* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Secession in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
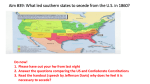
Chapter 14 Sectional Conflict Intensifies Aftermath of Mexican-American War The War had increased tensions question of whether or not slavery should expand westward Also, could slave holders retrieve escaped slaves? Wilmot Proviso August 1846 David Wilmot (D, PA) proposed an amendment “Neither slavery no involuntary servitude shall exist in any new territory gained from Mexico.” House passed it, but the Senate would not even vote on it. *Upset the Southerners They say it as a threat to slavery everywhere The Debate Goes On… Calhoun, weak from TB “States own the territories” “Congress has no right to ban slavery” Warned that a “civil war” would break out If the North didn’t deal with Southern concerns Popular Sovereignty Senator Lewis Cass (MI) proposed the idea of “popular sovereignty.” Citizens of the new territories should decided the issue Many supported this idea. It was democratic and kept the controversy at bay. *Abolitionists still argued that the right of AfricanAmericans not to be enslaved did exist. Election of 1848 Whigs: Zachary Taylor But.. Whigs split: Northern Whigs=“Conscience Whigs” Opposed slavery Opposed Taylor Slavery and Gold in California January 1848: James Marshall discovered gold in California By end of 1849: over 80,000 people in CA looking for gold Nicknamed “fortyniners.” Chaos and violence California Applies for Statehood To gain control, CA applies for statehood But this raises the question….. Would CA be a slave state or a free state Dec. 1849: CA applies for statehood as a free state Now, you’d think that would be the end of it…….. But, There’s a Problem! If CA is a free state, then slave states would be in the minority in the Senate Southern politicians began talking about secession. Compromise Henry Clay “The Compromiser” Comes up with compromises in pairs 1st: CA = free state, and the rest of Mexican land would have no restrictions on slavery 2nd: Border between NM and TX would favor NM And, Federal Government would take on debts of TX 3rd: Outlawed slave trade in DC, but not slavery 4th: Congress would not interfere with domestic slave trade But, they did pass the Fugitive Slave Act to help recover escaped slaves Debate over the Compromises Calhoun: “North’s opposition to slavery would destroy the South.” Daniel Webster: supported Clay’s plans, and warned against secession. Clay Gets His Way…Eventually Clays plans did not pass Largely because, Taylor opposed them But…..Taylor died in the Summer of 1850 New President, Millard Fillmore supported the plans. By the end of the summer… John C. Calhoun… DEAD! Webster…. SECRETARY OF STATE! Clay… WORN OUT! Compromise of 1850 Stephen Douglas (IL) split Clay’s plans into smaller bills By Fall 1850: all parts were passed, Fillmore signed into law Compromise of 1850 eased tensions over slavery….. TEMPORARILY!!!!!! Section 2 Mounting Violence Fugitive Slave Act A person points out someone and accuses him/her of being an escaped slave Accused person would go before a federal commission Testimony of white people was all that was needed to convict No trial and no chance to testify Federal Commissioner would be paid $10 if he sided with the slave owner, and $5 if he sided with the accused. Northern citizens were required to help capture people or face jail time Literature Harriet Beecher Stowe “Uncle Tom’s Cabin” in 1852 Sold 300,000 copies its 1st year Henry David Thoreau “Civil Disobedience” (1849) O.K. to disobey immoral laws Northerners were inspired Transcontinental Railroad Early 1850s Force NE and IA to develop territory and organize Travel to CA and OR in 4 days Big Question: “Where would it start?” Where Would It Start??? South North New Orleans Chicago But, you would have to go Senator Stephen Douglas through Northern Mexico Must organize territory Secretary of War 1853 bill to create Jefferson Davis sent James Gadsden Santa Anna sold 300,000 square miles for $10 million. territory of Nebraska MO Compromise called into question Southerners wanted the MO Compromise repealed Stephen Douglas tries to Compromise 1st bill: claimed “popular sovereignty” Would not repeal the MO compromise Southerners saw through this 2nd bill: undo MO Compromise Create 2 territories Kansas and Nebraska Known as the Kansas and Nebraska Act Mad Rush to Kansas Southerners rushed there Northerners rushed there, and established a majority MO Senator David Atchison called upon Missourians to go to Kansas May 1855 Thousands of armed Missourians rushed into Kansas They voted illegally and established a proslavery government Northerners Retaliate They held a convention and created an anti slavery government By the end of 1855: 2 governments in Kansas 1856: Armed Missourians attacked Northern settlers “Bleeding Kansas” Over 200 died Over $2 million in damages In the Senate May 1856 Senator Charles Sumner (MA) insulted Sen. Andrew Butler (SC) Said that he “had a mistress…the harlot of slavery!!!” May 22, 1856: Representative Preston Brooks (SC) entered the Senate chamber And beat Sumner with a metal and gold cane New Political Parties Kansas-Nebraska upset many in the North Whig Party split…again Northern Whigs + Free Soil + Anti-Slavery Democrats joined