ulakbim.gov.tr/dokumanlar İTU-Ninova – Web Security e-learning content http://ninova.itu.edu.tr 6. Conclusion For enterprise web security, implement modules of the Web Security Model Complexity versus protection Select the modules which suite your enterprise Primary objectives for the enterprise wide web security should be: Web system awareness Training web server administrators, web programmers Conclusion (contd.) Systems should be monitored for Intrusion Detection Web security firewall implementation if possible Future plans: Fully integrate this model Continue to increase web security awareness Continue to involve in documentation projects and translations Thanks for your interest .... Any questions? Contact: [email protected] [email protected] ULAK-CSIRT http://csirt.ulakbim.gov.tr/eng