* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells, Tissues, Organs and Systems
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
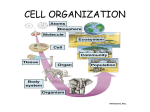
Cells (Division of Labour) Chapter 24 In this chapter, you will learn… • that cells of similar structures are organised into tissues • that several tissues may make up an organ • that organs are organised into systems • to explain the significance of division of labour Unicellular Organisms Paramecium Amoeba Unicellular Organisms • Paramecium – Microscopic organism – Found on surface of water (eg: pond, river) – Has hair surrounding the body for movement – Has a mouth Unicellular Organisms • Amoeba – Often found at bottom of ponds or under rocks – Does not move fast – No arms, legs, eyes, mouth – Eats by surrounding its prey with its body – Lives only for 2 days – Reproduce by spliting itself into 2 new amoebas Multicellular Organisms • Have many different cells • Different cells perform different functions • Examples – Plants – Humans Cells in a Human • Examples – Red blood cell (transport oxygen) – Nerve cell (have nerve fibres to transmit signals to and from the central nervous system) Cells in a Plant • Examples – Root hair cell – Leaf guard cell From cells to tissues • Tissue – Group of similar cells that are specialised to perform a particular function Tissues in a Human • Epithelial tissue – Covering or lining tissue to protect structure beneath it Connective tissue – Joins, stores or supports all parts of an organism Tissues in a Human • Muscle tissue – Cause movement • Nerve tissue – Carry messages from one part of body to another by conducting electrical signals Tissues in a Plant • Epidermal tissue – Protects plant against injury and losing too much water • Vascular tissue – Transports materials within a plant Tissues in a Plant • Photosynthesis tissue – Carries out photosynthesis in a plant From Tissues to Organs • Organ – Group of specialised tissues that are gathered in a certain part of the body to perform a particular function together Organs in a Human • Examples – Skin – Lungs – Heart Organs in a Plant • Examples – Leaves – Stem – Roots – Flowers From Organs to Systems • System – Different organs working together to perform a major function in an organism Main Organ Systems in a Human • • • • • Respiratory system Digestive system Blood circulatory system Skeletal system Muscular system Respiratory System Nasal Passage Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchioles Alveoli Bronchus Respiratory System • Respiration – Process in which cells release energy from the food we eat – Oxygen is required – Carbon dioxide is removed Respiratory System • Mechanics of breathing Exhalation Inhalation Digestive System Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Liver Stomach Large Intestine Small Intestine Villi Digestive System • Digestion – Process in which large, insoluble food substances are broken down into smaller, soluble food substances for absorption into blood Blood Circulatory System Blood Circulatory System • Transports nutrients, gases, water and hormones to different parts of the body • Include red blood cells, white blood cells, heart, blood vessels Red blood cells White blood cells Skeletal System Skeletal System • • • • Supports our body Gives us shape Protects our organs Enables movement Muscular System Deltoid Pectoralis major Biceps brachi Gluteus maximus Rectus femoris Gastrocnemius Muscular System • Enables movement by contraction and relaxation of muscles • 3 muscle types: – Skeletal muscles – Smooth muscles – Cardiac muscles Other systems in Human • Reproductive System - Produces sex cells (sperm, ovum) - For reproduction • Nervous System - Consists of the brain, spinal cord and nerves found throughout our body - Controls and coordinates functions throughout our body - Enables us to respond to changes around us Male Reproductive System Urinary bladder Vas deferens Prostate gland Urethra Seminal vesicle Epididymus Penis Testis Female Reproductive System Fallopian tube Uterus Urinary bladder Vagina Anterior View Sagittal View Fallopian tube Uterus Ovary Vagina Nervous System Cerebrum Corpus callosum Thalamus Hypothalamus Midbrain Pons Medulla oblongata Spinal cord Cerebellum Plant Transport System From Systems to Organisms • Organism – Made up of different systems working effectively in a coordinated manner The Human Body - An organism CELLS TISSUES ORGANS SYSTEMS ORGANISM Division of Labour • Each cell in a multicellular organism does not perform all the bodily functions. • Each type of cell specialises in performing one particular function. • Different functions in a multicellular organism can be performed at the same time by division of labour. Division of Labour • Division of labour – Sharing different functions in an organism among its cells, tissues, organs and systems – Ensures smooth running and effective working of the different parts in an organisms as well as the organism as a whole