* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Intro to the Circulatory System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
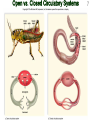
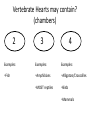
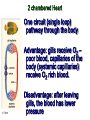
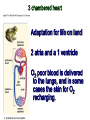
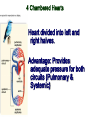
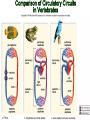
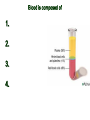
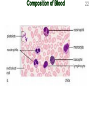
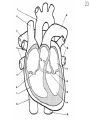
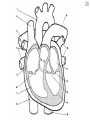
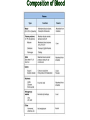
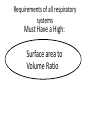
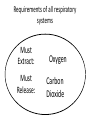
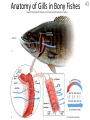
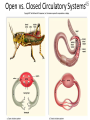
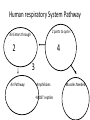
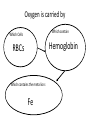
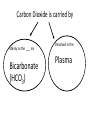
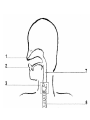
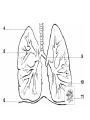
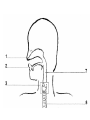
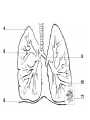
Intro to the Circulatory System Question of the Day: Do all animals have a circulatory system? Give support for your answer. Aquatic Organisms Without a Circulatory System 3 Goals for the Day 1. List the two types of circulatory systems, how they function, and examples of organisms that have each type of system. 2. Describe the hearts of different vertebrates including the number of chambers and the pathways of the blood. Review from Friday Circulatory Systems may be: Open Examples: •Arthropods or Closed Examples: •Annelids •Some Molluscs •Most Molluscs •All Vertebrate Animals Circulatory Systems may be: Open or Differences: •Hemolymph vs. Blood •Colorless vs. red •No O2 vs. O2 carriers Closed Open vs. Closed Circulatory Systems 7 Vertebrate Hearts may contain? (chambers) 2 3 4 Examples: Examples: Examples: •Fish •Amphibians •Alligators/Crocodiles •MOST reptiles •Birds •Mammals 2 chambered Heart One circuit (single loop) pathway through the body Advantage: gills receive O2 – poor blood, capillaries of the body (systemic capillaries) receive O2 rich blood. Disadvantage: after leaving gills, the blood has lower pressure 3 chambered heart Adaptation for life on land 2 atria and a 1 ventricle O2 poor blood is delivered to the lungs, and in some cases the skin for O2 recharging. 4 Chambered Hearts Heart divided into left and right halves. Advantage: Provides adequate pressure for both circuits (Pulmonary & Systemic) Comparison of Circulatory Circuits in Vertebrates The Human Heart has 4 Chambers Two of Which are: Atria Sing., Atrium Whose Job is to: Receive blood from circulation Two of Which are: Ventricles Whose Job is to: Pump Blood away from the heart The three types of blood vessels in the cardiovascular (Gk. kardia, heart; L. vascular, vessel) system are 1. Veins (L. vena, blood vessel) 2. Arteries 3. Capillaries (L. capillus, hair) Goals for the Day 15 Goals for the Day 1. Be able to list the components of the blood and the rough percentages of each component 2. Be able to label the major structures of the human heart. Question of the Day What is the major difference between a 2 chambered and a 3 or 4 chambered heart? List animals that have each type of heart. Giant Salamander & Lungfish Blood is composed of 1. 2. 3. 4. Blood is composed of 1. 2. 3. 4. Plasma is composed of 1. Water 90-92% 2. Proteins 7-8% 3. Gases 4. Salts 5. Nutrients 6. Other (Hormones) Composition of Blood 22 23 Goals for the Day 1. Be able to label the major structures of the human heart. Question of the Day 1. What are the major components of the blood? For each component list its characteristics. 