* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Policies promoting wireless broadband in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
SIP extensions for the IP Multimedia Subsystem wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
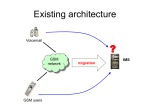
Mobile Multimedia and Multimedia Systems Perspectives Introduction Wireless is moving into broadband: - 3G, 4G mobile networks - WLAN - DVB-H - WIMAX How to make maximum use of these systems? Technology progress Broadband wireless media technology is behind the corner: WLAN ONBOARD 3G ONBOARD 4G ONBOARD ALL INTEGRATED ONBOARD COMPLEX MEDIA SYSTEMS BEHIND WLAN Wireless networks 3G-4G Mobile WLAN OTHER IEEE 802.11a+b+g +n Other System reqirements Operator wants efficient resource management: transmission coverage and cost User wants minimized cost of access and seamless operation Seamless challenge Seamless changeover (handover) between the systems is technical challenge Heterogenous networks may not be synchronised, even content stream may not be identical (e.g. different compression ratios) Gateways and managers The changeover problem can be solved by embedding gateways on the network side and/or managers on the terminal side Multisystem terminals for 3G+WLAN will have severe limitations on power consumption Handover requirements Seamless means perfect stream splicing This can be done when streams are aligned in buffers and synchronized In general time stamps and bitrates may not be identical Gateways and managers DVB-H NETWORK GATEWAY WLAN TERMINAL MANAGER 3G In case of operator controlled networks gateway ensures synchronization. In heterogenous networks terminal performs synchronization and handover FUTURE MOBILE SYSTEM IS BROADBAND FOR MULTIMEDIA IT SUPPORTS MULTIPLE NETWORK TYPES (3G, WLAN, 4G….) IT SUPPORTS MULTIPLE OPERATION MODES: UNICAST, MULITCAST, BROADCAST, MULTISTREAMING THE SYSTEM IS IP PROTOCOL BASED ! MOBILE DATA BANDWIDTH FUTURE MOBILE SYSTEM WILL HAVE DATA BANDWIDTH IN MEGABITS/SECOND 3G - 1-10 Mb/s 4G - 10-50 Mb/s WLAN - 1- 100 Mb/s THE FUTURE MOBILE SYSTEM THE FUTURE MOBILE SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE IS DEVELOPED THE STANDARD IS CALLED IMS (Internet Multimedia Subsystem) It is developed as an extension of 3G mobile standard (release 5,6) by 3GPP (www.3gpp.org) and IETF (www.ietf.org) THE IMS The IMS is based on SIP protocol This allows setup of most complex multimedia sessions The IMS basic idea The basic idea of IMS is integration of telephone CS (Circuit Switched) network and IP network running in wireless systems Radio access in 3G. 4G 3G version In USA User capabilities in IMS The IMS extends widely the capabilities of current systems as regards the usage of the system User may have two types of addresses: phone and Internet Users may have multiple identities: work and private in same equipment Users may have multiple terminals with different capabilities Mobile IP – Short Overview Key aspect of wireless networks is mobility. Mobility is realized in cellular systems based CS but it can be also realized in IP systems. Here we provide short overview of IP mobility. This does not mean it is realized in the IMS. IMS can use standard mobility realized in cellular systems. Mobile IP Key Principles The Wireless Internet is an IP-centric & mobility-enabled network: •IP addresses are used for all routing within the core network •IP protocols and technologies are used in the control plane •The network is functionally equivalent to a traditional cellular network (especially with respect to mobility and roaming) Mobile IP Key Principles IP Mobility focuses on Layer 3 of the core network: Mobility functions are independent of the access technology (2G, 3G, wire line, etc.) and the underlying network transport technology (ATM, Ethernet, etc.) Mobility is based on the user, not the terminal: •Users will have a single subscription in a home network •Service Level Agreements (SLA’ s) must exist between all networks users will roam in Mobile IP Components •Mobile Node (MN): laptop, mobile phone, communicator,..etc •Home Agent (HA): router of the home network •Foreign Agent(FA): router of the