* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 8
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Secession in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
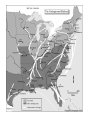
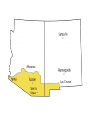
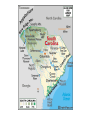
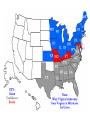
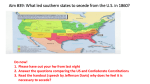
Chapter 8 Sectional Conflict Intensifies Section 1: Slavery and Western Expansion • Wilmot Proviso: legislation stated the new territory acquired from Mexico cannot have slavery. • Never passed Congress, why? • Senator from Michigan, Lewis Cass, came up with popular sovereignty to deal with issue of slavery • The citizens from each new territory should be able to decide if they are free or slave • Does this idea make sense? • What do you suppose the abolitionists thought of it? 1848 election • Zachary Taylor won election; Whig • Defeated Martin Van Buren and Lewis Cass GOLD! • 1848 gold discovered in California • People flocked to the West by 1849 “fortyniners” • CA’s population escalated and applied for statehood as a free state; will be annexed • How did the South react to this? • Southern states talked about secession b/c they now had the minority in the Senate • Taylor died in office and VP Millard Fillmore took over Compromise of 1850 • CA would be a free state, NM, AZ, NV and UT would decide through popular sovereignty • Slave trade would cease ONLY in Washington D.C. • Fugitive Slave Act: if someone spotted a runaway slave in the North, all they had to do was point them out (most controversial aspect of the compromise to Northerners) • The accused went to trial, but could not defend him/herself • Would be sent back to the South • Abolitionists quoted “Civil Disobedience”: “Unjust laws exist, shall we be content to obey them, or shall we endeavor to amend them, and obey them until we have succeed, or shall we transgress (overrule) them at once?” Underground Railroad • Series of routes, led by conductors, to get slaves to the North • Harriet Tubman is one of the most famous. • P. 289 Harriet Beecher Stowe • Wrote Uncle Tom’s Cabin • Got the idea from her sister living in Boston that had witnessed people being beaten and wrongfully accused b/c of the Fugitive Slave Act • Stowe lived for several years across the OH River, near KY • She once witnessed slavery when she visited KY • The book is about a slave named Tom and his master, Simon Legree. • Book sold very well in the North, while Southerners tried to ban it. • Some historians list the book as one of the causes for the Civil War Transcontinental Railroad • With the new territories, US needed a railroad system that reached both sides of the nation • Question was where it should begin and end • Southerners wanted it to go through New Orleans • If so, it had to run through Mexico • President Franklin Pierce bought the Gadsden Purchase from Mexico for $10 million (30,000 square miles of southern AZ and NM) • What was the Missouri Compromise? • IL Senator Stephen Douglas wanted a terminal in Chicago • In order for the RR to reach the W. Coast it had to go through new territory called Nebraska • Since NE is above MO’s southern border, it would be admitted as a free state • Douglas had to repeal the MO Compromise • All to get the RR in Chicago. . . • Douglas convinced Congress to divide the region into NE and KS • His plan was to drop the MO Compromise and NE admitted as a free state while KS was the slave state • Kansas-Nebraska Act passed Congress • Why do you suppose Congress approved this legislation? Bleeding Kansas • Pro slavery and abolitionists flocked to the new territory • Both sides hoped they could populate the area and when the states applied for statehood, they could use popular sovereignty • In KS, abolitionists vandalized shops and homes which caused a rebellion • Roughly 200 people were killed; Bleeding KS Section 2: The Crisis Deepens • Whig Party dissolved • Free Soil and anti-slavery democrats formed the Republican party • 1856, James Buchanan elected Pres. • Wanted to make concessions with the South to save the Union, but did nothing Dred Scott Case • A slave who moved with his MO master to a free territory • Scott returned to MO thinking he should permanently be free • Case went to Supreme Court • Court decided African Americans were not citizens • Court said they had no jurisdiction to abolish slavery in the new territories • Republicans said court was not called upon to decide such a measure • Southerners threatened northerners saying they would secede if North did not abide by ruling Back to Kansas. . . • Their constitution originally said slavery was legal • Referendum overruled this and KS became a free state (admitted to Union in 1861) Illinois Senate Race • Democrat: Stephen Douglas • Republican: Abraham Lincoln • Douglas won b/c during debates he came up with Freeport Doctrine • Accepted Dred Scott ruling but also stated that the people had the right to decide on accepting slavery • Lincoln gained national attention because of his well-versed speeches John Brown • An abolitionist who seized federal arsenal at Harper’s Ferry, WV • Goal was to arm and free the enslaved by rebelling • Colonel Robert E. Lee and Marines ended the rebellion • Brown was executed; seen as a martyr by Northerners Section 3: The Union Dissolves • • • • • 1860 Presidential election Stephen Douglas: democrat Abraham Lincoln: republican Lincoln won w/o campaigning in the South Promised to stop the spread of slavery, NOT completely abolish it Secession Begins • South Carolina voted to secede first • Their reasoning was that the federal gov’t was too powerful: STATES’ RIGHTS VS. FEDERAL RIGHTS • MS, FL, AL, GA, LA and TX joined the secession • AR, NC, TN and VA followed after bombardment at Ft. Sumter, SC Fort Sumter (Charleston, SC) • Secessionists took control of federal forts Sumter and Picks (Pensacola Harbor) • These forts were under Union control • Secessionists also decided to call their new nation the Confederate States of America (CSA) • Wrote a Constitution identical to Union’s except it guaranteed slavery and banned tariffs • Jefferson Davis was chosen as President of Confederacy • March, 1861, Lincoln made his inaugural address: intended to “hold, occupy and possess” federal property • His goal was to preserve the Union • April, 1861, Lincoln announced the resupply of Ft. Sumter • Confederacy did not want Northern troops in what the South perceived was their vital harbor • President Davis decided to capture the fort before the supply ship arrived • April 12, 1861, south fired canons at the fort • Lasted 33 hours, no fatalities • Union surrendered b/c they ran out of supplies • American Civil War has begun • 1861-1865 Border States • Sometimes called Buffer states • Lincoln declared martial law on MD • Military took control of an area, suspended civil rights • KY stayed neutral • MO threw their support to the Union