26 Composition of Blood Composition of Blood 29 Intro to the Respiratory System Goal for the Day: Learn the similarities and differences between the respiratory system of humans and other organisms Question of the Day: Do all animals have lungs or gills? What has to be true about animals that lack these? Question of the Day: Do all animals have either lungs or gills? What would have to be true of an organism that lacked these structures? Aquatic Organisms Without a Respiratory System 36 Requirements of all respiratory systems The Lining must be: Moist & Thin •In order for gas to move across a membrane there has to be a liquid for diffusion. Requirements of all respiratory systems Must Have a High: Surface area to Volume Ratio Requirements of all respiratory systems Must Extract: Must Release: Oxygen Carbon Dioxide Requirements of all respiratory systems Must Extract: Oxygen Must Release: Carbon Dioxide •What are the 3 “major” components of air • Nitrogen • Oxygen • Argon • Carbon Dioxide Respiratory surfaces include: aquatics In worms Skin Exceptions: •Some Aquatic worms or Gills Exceptions: •Aquatic Mammals •Organisms with no lungs or gills (high SA/V, and thin bodies) Respiratory surfaces include: aquatics In worms Skin Exceptions: •Some Aquatic worms or Gills Exceptions: •Aquatic Mammals •Organisms with no lungs or gills (high SA/V, and thin bodies) Anatomy of Gills in Bony Fishes 43 Respiratory surfaces include: In Insects & terrestrial arthropods Tracheae In terrestrial Vertebrates or Lungs Through spiracles •Does an insect have a closed or open circulatory system? •What do we know about its function then? Exceptions: •Amphibians (which also breath through their skin, thanks to the amazing properties of water!) Open vs. Closed Circulatory Systems45 Tracheae of Insects 46 Human respiratory System Pathway 2 parts to cycle: Air Enters through 2 4 3 Air Pathway: •Amphibians •MOST reptiles Muscles Needed: Oxygen is carried by Which contain Which Cells Hemoglobin RBCs Which contains the metal ion: Fe Carbon Dioxide is carried by Mainly as the ___ ion Bicarbonate (HCO3) Dissolved in the: Plasma Goals for the Day: Be able to describe the different types of respiratory systems in organisms. Review parts of human respiratory system Question of the Day: What are the 4 major types of respiratory surfaces? List examples of organisms that have each kind of respiratory surface? Which of the following has an open circulatory system? A. B. C. D. E. Hydra Earthworm Human Sponge Lobster Identify the curve that is characteristic of hemoglobin of a mammal that evolved at high elevations A. A B. B C. C Which hemoglobin has the greatest affinity for oxygen? A. A B. B C. C Closed circulatory system A. B. C. D. E. Annelida Chordata Echinodermata Arthropoda Platyhelminthes Goals for the Day: Be able to describe the different types of respiratory systems in organisms. Learn the major organs involved in digestion Question of the Day: When the diaphragm is contracted in which direction does air move? (In our out of the thoracic cavity) Explain why this is. Goal for the day • Be able to describe the basic path of digestion in most animals, and where the process begins. • Review the evolutionary relationships within animals RE: Question of the Day • When the diaphragm is contracted in which direction does air move? (In our out of the thoracic cavity) Explain why this is. Which is CORRECT about gas exchange in humans A. The diaphragm rises and air is pulled into the lungs B. Air is forced down the windpipe when a person inhales C. The breathing rate is controlled by the hypothalamus in the brain D. Hemoglobin carries carbon dioxide and oxygen in fairly equal amounts E. As humans inhale, the pressure in the chest cavity decreases and air is drawn into the lungs Tracheal tubes are found in A. B. C. D. E. Earthworms Hydra Fish Insects Birds Breathing in humans is usually regulated by A. B. C. D. E. The number of red blood cells The amount of hemoglobin in the blood Inherent genetic control CO2 levels and pH sensors The pituitary gland In humans, the largest amount of the carbon dioxide produced by the body cells is carried to the lungs as: A. CO2 attached to hemoglobin in the red blood cells B. Attached to hemoglobin circulating in the plasma C. The bicarbonate ion attached to hemoglobin D. CO2 gas in solution in the plasma E. The bicarbonate ion dissolved in the plasma Open circulatory system, protostome, exoskeleton A. B. C. D. E. Annelida Chordata Echinodermata Arthropoda Platyhelminthes Acoelomate, bilateral symmetry A. B. C. D. E. Annelida Chordata Echinodermata Arthropoda Platyhelminthes Deuterostome, radial symmetry as an adult A. B. C. D. E. Annelida Chordata Echinodermata Arthropoda Platyhelminthes