* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download U.S. History Core 100, Goal 3
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Carpetbagger wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
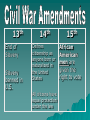
U.S. History Core 100, Goal 3 Crisis, Civil War, and Reconstruction (1848-1877) The learner will analyze the issues that led to the Civil War, the effects of the war, and the impact of Reconstruction on the nation. The people can decide by vote if they would like slavery in the territories or not Kansas, Nebraska = open to slavery through popular sovereignty in the 1850s Affected the new territory P.S. = people select ; popular sovereignty Stephen Douglas Transcontinental railroad Kansas, Nebraska = open to slavery through popular sovereignty in the 1850s Overturned Missouri Compromise Led to Bleeding Kansas Pro vs. Anti-slavery John Brown In 1830s, a growing number of Americans opposed slavery Demanded an immediate end to slavery in the South William Lloyd Garrison – The Liberator Frederick Douglass – The North Star Grimke Sisters 1857 Supreme Court ruled that African Americans were not citizens and therefore could not sue in court The decision outraged Northerners and was supported by Southerners Completely overturned Missouri Compromise Cause of Civil War 16th president; Republican from Illinois – President during Civil War Wanted to preserve the Union Passed the Emancipation Proclamation Assassinated by John Wilkes Booth on April 15, 1865 After the Battle of Antietam Passed by Abraham Lincoln on September 22, 1862 Slaves in states at war with Union would be freed as of January 1, 1863 – Many slaves fled to the North – As the Union army advanced in the South, thousands were freed Slavery officially ends w/ the 13th Amendment in Dec. of 1865 Changes goal of war to moral issue Causes Course States’ rights Ft. Sumter Nationalism Anaconda Plan Sectionalism Antietam Secession (CSA: Confederate States of America; President= Jefferson Davis) Gettysburg Slavery Vicksburg Sherman’s March to the Sea Appomattox Consequences Reunification of N. and S. Reconstruction (1865-1877) Civil War Amendments (13, 14, 15) July 1-3 1863 Gettysburg, Pennsylvania Union: George G. Meade Confederate: Robert E. Lee Union Wins Bloodies battle of the Civil War – 46,000 – 51,000 causalities Lincoln and Johnson Amnesty (pardon) to all Southerners taking an oath of loyalty to the U.S. and accepting its proclamation of slavery 10% of a state’s voters in 1860 presidential election take oath, can organize new state government Former members of CSA’s government would not receive pardon New state gov’ts Leaders: – Thaddeus Stevens of Penn. – Charles Sumner of Mass. Military Reconstruction Must ratify 14th Amendment PUNISH the south! 3 main goals: – Prevent CSA leaders from returning to power – Republican Party to become powerful in South – Federal government to help African Americans achieve political equality 13th End of Slavery Slavery banned in U.S. 14th Defines citizenship as anyone born or naturalized in the United States All citizens have equal protection under the law 15th African American men are given the right to vote Settled the disputed Presidential election of 1876 Rutherford B. Hayes wins election Ends Reconstruction in the South State and local laws in the U.S. from 1876 – 1965 Passed to legally separate the races in public places Facilities were supposedly “separate but equal” – Examples: Segregation in public schools, public transportation, public restrooms – Upheld in Plessy v. Ferguson in 1898 Sharecropping: farmers who farmed portions of the plantation but furnished nothing but their labor Tenant Farming: supplied their own mules, seeds, and provisions. The planter was given a percentage of the crop. Freedman’s Bureau: help former slaves by providing them with food, education, and helping them find work Carpetbaggers: Northerners who went South during Reconstruction for various reasons