foreign network Mobile IP Components (MN) (FA) (HA) How Mobile IP works Agent Discovery Registration Routing Agent Discovery 1- HA’s and FA’s: periodically advertise their presence on their subnets by broadcasting agent advertisements 2-MN Listen: Am I on my home sub net or I am visiting some other subnet? OR 1- MN sends an agent solicitation 2- Any agent on the subnet is forced to send an immediate advertisement Agent Discovery •MN determines that it is connected to an (FA) acquires a care of address •Care of Address: and IP address given to the MN by the FA (exit point of the tunnel from HA to FA) Registration •MN recieved the care of address: register it with the HA •HA creats a mobility binding table •HA advertises reachability to the home IP address of MN •Example: a device connected to the internet called corresponding node (CN) sends a packet to MN, how it will reach MN? CN HA FA MN •power down or go back to home sub net: MN will deregister •HA reclaims MN through tunnel IP Mobility:a lower level look Visited Network FA Mobility Manager IPSec SA 1 Security Gateway Security Gateway Internet Router IPSec SA 3 Home Network AAA+ Router AAA+ IPSec SA 2 IPSec SA 4 User Correspondent Node Security Associations IPSec SA 1 - between security gateways IPSec SA 2 - between AAA servers IPSec SA 3 - between user/terminal and mobility manager IPSec SA 4 - between user/terminal and correspondent node Mobility Manager HA IP Mobility Hand Over Mobility Manager Router Home Network Security Gateway Security Gateway 5 Router 2a Router Mobility Manager Router 9 6 10 AAA+ 7 AAA+ DNS Visited Network 2 Internet LSF 4 Router 1 7a 3 Mobility Manager Security Gateway 9a 9 11 Router 8 Router AAA+ Serving Network Correspondent Node Capabilities Of Mobile IP User identity and Addressability Signaling and packet routing Authentication and Authorisation Security associations Mobile client functionality IP industry compatibility How Does It Look like? Haroon@SubNet1 is at home. Please ensure his data comes here. HA FA Internet Backbone At home Haroon@SubNet1 is in our CDMA network. Please ensure his data comes here. FA HA Internet Backbone On the road How Does It Look like? Haroon@SubNet1 is at work. Please ensure his data comes here. FA HA Internet Backbone Why certainly, we have an arrangement with your Network operator. I can register you with free run of the house wireless LAN. Enterprise LAN At the office FA Haroon@SubNet1 is in our hotel. Please ensure his data comes here. In a hotel Internet Backbone HA Roaming in IMS Usser can roam in the CS (circuit switched) and IMS in different Combinations (being in CS directed to IMS and opposite) IMS layered architecture Acronyms in the IMS scheme CSCF Call Session Control Function PDF Policy Decision Function BGCF Breakout Gateway Control Function MRFC Mutlimedia Resource Function Controller MRFP Multimedia Resource Function Processor MGCF Multimedia Gateway Control Function MGW Multimedia Gateway Function SGW Signalling Gateway SEG Security Gateway SGSN Serving GPRS Support Node GGSN Gateway GPRS Support Node IMMGW Internet Multimedia Gateway HSS – Home Subscriber Server HSS has functions for CS and PS networks: Home Location Register HLR with Authentication Center AUC Signalling conversion in SGW Protocols from IMS domain (SIP) have to be converted to the CS domain IMS Architecture RAN – Radio Access Network SLP – Subscription Locator Function UE – User Equipment Some reference points: Gm – connection of UE to IMS (for SIP) Mw – connection between CSCF’s Cx – subscriber and service data Dx – connection to SLF (Sub. Locator Func. Conclusion IMS is a complicated system satisfying all possible multimedia requirements IMS will coexist with CS system At some point in the future all-IP systems may by used exclusively MULTIMEDIA SYSTEMS PERSPECTIVES MULTIMEDA SYSTEMS IREK DEFEE MULTIMEDIA SYSTEMS INTEGRATE ALL THE COMPONENTS DESCRIBED IN THIS COURSE: - SERVERS - NETWORKS - CLIENTS - SOFTWARE - CONTENT MULTIMEDA SYSTEMS IREK DEFEE WHAT WILL BE THE FUTURE IN MULTIMEDIA SYSTEMS? WHAT IS HAPENNING RIGHT NOW IS THAT NEW TECHNOLOGIES AND MULTIMEDIA SYSTEMS ARE COMING ALL THE TIME, ESPECIALLY IN THE MOBILE