* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Callyspongia plicifera
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
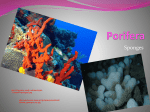
Sponges Ryan Baker, Markesh Patel P.3 http://www.palaeos.com/Invertebrates/Porifera/Porife PHYLUM Porifera Ryan Baker EXAMPLES Azure vase sponge (Callyspongia plicifera) http://reefguide.org/pixhtml/azurevase2.html Ryan Baker EXAMPLES Variable Boring Sponge (Siphonodictyon coralliphagum) http://reefguide.org/pixhtml/variableboring3.html Ryan Baker EXAMPLES Strawberry Vase Sponge (Mycale laxissima) http://reefguide.org/pixhtml/azurevase2.html Ryan Baker BODY CAVITY • Present • “Spongocoel” • Water passes through pores (“porocytes”) and into the spongocoel http://wps.aw.com/bc_campbell_biology_7/26/6664/1706153.cw/index.html FLOW OF WATER 3) … and out through the osculum (connects spongocel to the environment) 1) Water flows through the porocytes… 2) … into the spongocel … http://wps.aw.com/bc_campbell_biology_7/26/6664/1706153.cw/index.html BODY SYMMETRY NONE or Radial • Most sponges are asymmetrical • However, some may exhibit radial symmetry NERVOUS SYSTEM NONE • No nerve or sensory cells (only multicellular animal) • However: touch/pressure can cause body contraction CIRCULATORY SYSTEM • No true circulatory system, just water flow & amoebocytes • Amoebocytes transport nutrients to other cells http://wps.aw.com/bc_campbell_biology_7/26/6664/1706153.cw/index.html DIGESTIVE SYSTEM • Choanocytes (collar cells) create a water current with flagella to trap food particles and ingest with phagocytosis. • Amoebocytes digest and transport nutrients. http://wps.aw.com/bc_campbell_biology_7/26/6664/1706153.cw/index.html Excretory System None Locomotion/Musculature -Sessile -Sponge larvae use tiny hair structures called cilia to swim until they attach to a surface. (few days) http://www.biology.ualberta.ca/CMD/Pics/LeysLarva.jpg Skeletal Type The Body of a Sponge contains 2 layers of cells Mesohyl – A gelatinous part between the layers of cells contains Amoebocytes-carry nutrients to cell/manufacture skeletal fibers # 1 Spicules made from calcium carbonate/silcia # 2 Spongin = more flexible http://www.biology.iastate.edu/Course s/211L/Porif/%20Porifindx.htm Sensory Structures/Features • None/VERY simple • They may close their ostia if there is too much matter in the water or if it has been touched. Reproduction – All Sponges are Hermaphrodites = male/female and sperm/egg – Gametes come from choanocytes and amoebocytes. Zygote develops in mesohyl – Zygote becomes larvae – Cross Fertilization – Asexual reproduction via Gemmules Gas Exchange • Water flow allows for the sponges to obtain oxygen and remove waste. • They exchange gases mainly by diffusion. (Most efficient way, because they have a large surface area) Other Unique Features • Sponges are known to grow back lost body parts. • All sponges are aquatic. • Collar cells called choanocytes are only found in these kinds of animals. • They are the only animal to use silicon as a support structure. • They are suspension feeders, meaning they capture small food particles suspended in the water. Question #1 Porifera are the only phylum that do not have a(n): a) Digestive system b) Nervous system c) Skeletal system d) Circulatory system Question #1 Porifera are the only phylum that do not have a(n): a) Digestive system b) Nervous system c) Skeletal system d) Circulatory system Question #2 Which of these systems DO Porifera truly have? a) Excretory system b) Nervous system c) Skeletal system d) Circulatory system Question #2 Which of these systems DO Porifera truly have? a) Excretory system b) Nervous system c) Skeletal system d) Circulatory system Question #3 Identify the structure in the picture: a) Spongocoel b) Amoebocyte c) Porocyte d) Osculum Question #3 Identify the structure in the picture: a) Spongocoel b) Amoebocyte c) Porocyte d) Osculum Question #4 Identify the structure in the picture: a) Spongocoel b) Amoebocyte c) Porocyte d) Osculum Question #4 Identify the structure in the picture: a) Spongocoel b) Amoebocyte c) Porocyte d) Osculum