* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Levels of Organization
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Central nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
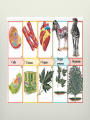
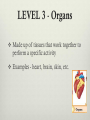
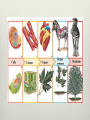
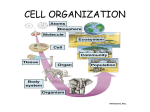
Levels of Organization September 15, 2011 Two types of organisms Unicellular (single-celled) organisms: the single cell performs all life functions. It functions independently. Multicellular (many celled) organisms: have various levels of organization within them. Individual cells may perform specific functions and also work together for the good of the entire organism. The cells become dependent on one another. Multicellular organisms have the following 5 levels of organization ranging from simplest to most complex: LEVEL 1 - Cells The basic unit of structure and function in living things. May serve a specific function within the organism Examples- blood cells, nerve cells, bone cells, etc. LEVEL 2 - Tissues Made up of cells that are similar in structure and function and which work together to perform a specific activity Examples - blood, nervous, bone, etc. Humans have 4 basic tissues: connective, epithelial, muscle, and nerve. LEVEL 3 - Organs Made up of tissues that work together to perform a specific activity Examples - heart, brain, skin, etc. LEVEL 4 - Organ Systems Groups of two or more tissues that work together to perform a specific function for the organism. Examples - circulatory system, nervous system, skeletal system, etc. The Human body has 11 organ systems: circulatory, digestive, endocrine, excretory (urinary), immune, integumentary, muscular, nervous, reproductive, respiratory, and skeletal. LEVEL 5 - Organisms Entire living things that can carry out all basic life processes. Meaning they can take in materials, release energy from food, release wastes, grow, respond to the environment, and reproduce. Usually made up of organ systems, but an organism may be made up of only one cell such as bacteria or protist (ex: Toxoplasma). Examples - bacteria, amoeba, mushroom, sunflower, human Examples Two human examples are: neurons (nerve cells) --> nervous tissue --> brain --> central nervous system --> human bone cells (osteoblasts) --> connective (bone) tissue --> bones --> skeletal system --> vertebrate