* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson 3
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
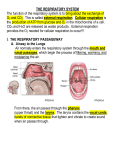
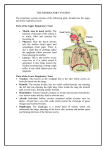
Chapter 16 Lesson 3 Did You Know Breathing is regulated by certain areas of the brain that send impulses to stimulate the automatic contraction of the muscles involved in respiration. Functions of the Respiratory System A. The main function of the respiratory system is respiration – the exchange of gases between the body and the environment. B. Respiration has two parts: 1. External respiration is the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide that takes place between air and the blood in the lungs. 2. Internal respiration is the exchange of gases between the blood and the body cells. C. The continual exchange of gases in both the external and internal respiration is essential for survival. Discussion Question Why does the body need oxygen? Structure of the Respiratory System A. The upper respiratory system included the nose and throat; the lower respiratory system consists of the lungs, larynx, trachea, and bronchi. B. The lungs are the principal organs of the respiratory system. 1. The lungs are in the chest, protected by the ribs. 2. The diaphragm is the muscle that separated the chest from the abdominal cavity. 3. Air moves into the lungs through the trachea, or windpipe. 4. The trachea branches out into bronchi, the main airways that reach into each lung. Structure of the Respiratory System C. The breathing process is made possible when your body creates a pressure difference between the lungs and the outside of the body. D. Air enters the body through the nose and mouth. It passes through the pharynx, or throat, and then into the trachea and then the bronchi. E. The larynx, or voice box, connects the throat and the trachea. F. The epiglottis is a flap of cartilage above the larynx. It fold down to keep food or drink from entering the respiratory system. Discussion Question Why should you try to inhale through your nose rather than through your mouth?