* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Class 22 - Basic stimulus control
Mentalism (discrimination) wikipedia , lookup
International Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Racial Discrimination wikipedia , lookup
Employment discrimination wikipedia , lookup
Racism in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Employment Non-Discrimination Act wikipedia , lookup
Employment discrimination law in the United States wikipedia , lookup
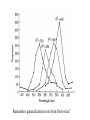
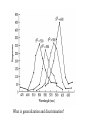
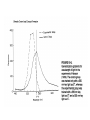
Basic Stimulus Control Thus Far in Operant… • Emphasis on the events following behavior – Differentiation from Pavlovian? • But control from antecedent stimuli also very important – “All behavior is under the exquisitely detailed control of surrounding stimuli, some impinging from outside the organism, others arising from within its boundaries” Dinsmoor (1995) STIMULUS CONTROL Examples: Basic discrimination and generalization, psychophysics, attentional control, conceptual and relational behavior, verbal behavior, remembering, applications to the physiology of perception, learning, and memory. Three-term Contingency SD SR SD: discriminative stimulus Ro Ro: operant class SR: reinforcer What is the D S ? • Tracking behavior in time • Control from the past vs. control by the present • Bringing history to bear on current behavior • The power of the SD – How do you get the salt? Discrimination Training • Basic definition – Rf in the presence of one stimulus (S+) – And not in its absence (S-) – Discrimination is acquired • Morse code training in the military (Keller, 1943) • Examples from Pavlovian conditioning Remember generalization tests from Pavlovian? What is generalization and discrimination? Theories of Generalization • Spread of activation • Discrimination hypothesis – Lack of discrimination – Lack of training • The deafened pigeon • Discrimination/Generalization is learned – How would we show that? Compare to This: 350 300 NUMBER OF RESPONSES Have we disproved the hypothesis? GUTTMAN & KALISH (1956) 250 200 150 100 50 0 520 540 560 580 600 WAVELENGTH (nm) 620 640 Is Discrimination “Observation”? • Dinsmoor’s hypothesis – Observation increases discrimination No differential reinforcement Observing Positive and Negative Stimuli Inhibitory Gradients Combined Gradients Attention • Another one of those things we possess • Controlling relation between stimuli and behavior