* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Immunity and Infection Sexually Transmitted Diseases`
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Cross-species transmission wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
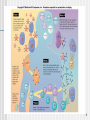
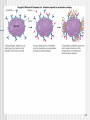
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Antiviral drug wikipedia , lookup
Visceral leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Immunity and Infection Chapter 17 Chain of Infection Transmitted through a chain (six links) Pathogen - disease causing microorganism Reservoir - natural environment of the pathogen: Person, animal or environmental component Portal of Exit Means of transmission • Direct transmission • Indirect transmission Portal of entry New host Breaking the Chain 2 3 Body’s Defense System Physical and Chemical barriers Skin, mucous membranes, respiratory tract Immunulogical Defenders • Neutrophils • Macrophages • Lymphocytes • T-cells • Helper, Killer, and Suppressor • B-cells • Antibodies • Memory T and B cells 4 5 The Body’s Defense System The Inflammatory Response. Histamine. • Dilation of blood vessels, heat, redness, and swelling. 6 Body’s Defense System Immune Response Phase 1 – Macrophages Phase 2 – Helper T cells multiply • Production of Killer T and B cells • Cytokines Phase 3 – Killer T cells strike • Cell-mediated immune • Anti-body mediated immune response Phase 4 – Last Phase – • Suppressor T-cells 7 8 Immunization The process of ‘priming’ the body to remember an encounter with a specific antigen. VACCINE- Introduction of a killed or weakened pathogen to stimulate the body to produce antibodies. (active immunity). PASSIVE IMMUNITY- Injection of antibodies produced by other human beings or animals. ACQUIRED IMMUNITY-The ability of a memory lymphocytes to remember a previous infection. (chicken pox). 9 Allergy The Body’s Defense System Gone Haywire Allergies Allergens • Pollen, Dander, Dust mites, Molds, Food, Insects The Allergic response • Immunoglobulin (IgE) • Anaphylaxis 10 11 Dealing With Allergies Avoidance Medication Immunotherapy 12 Type of Pathogens Bacterium – Microscopic single celled organism Pneumonia Meningitis Strep Throat and other streptococcal infections Toxic shock and other staphylococcal Tuberculosis Lyme Disease Ulcers Antibiotic Treatment 13 Type of Pathogens Viruses Common Cold Influenza Measles, Mumps and Rubella Chickenpox, Cold Sores Other Herpes virus infections Viral encephalitis Viral Hepatitis Poliomyelitis Rabies Warts Treatment 14 15 Types of Pathogens Fungus – Protozoan – Microscopic single-celled animal – Malaria, African sleeping sickness. Parasitic worm – Primitive plant – Yeast infections, athletes foot Largest organism that can enter the body – Tapeworm, Hookworm, and Pinworm. Prions Fetal degeneration disorders of the CNS, linked to “proteinaceous infectious partilces. 16 17 Emerging Infectious Diseases Drug Resistance Poverty The breakdown of public health measures Environmental changes Travel and Commerce Mass food production and Distribution Human Behaviors 18 Other Immune Disorders Cancer and Autoimmune Diseases If the immune system breaks down • Getting older • HIV infection • Chemotherapy Autoimmune diseases • Rheumatoid arthritis • Systemic lupus erythmatosus 19 Giving Yourself a Fighting Chance How to support your immune system Public Health Taking care of yourself • Nutrition • Exercise • Rest • Moderation of Lifestyle • Controlling Stress 20 Thank You! 21