* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pluto(2274km)- Pluto is a dwarf planet, and was classified as such in
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Discovery of Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
High-velocity cloud wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
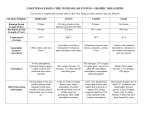
Pluto(2274km)Pluto is a dwarf planet, and was classified as such in 2006. Its temperature is extremely cold due to the fact that it averages around -393°F. The composition and atmosphere are not well known considering how far away Pluto is from Earth. Mercury(4878km)Mercury is a terrestrial planet. It is extremely hot (800°F) during the day, and also very cold(-270°F) during the night. This drop in temperature is due to the fact that its atmosphere (which consists of trace amounts of hydrogen and helium) is very thin so it does not help to retain heat. Mars(6,792km)Mars is a terrestrial planet. The temperature ranges from a high of 68°F to -220°F. The atmosphere of Mars is mostly made up of carbon dioxide and contains no oxygen. There are occasionally clouds in the atmosphere usually made up of carbon dioxide ice crystals, or less frequently, frozen water crystals. Venus(12,104km)Venus is a terrestrial planet. It is the hottest planet (870°F) in our solar system due to being covered by sulfuric acid clouds which trap heat from the sun. It has a thick atmosphere made up of mostly carbon dioxide. Furthermore, a person would not only die from the poisonous air, but also be killed from the extreme heat, and the overwhelming atmospheric pressure. Earth(12,756km)Earth is a terrestrial planet and our home. Its temperature ranges between -127°F to 136°F depending where on Earth one is. The atmosphere is thin layer of gases around the planet made up of mostly nitrogen, some oxygen, very little argon and carbon dioxide and trace amounts of other gases. It is the only planet known so far that can support life. Neptune(49,528km)Neptune is an ice giant. It has a mean temperature of -373°F. It has a hazy atmosphere that contains methane which is why it appears blue considering that methane absorbs red light. Neptune was also the first planet whose existence was predicted mathematically. Uranus(51,118km)Uranus is an ice giant. The mean temperature on the surface of its cloud layer is -350°F. Its atmosphere consists of mostly hydrogen, some helium, and very little methane. However, this methane in the atmosphere causes the appearance to be blue, same as Neptune. Saturn(1.2x10^5km)- Saturn is a gas giant. It has amazing rings that are made of mostly ice chunks and some rocks. The rings range in size from that of a fingernail to that of a car. The mean temperature on the surface of the clouds is -290°F and it is composed of mostly hydrogen and helium gas. Jupiter(1.4x10^5km)Jupiter is a gas giant. The average temperature at the cloud tops is -244°F. It has a very thick atmosphere and thick bands that stretch across the latitudes of the planet. Furthermore, it has a very large red spot which is a storm that has been raging for at least 186 years and possibly as long as 351 years or more. Sun(1.39x10^6km)The Sun is a G-type main sequence star based on its spectral class. The temperature of the photosphere (the outer shell of a star) is about 10,000°F. It is composed mostly of hydrogen, some helium, and smaller quantities of heavier elements including oxygen. It is the most important source of energy for life on Earth. Solar System(9x10^9km)The solar system contains the Sun and the planets including Earth. It was created around 4.6 billion years ago when interstellar clouds, in space, were pulled together by gravity and began to rotate which then pulled mass into the center to create a primordial solar nebula. The planets are believed to have been formed by the gas and dust that remained in the surrounding area. Diffuse Nebula(30ly)This is a nebula that is visible to the naked eye which is close to the three aligned stars of the Orion. Its shape resembles that of a bird with wings spread and is approximately 1500 light years away from the Sun. This nebula consists of glowing interstellar gas, and is known to contain many newborn stars. Milky Way Galaxy(1x10^5ly)Our solar system is inside this galaxy. It contains roughly 200 billion fixed stars (the Sun is one of them). The bulge is the central thick area, while the surrounding flat area is known as the disc. The halo is the high temperature cluster of glass which surrounds the galaxy in a spherical shape. The solar system is 30,000 light years away from the center of the galaxy in the disc area. Local Group of Galaxy(6x10^6ly)This is a collection of dozens of galaxies which includes the Milky Way. Another galaxy in the local group is the Andromeda Galaxy, which happens to be twice the size of the Milky Way. It is also 2.3 million light years away from the Milky Way, which in astronomical terms is near, but for humans is a ludicrous distance. The Observable Universe(1.38x10^10ly)This number is calculated by observing the cosmic background radiation. The universe was created from the Big Bang, which was an explosion of immense energy. Furthermore, the reason it is observable is because the universe is expanding but since light has a finite speed, it takes time for humans to see the bounds moving farther and farther away.