* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Simple Animals
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
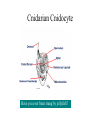
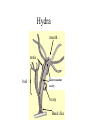
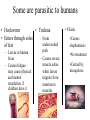
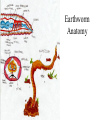
Simple Animals L2 Biology A breakdown of the animal kingdom reveals many phyla SIMPLE ANIMALS • • • • • • • • • Porifera - sponges Cnidaria – jellyfish, coral Platyhelminthes – flat worms Nematoda – round worms Annilida – segmented worms Mollusca – clams, snails, squid Echinodermata - starfish Arthropoda – insect, spider, crustacean Chordata – frogs,fish, humans Cnidaria (formerly called Coelenterata) • All have stinging cells (cnidocytes) • Two body forms: – Medusa – like a jelly fish – Polyp – like a hydra • Radial symmetry • Have tentacles Cnidarian Cnidocyte Have you ever been stung by jellyfish? Cnidarian Life Cycle – medusa and polyp alternate medusa polyp egg larva Polyp body form Hydra on water plants Hydra Anatomy mouth tentacles testis bud Gastrovascular cavity ovary Basal disc Coral is actually a colony of polyps, most of which are the size of a single hydra – they just make a case around them for their home. Here are a variety of anemones – polyp body form - Platyhelminthes • Have flat bodies • Some are parasitic • Most are free-living These are free-living flatworms Planaria Scolex – head with hooks and suckers Tapeworms – the ultimate parasite – only highly developed system is its reproductive system hermaphroditic Phylum Nematoda - roundworms • • • • Mouth – digestive tube – anus Most free-living Some parasitic Look like threads in the microscope Some are parasitic to humans • Trichina • Hookworm – From • Enters through soles undercooked of feet – Larvae in human feces – Causes fatigue – may cause physical and mental retardation if children have it pork – Causes severe muscle aches when larvae migrate from intestine to muscles • Filaria •Causes elephantiasis •No treatment •Carried by mosquitoes This lesion is caused by a nematode infestation -Caused by filaria – the worm blocks the lympatic vessels and the area swells with lymph. No treatment is available. Phylum Annelida • • • • • Segmented worms Includes earthworms and leeches Most are free-living Complex body with organ systems hermaphroditic Leech Earthworm Earthworm Anatomy Phylum Arthropoda •Jointed legs •Chitinous exoskeleton •Ventral nerve cord •Must molt to grow •Some undergo metamorphosis •Includes insects, crustaceans, spiders, millipedes and centipedes Class Insecta •Six legs •May have wings •Undergo metamorphosis •Varied mouthparts •Breathe using spiracles Class Arachnida – 8 legs, no antennae, simple eyes, chelicerae, tick scorpion Dust mites spiders CCrustacea – two body regions = cephalothorax most live in water Millipedes and Centipedes The End