* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 19
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Fluorescent glucose biosensor wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacometabolomics wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Metabolomics wikipedia , lookup
Animal nutrition wikipedia , lookup
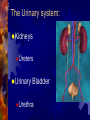
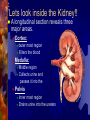
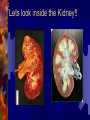
Excretion: The process by which the wastes of cellular metabolism are removed from an organism. Metabolic reactions: 1. 2. 3. 4. Respiration Deamination (break down of proteins) Hydrolysis (digestion) Other Metabolic activities ( inorganic salts) Metabolic reactions produce Metabolic Reaction Aerobic (cellular) Respiration also Excretory waste Produced Carbon Dioxide Water (Dehydration synthesis) Deamination Nitrogenous waste Other Metabolic activities Inorganic mineral salts (sodium chloride, potassium sulfate Nitrogenous waste: Or nitrogen containing wastes accumulate from the break down of amino acids (proteins) Ammonia, (NH3) most toxic Urea, Uric Acid, least toxic Urinary system: A group of organs whose sole function is to perform EXCRETION. All of these organs play a major role in maintaining the body’s HOMEOSTASIS. Homeostasis: the maintaining of a stable internal environment The Urinary system: Kidneys Ureters Urinary Bladder Urethra The Kidneys: Roughly 10cm long Located against back muscles Two functions: Remove cellular metabolic wastes from blood, producing urine. Control varying concentrations within the blood (H20, salt, glucose) URINE: Liquid produced by the kidneys composed of: Water Urea, Salts NORMAL URINE: Normal Urine Color Clarity Ph range Inorganics Protein Glucose RBC WBC Normal Urine Color Pale yellow ----amber Clarity Clear Specific Gravity Ph range 1.016 4.5---8 Inorganics Sulfates, ammonia, salts, phosphates, potassium Protein NONE Glucose None RBC NONE WBC None The Arethra: Oops, wrong one The Urethra Tube that carries urine out of the body Boys and Girls both have a urethra!!!! Lets look inside the Kidney!! A longitudinal section reveals three major areas. Cortex: outer most region Filters the blood Medulla: Middle region Collects urine and passes it into the Pelvis Inner most region Drains urine into the ureters Lets look inside the Kidney!! disorders Gout Kidney Stones Renal Failure (nephritis) Dialysis: When a set of kidneys don't do their job, their owner has what is called a chronic kidney condition. Eventually, those kidneys may be considered failing. But instead of a bad grade, they can get help from something called dialysis (say: die-al-ih-sis). Much like a filter system hooked up to a pool, dialysis gives the kidneys a break by skimming waste for them. How does it work? There are two types. The first kind of dialysis, called hemodialysis (say: heemoh-die-al-ih-sis), uses a filtering machine to remove waste and extra fluid from your blood. In the second type, called peritoneal dialysis (say: peh-rih-tuh-nee-ul), the actual filtering is done by The Liver Detoxification: Removal of harmful or toxic substances from the blood Converts substance into a less toxic forms and released back into the blood stream Excretion of bile: used for emulsification of fats. Excess passed out in the feces (bile salts, cholesterol, recycled hemoglobin) Urea formation: ammonia from protein breakdown is converted into a LESS toxic urea The FDA recommends that we get 60 mgs of vitamin C per day. Dr Linus Pauling, often referred to as the "Father of Vitamin C" and twice awarded the Nobel Prize, declared that large intakes of up to 10 grams of vitamin C each day aids anti-cancer activity within the body. The Lungs Get the body rid of carbon dioxide and water (in the form of water vapor) End products of cellular respiration AND ALCOHOL particles The Skin Protection Excretion Nerve endings Regulates body temperature The Skin Finis’