together in 1854 Also… Anti-Nebraska Party, Fusion Party, People’s Party, and Independent Party Held a convention and became the “Republican Party” in July 1854 All agree that slavery should not exist in the new territories. “Know-Nothings” made gains in 1854 Republican Party absorbed the “Know-Nothings.” Election of 1856 Republican: John C. Fremont Known as the “pathfinder” Believed that KS should be a free state Democrats: James Buchanan In Congress for 20 years Ambassador to Russia and Great Britain No real stand on KS But, he did believe that the only way to save the U.S. was to give the South what they wanted. He won Lecompton Constitution Violence in KS Buchanan’s solution is to make KS a state 1857: The Anti-Slavery government banned slavery The Pro-Slavery government legalized slavery Referendum was put out “yes” or “no” on the “Lecompton Constitution” (pro-slavery). Kansas Becomes a State Buchanan accepted the pro-slavery vote Asked Congress to admit KS as a slave state Senate: accepted House: blocked Fights broke out Buchanan and Southern leaders agreed to have another referendum But there’s a catch….. If KS voted against the Lecompton Constitution, they would delay statehood for 2 years. 1858: KS voted against the Lecompton Constitution 1861: KS admitted to the U.S. as a free state Lincoln v. Douglas 1858: Illinois Republicans nominated Lincoln to challenge Douglas for the Senate Background on Lincoln Born in Kentucky Store owner Practiced law Little formal education Was NOT an abolitionist But did think it was immoral and should not exist out West Stephen Douglas on Slavery Douglas believed in “popular sovereignty” Supported the Dred Scott decision (slaves are and never were meant to be included in the constitution) But people could refuse to enforce it Known as the “Freeport Doctrine” John Brown Radical abolitionist Believed that God wanted him to end slavery Killed 5 pro slavery settlers and was never punished Harper’s Ferry and John Brown’s Raid October 16, 1859 Brown led 18 people to a federal arsenal in modern West Virginia (Harper’s Ferry) U.S. Marines led by Colonel Robert E. Lee stopped Brown Took 36 hours Tried, and convicted of treason December 2, 1859 he was executed North saw him as a martyr South saw this as evidence that the North was going to attack the South The Union Dissolves South believed that John Brown represented the North 1860: The Democrats finally split over slavery Election of 1860 Northern Democrats: popular sovereignty Nominate Stephen Douglas Southern Democrats: wanted to keep slave codes Nominate John C. Breckenridge Republicans: denounced John Brown, acknowledges the South has a right to slavery Nominate Abe Lincoln Constitutional Union Party: John Bell Lincoln wins, and this ultimately causes secession Dates of Secession SC: 12/20/1860 MS: 1/9/1861 FL: 1/10/1861 AL: 1/11/1861 GA: 1/19/1861 LA: 1/26/1861 TX: 2/1/1861 VA: 4/17/1861 AR: 5/6/1861 NC: 5/20/1861 TN: 6/8/1861 Secession Secessionists would seize federal property Including forts and arsenals 2 exceptions Ft. Sumter (for a little bit) and Ft. Pickens stayed in Union hands U.S. still wants to compromise Crittenden’s Compromise KY Senator John Crittenden Guarantee slavery Extend MO compromise line to CA Did not pass Confederacy Feb. 1861 Confederate leaders met in Montgomery, AL Formed the “Confederate States of America.” Drafted a constitution Each state was independent Guaranteed slavery Banned protective tariffs Limited Presidency to one 6 year term Elected Jefferson Davis March 4, 1861: Lincoln is inaugurated President of the United States The Civil War Begins Lincoln takes office March 4, 1861 Inaugural address, “the Union of these states is perpetual.” Tried to reassure the southern states that the North was not the aggressor Fort Sumter Falls April 1861 Lincoln announces that he will re-supply Ft. Sumter Confederacy has a dilemma Can’t let the U.S. come into their territory But, can’t really fire on them cause it will lead to war Ft. Sumter Davis decides to take Ft. Sumter before the U.S. troops get there. Major Robert Anderson (Union) was told to surrender the fort by April 12, 1861 Anderson refused to leave Confederate troops bombarded the fort for 33 hours No one died, but Anderson finally surrendered Civil War has now begun Upper South Secedes Lincoln calls for 75,000 volunteers They would serve in the military for 90 days This created panic in the Upper South They didn’t necessarily want to secede, but felt they had no choice Virginia was first Trying to Keep the Border States Lincoln knew it was important to keep the slave-holding border states KY, MO, and MD were particular concerns If MD seceded, then the nation’s capital would be surrounded by Confederate states Maryland Lincoln imposed martial law in Baltimore Soldiers would arrest anyone suspected of supporting secession Kentucky KY was important because it controlled the Ohio River KY declared itself neutral Lincoln promised to leave it alone if the Confederacy did too. Sept. 1861 Confederate troops moved into southwest corner Union troops moved in too KY legislature voted to go to war with Confederacy While pro-confederacy Kentuckians seceded and formed own government Missouri Many sympathized with the Confederacy But voted to stay in the Union Federal forces helped keep Missouri in the Union