* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Civil War Begins
Battle of Port Royal wikipedia , lookup
Kentucky in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Malvern Hill wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Island Number Ten wikipedia , lookup
Texas in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
East Tennessee bridge burnings wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Blockade runners of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Roanoke Island wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fredericksburg wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
Maryland Campaign wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Confederate privateer wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Antietam wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
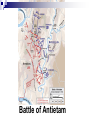
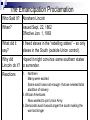
Mobilizing for War Critical Thinking Questions: •What makes a civil war different from a foreign war? •How might a civil war affect society and the U.S. economy? 1 Long Term Causes Sectional differences - economic + cultural Debate over expansion of slavery Political compromises don’t solve problems - MO Compromise, Compromise of 1850, KS-NE Act Laws + court decisions increase tension - Fugitive Slave Act, Dred Scott decision Growth of antislavery movement Uncle Tom’s Cabin Pierre Beauregard led the bombardment of Fort Sumter for the Confederacy The bombardment amazingly killed zero Soldiers Reactions to Fort Sumter Northerners united and Lincoln’s call for troops received overwhelming volunteer support Virginia seceded from the Union to join the Confederacy on April 17th Arkansas, Tennessee, and North Carolina also seceded in May 1861 bringing the total to 11 Confederate states Both sides expected a short war Union Leaders Abraham Lincoln: President of the Union -Main reason for war was to preserve the Union “I believe I have no lawful right to [free the slaves], and I have no inclination to do so.” Confederate Leaders Jefferson Davis: President of the Confederacy The Union Advantages Big population Industrialized: produce more ammunition, arms, medical supplies Larger railroad network Small, well-organized navy Established government Leadership of Lincoln Disadvantages Must travel farther to reach battles Fighting in enemy territory Difficult to find good military leader The Confederacy Advantages Fighting for survival – more passion for war Strong military leaders (Robert E. Lee) Strategic advantages – a defensive war on familiar ground Disadvantages Smaller population No navy – vulnerable to naval blockades New, inexperienced gov. Very little industrialization (supplies) Military Strategies Union Anaconda Plan: Idea to coil around the South and squeeze it to death (like a snake) Naval Blockade Get control of the Miss. River to split Confederacy in two Capture the Confederate capital at Richmond, VA Confederacy Do enough damage to break Union’s will to fight Get military support from Britain and France (they rely heavily on southern cotton) The Anaconda Plan First Battle of Bull Run aka First Manassas July 21, 1861 First major battle of the Civil War Two very inexperienced armies met in VA Reinforcements turned the tide in favor of the South on the third day Union soldiers retreated in chaos Picnic lunches were disturbed as DC society people had gathered for lunches near the battlefield A Legend is Born at Bull Run Another Confederate general made a comment about Thomas Jackson during the Battle of Bull Run that he was “standing like a stone wall.” Thus, he earned the nickname ‘Stonewall Jackson’ Bull Run Battlefield Photo taken in July 1861 Reaction to Bull Run Confederates score the first victory Many Southerners returned home believing that the war was over Lincoln called for 500,000 more troops for a three year enlistment Lincoln named General George McClellan to lead the new Union Army Grant having success in the West Battle of Antietam “Bloodiest Single Day of the War” September 17, 1862 Casualties numbered as many as in the War of 1812 and the MexicanAmerican War combined. 23,000 killed or wounded in one day! 19 For over 4 hours, Union and Confederate infantry fought for this sunken country road resulting in over 5,000 casualties. Today it is known simply as “Bloody Lane”. Battle of Antietam Impact of Antietam September 17, 1862 Union Army wins? Tactical Victory: CSA, Strategic Victory: USA Stopped Lee from forcing Lincoln to ask for peace Allowed Lincoln to use the “victory” to announce in 1863 the Emancipation Proclamation Discouraged England and France from joining the war on the Confederate side Caused Lincoln to fire McClellan for not The Emancipation Proclamation All persons held as slaves within any State or designated part of a State the people whereof shall then be in rebellion against the United States, shall be then, thenceforward, and forever free… And upon this act, sincerely believed to be an act of justice, warranted by the Constitution upon military necessity, I invoke the considerate judgment of mankind, and the gracious favor of almighty God. 24 The Emancipation Proclamation Who Said It? Abraham Lincoln When? Issued Sept. 22, 1862 Effective Jan. 1, 1863 What did it say? It freed slaves in the “rebelling states” – so only slaves in the South (outside Union control). Why did Hoped it might convince some southern states Lincoln do it? to surrender. Reactions 1. Northern • Many were excited • Some said it was not enough- that we needed total abolition of slavery 2. African Americans • Now wanted to join Union Army 3. Democrats said it would anger the south making the war last longer Union Change of Command General Ambrose Burnside reluctantly replaced General McClellan on November 9, 1862 General George B. McClellan Disaster for Burnside Battle of Fredericksburg leads to defeat for Burnside’s Army of the Potomac in late 1862 Following a ‘mud march’ through VA swamps, Burnside experiences insubordination from many of his senior officers Ultimatum: Court-martial and relieve many of the officers or accept Burnside’s resignation