* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 20
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
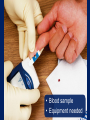
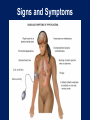
Chapter 20 Acute Diabetic Emergencies Prehospital Emergency Care, Ninth Edition Joseph J. Mistovich • Keith J. Karren Copyright ©2010 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. Objectives 1. 2. Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Describe the following regarding glucose (slides 1213): a. The function of glucose in the body b. Response of brain cells and other body cells to insufficient glucose levels c. Relationships of glucose and water 3. 4. 5. Describe how insulin and glucagon function to control blood glucose levels (slides 14-17). Describe how glucose levels are regulated in normal metabolism (slides 20-21). Explain the purposes and process of checking blood glucose levels. (slides 22-26). Objectives 6. 7. 8. 9. Discuss the pathophysiology of diabetes mellitus (DM) and contrast type 1 insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) with type 2 noninsulin- dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) (slides 27-29). Discuss the pathophysiology, assessment, and emergency medical care of a hypoglycemic emergency (slides 30-36). Identify indications and contraindications to the administration of oral glucose (slides 37-39). Discuss the pathophysiology, assessment, and emergency medical care of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) (slides 40-47). Objectives 10. Compare and contrast the speed of onset and the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia (slides 34, 45). 11. Describe the primary differences between DKA and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic syndrome (HHNS) (slides 43, 48, 50). 12. Discuss the pathophysiology, assessment, and emergency medical care of HHNS (slides 48-52). 13. Discuss the assessment-based approach to a patient with an altered mental status in a diabetic emergency (slides 53-63). Multimedia Directory Slide 26 Slide 29 Slide 39 How to Use a Blood Glucose Meter Video Information about Diabetes Video The Use of Oral Glucose Animation Topics Understanding Diabetes Mellitus Acute Diabetic Emergencies Assessment-Based Approach: Altered Mental Status in a Diabetic Emergency CASE STUDY Dispatch EMS Unit 106 Respond to 514 Chicago Avenue for a 66-yearold male who is disoriented and belligerent. The neighbor placed the call. Time out 1402 Upon Arrival • Neighbor found patient in her garden next door • When she approached him, the patient began cursing at her • Patient is acting strange and not making sense How would you proceed to assess and care for this patient? Understanding Diabetes Mellitus Back to Topics Glucose (Sugar) Back to Objectives • Sources • Roles • Brain cells Hormones That Control Blood Glucose Levels Insulin Back to Objectives Insulin • Main functions • How it works Hormones That Control Blood Glucose Levels Glucagon Glucagon • Role • Functions Hormones That Control Blood Glucose Levels Other Hormones Epinephrine • Released by the adrenal glands • Stops the secretion of insulin • Promotes release of stored glucose from the liver • Promotes conversion of other substances into glucose Normal Metabolism and Glucose Regulation Back to Objectives Normal Glucose Regulation Checking the Blood Glucose Level Back to Objectives • Glucose meters • Hypoglycemia • Hyperglycemia Checking the Blood Glucose Level Testing the Blood Glucose Level with a Glucose Meter • Blood sample • Equipment needed How to Use a Blood Glucose Meter Click here to view a video on how to use a blood glucose meter. Return to Directory Diabetes Mellitus (DM) Back to Objectives • Primary problem • Type I diabetes • Type II diabetes Information about Diabetes Click here to view a video on information about diabetes. Return to Directory Acute Diabetic Emergencies Back to Topics Hypoglycemia Pathophysiology of Hypoglycemia Back to Objectives • Cause • Reasons for drop Pathophysiology Hypoglycemia Assessment Findings in Hypoglycemia and Hypoglycemia Unawareness Assessment Findings Back to Objectives • Cause • Signs and symptoms • Hypoglycemia unawareness Hypoglycemia Emergency Medical Care for Hypoglycemia Emergency Medical Care • For a responsive patient • For an unresponsive patient Oral Glucose Back to Objectives • Purpose for administration • Criteria for administration Information about the Use of Oral Glucose Click here to view information about the use of oral glucose. Return to Directory Hyperglycemia Back to Objectives • Hyperglycemia • Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) • Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic syndrome (HHNS) Hyperglycemic Condition: Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) Pathophysiology of DKA Pathophysiology • Cause • Results in the body • Factors causing hyperglycemia in DKA patients Back to Objectives Hyperglycemic Condition: Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) Assessment Findings in DKA Assessment Findings • Signs and symptoms – Polyuria – Polydipsia – Polyphagia • Kussmaul’s respirations Back to Objectives Hyperglycemic Condition: Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) Emergency Medical Care for DKA Emergency Medical Care • • • • • ABCs Provide O2 Assist ventilation Check BGL Contact medical direction Hyperglycemic Condition: Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Syndrome (HHNS) Pathophysiology of HHNS Back to Objectives Pathophysiology • Blood glucose level • Precipitating factors Hyperglycemic Condition: Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Syndrome (HHNS) Assessment Findings in HHNS Back to Objectives Assessment Findings Signs and symptoms Emergency Medical Care • • • • • ABCs Provide O2 Support respirations Determine BGL Medical direction Assessment-Based Approach: Altered Mental Status in a Diabetic Emergency Back to Topics Scene Size-Up and Primary Assessment Back to Objectives Look for scene clues • Medic alert tags • Insulin pumps History and Secondary Assessment • SAMPLE • Common medications • Questions to ask History and Secondary Assessment Signs and Symptoms Signs and Symptoms • Place redrawn picture 2009 here – did not have yet, WDS Emergency Medical Care • ABCs • Determine if patient can swallow • Administer oral glucose • Transport Reassessment • • • • May take 20 minutes to see improvement Recheck BGL Continue O2 Manage airway as needed CASE STUDY Follow-Up CASE STUDY Primary Assessment • Patient sitting on couch • Find Digoxin in kitchen and insulin in refrigerator • Patient is pale and sweating profusely • Patient speaking in mumbled words CASE STUDY Primary Assessment • Partner places a nonrebreather mask at 15 lpm • RR: 15; P: 100 and strong CASE STUDY Secondary Assessment • Do rapid assessment • BP: 102/60 mmHg; P: 108; RR:16; skin pale, cool, and moist; SpO2: 97 percent • BGL: 48mg/dL • Administer one tube of glucose • Place patient in left lateral position CASE STUDY Treatment and Reassessment • Becomes oriented to name and place • Pulse rate, skin, and SpO2 improve • Change over to nasal cannula • Alert and oriented upon arrival • Transfer care without incident Critical Thinking Scenario • 34-year-old female with an altered mental status • Responds to painful stimuli only with moans • A neighbor called 911 after finding her on the couch and not responding Critical Thinking Scenario • S – Supine on the couch, not alert • A – Unknown • M – Her neighbor brings you the patient’s medications: Zoloft and Novolin • P – Her neighbor doesn’t know the patient’s medical history • L – Unknown • E – Patient called the neighbor 20 minutes ago and said she wasn’t feeling well Critical Thinking Scenario Vital signs: • BP: 108/62 mmHg • HR: 122 bpm • RR: 12 per minute with snoring respirations but adequate chest rise • Skin is pale, cool, and very diaphoretic Critical Thinking Questions 1. What emergency care would you provide during the primary assessment? 2. Based on the signs, what condition do you suspect the patient is experiencing? 3. What other assessment procedures would be helpful to you for this patient? 4. What would you expect the blood glucose reading to be in the patient? 5. Why is the onset of the altered mental status significant in this patient? Reinforce and Review Please visit www.bradybooks.com and follow the myBradykit links to access content for the text.