* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download How does the immune system protect the body against disease?
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
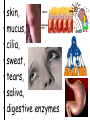
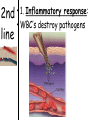
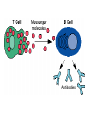
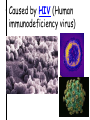
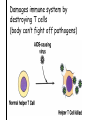
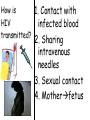
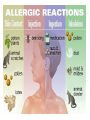
TOPIC: Immunity AIM: How does the immune system protect the body against disease? Immune system • Protects the body against disease What is a • Materials that cause pathogen? disease (germs) • Microorganisms • Bacteria, viruses, parasites, fungi… • Proteins found on Antigen the “bad guy or substances” that are foreign to your body. • Bad guys = pathogens, microorganisms, allergens etc. The Body’s Lines of Defense st 1 line • Physical barriers • keep pathogens out of the body • skin, • mucus, • cilia, • sweat, • tears, • saliva, • digestive enzymes • 1. Inflammatory response: 2nd • WBC’s destroy pathogens line Antibodies • Proteins that (3rd line) help destroy pathogens • Made bc of an immune response • Attach to antigen & slow it down so WBC’s can destroy them How are • 2 types of WBC’s antibodies • T cells tell B cells to make antibodies made? • 1. Infectious = 2 types of • pathogens spread to another person disease • Ex: cold, flu, AIDS • 2. Noninfectious = cannot be spread • (not caused by pathogen) • Ex: Diabetes, cancer AIDS • Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome • Infectious disease • Caused by HIV (Human immunodeficiency virus) Damages immune system by destroying T cells (body can’t fight off pathogens) How is HIV transmitted? 1. Contact with infected blood 2. Sharing intravenous needles 3. Sexual contact 4. Motherfetus Allergies • An immune response or reaction to substances you are allergic (sensitive) to • Allergen = what you are allergic to • (pollen, dust, etc) • Histamines produced (chemicals released by cells that cause symptoms) Review: 1. What is a pathogen? 2. Explain what makes up your body’s first line of defense. 3. How are antibodies produced? 4. How are infectious diseases different from noninfectious diseases? 5. How does HIV affect the body? 6. What is an allergy?