* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WWI
Kienthal Conference wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of World War I wikipedia , lookup
American entry into World War I wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the causes of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War I wikipedia , lookup
United States home front during World War I wikipedia , lookup
History of Germany during World War I wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War I wikipedia , lookup
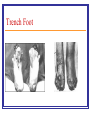
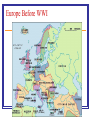
WWI Chapter 27 “Civilization has climbed above such perils; the interdependence of nations in trade and traffic, the scope of public law, Christian charity, and common sense has branded such nightmares impossible… It would be a pity to be wrong…” ~ Winston Churchill Setting the Stage: WWI Causes WWI Militarism Alliances Imperialism Nationalism The Spark = Assassination Archduke Franz Ferdinand June 28, 1914 Gavril Princep and the Blackhand Set into motion deadly web of alliances Franz Ferdinand’s Death Set into Motion a Deadly Web of Alliances WWI Sides: The Belligerents Allied Powers France GB Russia Italy United States and Japan (eventually) Central Powers Germany Austria-Hungary Ottoman Empire Bulgaria WWI: A TOTAL WAR Total War = All resources used for war Propaganda Civilian responsibility New Industrial weapons/inventions in land, air, sea Weapons by Sea: Dreadnoughts and U-Boats Weapons by Air: Airplanes and Zeppelins Red Baron Weapons by Land: Machine Gun Weapons by Land: Railroad Guns Trenches Trench Foot Weapons by Land: Gas Burns from Mustard Gas Animal Messengers and Gas Masks Weapons by Land: Tanks Total War made WWI a… War of Attrition: A slow wearing-down war in which each side tried to outlast the other Theaters of War Major Battles WWI 1914 Battle of Marne: W-front France stops German adv. into Paris Trench warfare begins Battle of Tannenberg E-front Huge German Win! Prob. Germany in 2-front war Verdun – February, 1916 e German offensive. e Each side had 500,000 casualties. The Somme – July, 1916 e 60,000 British soldiers killed in one day. e Over 1,000,000 killed in 5 months. Major Battles WWI continued… 1915 Battle of Gallipoli Turkish-front Allie’s defeated by Ottoman E! Russia remains landlocked United States Entry into WWI U.S. “neutral” until April 6th, 1917 / May 28th 1918 our first victory at Cantigny (North of Paris) Events that pushed U.S. into WWI: 1. Unrestricted Germ. submarine warfare Sinking of Lusitania Zimmerman Note / O throw of Russian Czar. WWI Causalities – 16 mill. Dead Paris Peace Conference Meeting of the Big 4: GB: David Lloyd George France: George Clemenceau United States: Woodrow Wilson Italy: Vittorio Orlando Who were these men and what kind of “peace” did each of them want? Areas of Concern Blame? Reparations? Colonies of Central Powers? Rhineland? Alsace-Lorraine? Saar? Poland? Danzig? Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Estonia? Czechoslovakia? OTHER PROBLEMS W/ PARIS PEACE CONFERENCE… No Russia or Central powers invited! Other Problems w/ the Paris Peace Conference 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Russia and Central Powers not invited Political Problems Territorial Conflicts Reparations How to maintain peace Force Wilson’s 14 Points Freedom of seas, no secret treaties, no economic barriers, reduce arms, fair land divisions, establish League of Nations WWI Causalities Treaty of Versailles Officially ended WWI 1919 Treated Germany Harsh Formed Independent Republics Formed League of Nations Europe Before WWI Europe After WWI