* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cnidarian part 1 - biology-rocks
Surface wave detection by animals wikipedia , lookup
Animal cognition wikipedia , lookup
History of zoology since 1859 wikipedia , lookup
Animal communication wikipedia , lookup
Aquatic locomotion wikipedia , lookup
History of zoology (through 1859) wikipedia , lookup
Animal coloration wikipedia , lookup
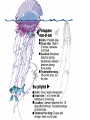
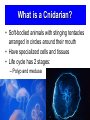
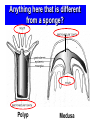
Man-o-War • Not really a jellyfish • Not a single animal Cnidarians Chapter 26-3 Pages 564-569 Coral Reefs Northern Queensland 2000km long 80km wide Coral Reefs • Corals produce skeletons of Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) or limestone • Grow in colonies • Food for animals • Home for animals • Pearls and shells • Softens waves – Protects shorelines What is a Cnidarian? • Soft-bodied animals with stinging tentacles arranged in circles around their mouth • Have specialized cells and tissues • Life cycle has 2 stages: – Polyp and medusa Two body forms • Polyp • Sessile • Flower-like • Medusa • Motile • Bell-shaped Polyp or Medusa? Anything here that is different from a sponge? Polyp Medusa Cnidaria vs Porifera • Has body wall that surrounds a space – This space = the stomach, the gut (gastrovascular cavity) – Digestion takes place there • Body wall has 3 layers: – Epidermis – outer surface of cnidaria – Mesoglea – usually jellolike substance – Gastroderm – covers the inner surface Characteristics of Cnidaria • Feeding: Mostly Carnivorous + symbiotic relationships • Symmetry: Radial • Movement: Sessile (young), Motile (adult) • Response: Nerve nets + nematocysts • Reproduction: asexual and sexual • Internal Transport: diffusion • Respiration: exchange O2/CO2 by diffusion • Excretion: diffusion Feeding • Carnivorous – Eat small animals by using stinging structures called nematocysts (located on it’s tentacles) • Symbiotic relationships – Tiny photosynthetic protists grow inside of the gastroderm – Use cnidarian’s waste (CO2/NH3) to make oxygen First animal to move?? Movement • Polyp – Sessile – Can expand, shrink – Move tentacles by relaxing and contracting epidermal cells • Medusa – Free to move in water – Relax and contract epidermal cells can change the bell-shape – “closing” the bell pushes water out of the jellyfish – Moves forward by jet propulsion Once Thought As Plants?! They are creatures so simple that scientists once considered them plants. But they're the critical group to study, if you want to understand motion and behavior. -- Jack Costello