AREA -TERMINALS -NETWORKS -SOFTWARE MULTIMEDA SYSTEMS IREK DEFEE Historical development • From mobile phone to smartphone MULTIMEDA SYSTEMS IREK DEFEE MOBILE PHONES EVOLVED INTO MOBILE MEDIA AND SERVICE DEVICES THEY CHALLENGE PHOTOGRAPHIC CAMERAS, VIDEO CAMCORDERS, PORTABLE MUSIC PLAYERS, GAME CONSOLES AND SERVICE ACCESS DEVICES MULTIMEDA SYSTEMS IREK DEFEE Heterogenous networking From GSM radio network via Bluetooth to… WIRELESS BROADBAND or… From tens of kilobits to megabits per second • 3G onboard WLAN onboard 4G onboard • ALL onboard MULTIMEDA SYSTEMS IREK DEFEE •SO WE MAY THINK THAT MOST DEVICES •WILL BE MEDIA DEVICES AND CONNECTED BY • WIRELESS. •HOW THIS MAY HAPPEN? IN THE FUTURE •WE WILL HAVE HUGE RANGE OF APPLICATIONS •AND SERVICES: MULTIMEDA SYSTEMS IREK DEFEE WE WILL HAVE VARIETY OF TERMINAL DEVICES.... MULTIMEDA SYSTEMS IREK DEFEE NETWORKING PLATFORMS WILL BE INTEGRATING – ONE DEVICE WILL BE ABLE TO CONNECT TO DIFFERENT NETWORKS MULTIMEDA SYSTEMS IREK DEFEE HOWEVER, ALL THESE NETWORKS WILL BE BASED ON THE IP PROTOCOL: MULTIMEDA SYSTEMS IREK DEFEE •HERE WE MOVE TO IP PROTOCOL •HERE THE BANDWIDTH GROWS •HERE ARE DIFFERENT NETWORK TYPES MULTIMEDA SYSTEMS IREK DEFEE From Telephone to Internet Telephone network for speech Internet for data and… everything •WLAN IP networking is the future MULTIMEDA SYSTEMS IREK DEFEE New data transfer ways From: person-to-person phone call To: Data center-to-mass public - TV - Multicast Internet • • • • 3G MBMS WLAN IP Multicast Multimedia Broadcast & Massive distribution of content is possible rather soon Multicast MULTIMEDA SYSTEMS IREK DEFEE What is mobile device? • • camera camcorder TV radio makeup device? game PDA Swiss army knife? MULTIMEDA SYSTEMS IREK DEFEE The Service Case: Mobile IPod • • • • IPod, Portable Music Player Music Web shop Mobile Music device with hard disc • • Mobile device is an IPod, and phone, and much more…. MULTIMEDA SYSTEMS IREK DEFEE And the final destination... • LONG IN THE FUTURE…. • TECHNOLOGY MAY BECOME INVISIBLE MULTIMEDA SYSTEMS IREK DEFEE MULTIMEDIA SERVICES MANY INNOVATIONS ARE POSSIBLE IN THIS AREA: - CONTENT, NETWORKING AND USER NEEDS ARE IMPORTANT - SERVICE IDEA IS NOT SIMPLE TO GET - PRESENT SERVICES: TV, VIDEO, GAMES – they look traditional in a way INNOVATIVE SERVICES THEY ARE POSSIBLE BUT ONE HAS TO HAVE INNOVATIVE IDEA. HOW TO GET AN IDEA??? No rules for this, one has to think about it INNOVATIVE SERVICE EXAMPLE NEW SERVICES ARE POSSIBLE BUT ONE HAS TO HAVE INNOVATIVE IDEA. HOW TO GET AN IDEA??? No rules for this, one has to think about it. Example: service for fitness called iFit, www.ifit.com iFit service example Service idea: Many people are concerned with fitness and buy specialized devices like fitness bikes and treadmills • Treadmill is a substittute for running when when it is cold, rainy or unsuitable surrounds BUT, running on a treadmill is boring without any new visual stimulation SERVICE IDEA Install display in the treadmill and show running tracks in it There will be new visual stimulation making running less boring IMPLEMENTATION OF THE IDEA How to realize this, since users want new tracks? Solution: Use Google Streetview and maps Users can design their own tracks then BUT, running requires that the track changes with the progress of running How to do this? IMPLEMENTATION OF THE IDEA Solution: Built network connection into the fitness device: Wireless module inserted into device Now the fitness device may send and receive control signals about the speed and Incline. Device operation is synchronized with the running track SERVICE IMPLEMENTATION This service requires special fitness devices compatible with wireless connectivity – user has to buy it Company charges monthly fee for providing Web site which displays the track and provides synchronization and tools. THIS IS EXAMPLE OF INNOVATIVE MULTIMEDIA SERVICE • CONCLUSIONS TO THIS COURSE: •WE WILL SEE HUGE PROGRESS IN MULTIMEDIA •SYSTEMS IN THE FUTURE. •SYSTEMS WILL BECOME MUCH MORE COMPLEX •NETWORKS WILL BE BROADBAND WIRELESS. •INFORMATION WILL BE DOWNLOADED ONLY •BY NETWORKS, PHYSICAL CARRIERS (LIKE E.G. •CD) WILL BE DISAPPEARING. MULTIMEDA SYSTEMS IREK DEFEE