* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Byzantine Empire and Russia
East–West Schism wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Empire under the Komnenos dynasty wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Greeks wikipedia , lookup
History of the Byzantine Empire wikipedia , lookup
Monothelitism wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Empire under the Heraclian dynasty wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Empire under the Angelos dynasty wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine art wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine music wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine economy wikipedia , lookup
History of the East–West Schism wikipedia , lookup
Decline of the Byzantine Empire wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Papacy wikipedia , lookup
Constantinople wikipedia , lookup
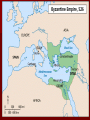
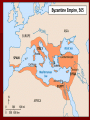
Byzantine Empire • Middle Ages / Medieval Period All the empires we • have studied to this point have been referred to as ancient civilizations. – – – – – – – Mesopotamia Fertile Crescent Egypt India China Greece Rome Ancient history is the study of the written past from the beginning of recorded human history until the Early Middle Ages in Europe. • The Middle Ages or Medieval Period began with the fall of the Roman Empire in 476 A.D. and lasts to about 1500. 3 The New Rome 395—Roman Empire split Roman Empire (West) & Byzantine Empire (East) Greeks=most of Byzantine Empire’s population Wealthy families moved to Constantinople when barbarians invaded Rome Constantinople (crossroads of Europe & Asia) Bosporus & Dardanelles— 2 important waterways Emperor Justinian 527- 565 Nicknamed “Emperor who never sleeps” Justinian’s Code code: Corpus of Civil Law (Justinian’s Code) Law –Based on Roman laws http://www.fordham.e du/halsall/basis/535in stitutes.html#XV.%20 Agnate%20Tutorship. Theodora Justinian’s wife & advisor Allowed women to own land 532: Nika Revolt – Theodora talked him into staying – General Belisarius- put down revolt & won back Roman lands Hippodrome- Chariot races (like Rome’s Circus Maximus) http://www.knowledgerush.com/kr/encyclopedia/Hippodrome_of_Constantinople/ http://www.livius.org/a/1/maps/istanbul_hippodrome_map.gif Justinian wanted strength of old Roman Empire By 554— reclaimed Italy, North Africa, & Spain from Germanic tribes – Chemical weapon “Greek fire” – After Justinian’s death, Germanic tribes reclaimed lands Christian Church Emperors crowned by Patriarch of Constantinople –Defend Christianity –Appoint Church officials Icons (religious images) – Iconoclasts believed having icons was idol worship 726: Byzantine Emperor Leo III– destroyed icons – 787: Pope in Rome-- heresy not to allow icons (some couldn’t read & icons helped them learn Christianity) – Church council threatened iconoclasts with excommunication Pope and Patriarch excommunicated each other – 700s: Lombards invaded Italy, Byzantine emperor refused to help Pope – Frankish leader helped--Pepin the Short—Pope gives him title “emperor” – 1054: SPLIT---WEST (Roman Catholic Church) EAST (Eastern Orthodox Church) Church supported marriage (sacred institution) – Roman Catholic Priests not allowed to marry Divorce - difficult to get Trade: –Goods from Asia & Europe –Silk Road –2 Orthodox monk missionaries brought silkworms from China Art- religious subjects – Icons- displayed saints – Mosaics- pieces of tile or glass – Religious scholars used art in books – Illuminated manuscripts (decorated books) Literature focused on salvation, obedience to God, & preserving Greek & Roman works Architecture 532: Church of Hagia Sophia (meaning “holy wisdom”) in Constantinople Cyril & Methodius-missionaries –860: Cyril created alphabet for Slavic people –Cyrillic Alphabetused by Russia today AD 1071—Seljuk Turks threaten Constantinople Byzantine emperor asked Pope to help “defend Christianity” Europeans went to Palestine to fight Muslims-Crusades (holy wars) 1204—Venetians looted Constantinople 1453—Ottoman Turks attacked –Byzantine emperor killed –End of Byzantine Empire The Slavs Steppe- treeless grassland Taiga- thick forests Long, cold winters 3 major rivers –Dnieper All flow North to South –Dniester –Volga The Eastern Slavs Setting and People 3 major ethnic groups lived in the area north of the Black Sea 1.) Western Slavs – Poles, Czechs, Slovaks – Close ties to Roman Catholic Church and Western Europe 2.) Southern Slavs – Serbs, Croats, Slovenes – Located on the northern part of the Balkan Peninsula – Lots of contact with the Byzantines 3.) Eastern Slavs – Largest group – Ukranians, Russians, Belarussians – Lived between the Dnieper and Dniester Rivers Kievan Rus 800s AD- Vikings from Scandinavia (Norway, Denmark, Sweden) settled town of Novgorod Vikings=Ruotsi=Rus=Russia Kiev (major trading village) Kiev grew into group of principalities called Kievan Rus Principalities ruled by princes –Grand Prince—like emperor –Princes—paid tribute to GP –Boyars—landowners –Artisans & merchants –Peasants 988 AD—Grand Prince Vladimir I adopted Christianity & Cyrillic Alphabet Yaroslav the Wise (10191054) –1st library of Kiev –Built churches, created 1st law code http://z.about.com/d/goeasteurope/1/5/T/3/-/-/UkraineStSophia.jpg 1240—Mongols invaded 1240—Alexander “Nevsky” defeated Swedes at Neva River 1380—Mucovites (people of Moscow) defeated Mongols at Battle of Kulikovo 1493—Ivan III ruler of Moscow refused to pay Mongol taxes, made himself sovereign of all Russia— “Ivan the Great” Orthodox Church called rd Russia the “3 Rome” Ivan IV “the terrible” Paranoid- mentally unstable Killed his own son Massacre at Novgorod Took title czar “caesar” http://www.uoregon.edu/~alayne/Images/stbasil-cathedral-exterior.jpg http://www.uoregon.edu/~kimball/images/repin%20I-4%20ssn.jpg