* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3.1 Early Rome
Ancient Roman architecture wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican governors of Gaul wikipedia , lookup
History of the Roman Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
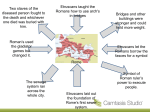
The Beginning of an Empire Early Rome The Founding of Rome Around 1000BC a group of tribes called the Latins settle in central Italy. Some choose to build villages on the south side of the Tiber River • surrounded by a ring of hills for defence • close to sea but safe from pirates • the river narrowed and had an island The people lived in little villages on the hilltops above the river. During the 8th century BC. the villages merged to form the city of Rome. The Romans wanted a glorious past like the Greeks so they invented their own version of the founding of the city, Romulus and Remus In the 8th century the Romans were just one of many groups in the Italian peninsula. They were heavily influenced by their neighbours The Greeks The Greeks settled in Southern Italy and Sicily. The influenced the Romans with their • goods (pottery, metalwork and wine) • science • literature • art • architecture The Etruscans The Etruscans lived North on Tiber River and had the biggest influence on the early Romans. Many things we think of as being Roman were adopted from the Etruscans. They enjoyed chariot races and gladiator fights, built aches, aquaducts and sewers. They were also important in shaping the government in early Rome The Kings of Rome Early Rome was ruled by a king who was chosen by a council of elders. Around 600BC the Etruscans took control of Rome and installed Etruscan Kings. Under their rule Rome grew to be an impressive city with. • public square surrounded by temples • proper drainage systems • huge defensive walls The last King of Rome, Tarquinius Superbus was very unpopular In 509 BC he was exiled and Rome became a republic. Tarquinius appealed to other Etruscan cities to attack Rome. Lead by Horatio the Romans held them off at wooden bridge that crossed the Tiber River. The Conquest of Italy The Early Roman Republic was surrounded by enemies. To North was the Etruscans and central Italy was swarming with fierce mountain tribes. The Romans were also at war with rival Latin cities and foreign invaders. By using a mixture of military power and clever politics Rome gradually fought off their enemies and gain control of the Italian peninsula. In 400BC Rome Allied itself with other Latin cities, The Latin League, together they defeated Etruscan city of Veii. Making Rome central city in Latium region In 390 BC Roman conquest was put on hold for when Rome was invaded by the Gauls. The Gauls sacked and burned Rome and left only after being paid 1000lbs in gold As the Romans rebuild their city the other cities in the Latin League began to resent Rome’s power and war broke out. In 338 BC Rome defeated the league and incorporated their cities in the growing Roman State. By 290BC the Romans had defeated • Samnites, • Etruscans • Gauls Rome controlled all of Central and Northern Italy and with each victory Rome seemed to gather strength. In 282 BC Rome was drawn into the Pyrrhic wars and defeated the Southern Greeks. By 264 BC Rome dominated all of Italy and had made itself one of the most powerful states in the Mediterranean.