* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WORLD WAR I - hhhsuspreap
Historiography of the causes of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Allied intervention in the Russian Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War I wikipedia , lookup
History of Germany during World War I wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War I wikipedia , lookup
WORLD WAR I
“The War to End War”
1917 - 1918
LONG-TERM CAUSES
OF THE WORLD WAR I
Woodrow Wilson’s Diplomacy
President Wilson opposed
imperialism; believed
democracy was
necessary to keep the
nation prosperous.
He said he wanted a
world free from
revolution and war.
Woodrow Wilson
But.......
• 1911 - Revolution broke out in Mexico.
• Wilson refused to recognize the
new government.
• 1914 - Wilson sent U.S.
Marines to seize the Mexican
port of Veracruz and
overthrow Huerta, the new
leader.
• Anti-American riots broke out
in Mexico.
• Pancho Villa led a
guerrilla attack into New
Mexico, and a number of
Americans were killed.
Pancho Villa
• Wilson sent General
John J. Pershing and
his troops into Mexico to
capture Villa; they were
unsuccessful.
• Wilson’s Mexican policy
damaged U.S. foreign
relations.
Gen. John J. “Black
Jack” Pershing
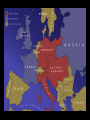
The Outbreak of World War I
• By 1871 German states were united.
• The new Germany
changed European politics;
France and Germany were
enemies.
• Germany formed the
Triple Alliance with
Austria-Hungary and
Italy.
• In the early 1900s, as a result of imperialism,
Great Britain began an arms race with Germany.
• Britain entered into an alliance with France
and Russia.
Britain
Russia
• The three countries
became known as
the Triple Entente.
France
• Nationalism, intense pride for one’s
homeland, was BIG in Europe in the
late 1800s.
• The right to self-determination (idea
that people should have their own
country and government) was a basic
idea of nationalism.
• Led to Balkans crisis;
different national groups
in the Ottoman and
Austro-Hungarian
Empires began to seek
independence.
• June 1914 - Archduke Franz Ferdinand (heir
to Austro-Hungarian throne) was killed by a
Bosnian revolutionary.
• This act set off a chain of events that led to
World War I.
Archduke
Franz Ferdinand
and Sophie -just minutes
before they were
assassinated.
• The Allies – France, Russia, Great Britain, and
later Italy – fought for the Triple Entente.
• Germany and Austria-Hungary joined the
Ottoman Empire and Bulgaria to form the
Central Powers.
• Germany and France
became locked in
a stalemate along
hundreds of miles of
trenches.
• The stalemate lasted
three years.
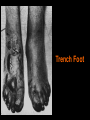
Trench Warfare
Trench Foot
Rats
in the
Trenches
American Neutrality
• Wilson declared the United
States to be neutral.
• Americans, however, began
showing support for one
side or the other. Many
immigrants supported their
homelands.
• Most Americans favored
the Allied cause.
• American businesses had close ties to the
Allied countries.
• Many American
banks gave loans
to the Allies.
• As a result,
American
prosperity was
tied to the war.
• The money would
be paid back only
if the Allies won.
Propaganda was an
important tool in
building up the
American public’s
support of the Allied
Powers.
British propaganda
aimed at the USA.
Caption:
"It should be
America's duty to
help us subdue
the mad dog of
Europe."
Moving Toward War
While most Americans supported the Allies,
they did not want to enter the war.
• The British navy blockaded Germany to keep
it from getting supplies.
• To get around the
blockade, Germany
deployed submarines
known as U-boats.
• Germany threatened to sink any ship that
entered the waters around Britain.
• Attacking civilians ships without warning
violated international law; U.S. was outraged!
• The Lusitania,
British passenger
liner, was hit by the
Germans, killing
almost 1,200
passengers –
including 128
Americans.
• U.S. warned Germany to stop U-boat strikes!
• Germany did not want the U.S. to join the war
and strengthen the Allies, so it agreed to stop.
• Sussex Pledge - promise made by Germany
to stop sinking merchant ships; kept the United
States out of the war for a bit longer.
German Imperial
Army flag
• German official, Arthur
Zimmermann, cabled the
German ambassador in
Mexico; offered Mexico an
alliance with Germany and
territory Mexico had
previously lost to the U.S.
