* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Midterm # 4 Tuesday Dec. 04 / 12 noon chapters 21, 22, and
Survey
Document related concepts
Postpartum depression wikipedia , lookup
Parkinson's disease wikipedia , lookup
Major depressive disorder wikipedia , lookup
Dementia with Lewy bodies wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral theories of depression wikipedia , lookup
Biology of depression wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
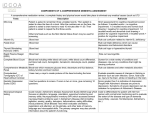
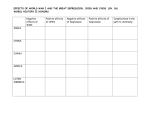
Introduction to Biopsychology [PSB 4002] Professor Robert Lickliter DM 260 / 305-348-3441 [email protected] website: dpblab.fiu.edu Midterm # 4 Tuesday Dec. 04 / 12 noon chapters 21, 22, and 2 lecture through Thursday, Nov. 29 sample study questions and slides available by Tuesday, Nov. 27 at course website / dpblab.fiu.edu Effects of Aging Effects of Aging Alzheimer's Disease • Onset – Early onset symptoms of Alzheimer’s appear before the patient turns 60. Less common than later onset. Some evidence that genetic factors are at play. – Late onset Alzheimer’s is the most common form of the disease. Some inherited traits that run in families, but the genetic factor is less clear than early onset. Alzheimer’s Disease • Early Symptoms – Memory impairment – Decreased language function – Change in emotional behavior/personality – Altered perception – Decreased problem-solving ability/cognitive skill Alzheimer’s Disease Alzheimer's Disease • Post mortem examination of brain tissue from Alzheimer’s patents is the only way to diagnose the disease with absolute confidence. – Neurofibrillary tangles (fibers of protein that have twisted and clogged the cell – Neuritic plaques (abnormal clusters of dead and dying nerve cells, proteins, and neural tissue) – Senile plaques (dying nerve cells around areas that have accumulated protein build-up. Alzheimer’s Disease • Treatment – There is no cure for Alzheimer’s at this time. Medicines (Dnepezil, Memantine) can help slow the progression of the disease, but not stop it. – Management of the disorder can include • Change in the home environment • Alterations of daily activities to promote healthy sleep and less confusion • Support from family members Depression • A spectrum disorder, it can range from mild to severe and chronic with differential prognosis, treatment, and outcomes – Some evidence for heredity, but no single genetic link has yet been found. • Everyone at some point has felt sad, blue, miserable, unhappy, or “down in the dumps”. • True clinical depression affects the mood for long periods of time, with intense feelings of: – Anger – Loss – Frustration – Sudden loss of interest in everyday activities that you used to love Depression • Onset of depression is a process of equifinality – Alcohol or drug abuse – Certain medical conditions – Steroid use – Sleep problems – STRESS! Depressive Symptoms Depression Depression • Symptoms of major depression include – Fatigue and lack of energy – Becoming withdrawn or isolated – Difficulty concentrating – Lack of interest in pleasurable activities – Thoughts of death or suicide – Altered sleep patterns – Feeling of hopelessness Depression • Treatment options – “Talk therapy” is popular. Patients try to discover the root cause of their depression and confront the issue – Antidepressant medications are typically Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) • Fluoxetine • Sertraline • Paroxetine