• Zimmermann telegram
was intercepted by British
intelligence and leaked to
US newspapers.
• Americans were furious!!!
Arthur
Zimmermann
• February 1917 - Germany went back to using
unrestricted submarine warfare; soon after,
sank six American merchant ships.
• On April 6, 1917, the United States declared
war against Germany.
President
Woodrow Wilson
asking Congress for
a Declaration of War
Building Up the Military
• More U.S. soldiers needed!
• Many progressives thought
conscription (forced
military service) violated
democratic principles.
• A new system of
conscription, called
selective service,
resulted in about 2.8
million Americans being
drafted.
• The navy enlisted some 11,000 women; jobs included
clerks, radio operators, electricians, pharmacists,
photographers, chemists, and torpedo assemblers.
• The army, choosing
not to enlist women,
hired them as
temporary employees
to fill clerical
positions.
Organizing Industry
• President Wilson
and Congress wanted
establish a
cooperative
relationship between
big business and
government to
efficient use
resources during
the war.
to
ensure
of
• The Food Administration,
under the direction of
Herbert Hoover, was
responsible for increasing
food production while
reducing consumption.
• Hoover asked people to plant victory gardens to
raise their own vegetables in order to leave more
food for the troops.
• The Fuel Administration
encouraged
people to
conserve coal and oil.
• Daylight savings
time was
introduced to
conserve energy.
• To raise money to pay
for the war, the
government began
selling Liberty Bonds
and Victory Bonds.
• By buying bonds,
Americans were
loaning the
government money
that would be repaid
with interest in a
specified number of
years.
Mobilizing the Workforce
• To prevent strikes, the government established
the National War Labor Board (NWLB) in 1918.
• In exchange for wage
increases, an 8-hour
workday, and the right to
organize unions and bargain
collectively,
labor leaders
agreed not to
strike during
the war.
Ensuring Public Support
• Espionage, or spying to
acquire secret government
information, was addressed
in the Espionage Act of
1917.
• It set up consequences for
people who aided the
enemy.
• The Sedition Act of 1918
made it illegal to criticize
the president or the
government.
• Suspicions of disloyalty led
to mistreatment of German
Americans. Anti-German
feelings sometimes led to
violence.
• Radical labor activists, socialists, pacifists, and
anyone appearing disloyal also came under
attack.
• In the case of Schenck v. United States
(1919), the Supreme Court ruling limited an
individual’s freedom of speech if the words
spoken constituted a “clear and present
danger.”
Combat in World War I
• By 1917 World War I had claimed millions of
European lives.
• Americans believed their troops could bring the
war to a quick end.
• Soldiers dug trenches
as protection from
modern weapons.
• “No man’s land” was
the space between the
opposing trenches.
• To break through enemy
lines, new technologies
were created.
• Poison gas, first used by
the Germans; caused
vomiting, blindness, and
suffocation.
• Tanks did not work well.
• Airplanes dropped
small bombs on the
enemy and engaged in
air battles ("dogfights").
The Americans and Victory
• “Doughboys” - nickname for
American soldiers.
• Entry of American soldiers boosted
the morale of Allied forces.
• Convoys - merchant ships and
troop transports were gathered into
groups and brought across the
Atlantic by warships.
• Result: reduced shipping losses; ensured that
American troops would get to Europe safely.
• Although Russians supported the
war effort, their government was not
equipped to handle the major
problems of the nation.
Lenin
• In 1917 Vladimir
Lenin, leader of
the Bolshevik
Party, overthrew
the czar’s
government and
replaced it with
Communism.
• Lenin pulled Russia
out of the war.
• Signed the Treaty of
Brest-Litovsk with
Germany.
• This closed the Eastern
Front for Germany.
Territories
surrendered by Soviet
Russia due to BrestLitovsk Treaty
• September 1918 General Pershing put
together the most
massive attack in
American history;
devastated German
troops.
• On November 11, 1918,
Germany finally signed
an armistice, or ceasefire, that ended the war.
A Flawed Peace
• January 1919 - Allied nations met to
resolve issues caused by WWI.
• Wilson’s plan - called the
Fourteen Points.
• Tried to eliminate general causes of the war:
1. Free trade
2. Disarmament
3. Open diplomacy
4. Self-determination
(Imperialism)
X
(Militarism)
X
XAlliances)
(Secret
(Nationalism)
X
• Fourteenth point, known as the League of
Nations, called for member nations to help
preserve peace and prevent future wars.
THE FOURTEEN POINTS
1. Open alliances
Woodrow Wilson – 1/18/1918
6-13. Specific provisions for:
2. Freedom of the seas
Russia, Belgium, France
3. Open trade
Italy, Austria-Hungary
4. Disarmament
Balkan Nations, Turkey
5. Self-determination
for nations
14. League of Nations
“The Big Four”
Lloyd George (Great Britain);
Orlando (Italy); Clemenceau
(France); Wilson (US)
Peace Conference
at Versailles
• The other Allied governments felt that Wilson’s
plan was too lenient toward Germany.
• Treaty of Versailles - weakened Wilson’s
proposal. Stripped Germany of its armed
forces and made it pay reparations (war
damages) to Allies.
• Treaty of Versailles
and League of
Nations were
opposed by many
U.S. lawmakers.
• The Senate refused to ratify the treaty.
• Instead, the United States negotiated
separate peace treaties with each of the
Central Powers.
An Economy In Turmoil
• Rapid inflation resulted when government
agencies removed their controls from the
American economy. Inflation increased the
cost of living.
• Workers needed
higher wages to keep
up with the cost of living,
companies wanted
lower wages due to
increase in operating costs.
but
to
an
• The number of members in unions increased
greatly during the war.
• Unions were better
organized than before.
• Business leaders
wanted to break
the power of unions.
• Result: Lots of strikes!
• Led to fear among
U.S. public.
• General strikes – strikes that
involve all workers living in a
certain location; worried
Americans because they
were commonly used in
Europe by Communists and
other radicals.
• The Seattle general
strike involved more than
60,000 people and
brought the city to a halt
for five days.
• 1919 - 75 percent of the police
force of Boston went on strike.
• Governor of Massachusetts,
Calvin Coolidge, called in the
National Guard to stop looting.
• When police tried to return to
work, Coolidge fired them; a
new police force was hired to
replace the striking policemen.
Racial Unrest
• 1919 - race riots in
many Northern
cities.
• Cause: return of
thousands of
American soldiers who needed to find jobs.
• African Americans, who had moved north to
work, were now competing for the same jobs
as the returning soldiers.
• The worst violence occurred in Chicago
where whites and African Americans entered
each others’ neighborhoods and attacked one
another.
• The violence lasted almost two weeks.
Fear of Communism
• After World War I, Americans
associated communism with
disloyalty and unpatriotic behavior.
• The numerous strikes in the U.S. in 1919
made Americans fear that Communists, or
“reds,” might take control.
• This led to a nationwide panic known as the
Red Scare.
• Numerous mail bombs
• One bomb damaged home
of U.S. Attorney General
A. Mitchell Palmer.
• Most people felt it was
Communists trying to
destroy the American
way of life.
US Attorney General
A. Mitchell Palmer
Reviewing Key Terms
Define Match the terms on the right with their definitions on
the left.
__
D 1. German submarine, term means
Unterseeboot (undersea boat)
A.
guerrilla
B.
propaganda
C.
contraband
D.
U-boat
C 3. goods whose importation,
__
exportation, or possession is
illegal
E.
conscription
F.
victory
garden
B 4. the spreading of ideas about an
__
institution or individual for the
purpose of influencing opinion
G.
espionage
H.
armistice
__
E 5. requiring people enter military
service
I.
reparations
J.
deport
__
I 2. payment by the losing country in
a war to the winner for the
damages caused by the war
Reviewing Key Terms (cont.)
Define Match the terms on the right with their definitions on
the left.
__
F 6. gardens planted by American
citizens during war to raise
vegetables for home use,
leaving more for the troops
A.
guerrilla
B.
propaganda
C.
contraband
__
J 7. to expel individuals from the
country
D.
U-boat
E.
conscription
__
G 8. spying, especially to gain
government secrets
F.
victory
garden
H 9. a temporary agreement to end
__
fighting
G.
espionage
__
A 10. armed band that carries out
surprise attacks and sabotage
rather than open warfare
H.
armistice
I.
reparations
J.
deport