* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1. - Cloudfront.net
Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Red River Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Island Number Ten wikipedia , lookup
Texas in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Kentucky in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union blockade wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Blockade runners of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Secession in the United States wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Lexington wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Hampton Roads wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
East Tennessee bridge burnings wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
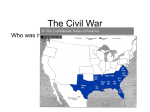
Ch. 16: The Civil War pg. 458 Why It Matters: The Civil War-a war in which Americans fought other Americanstransformed the United States. It shattered the economy of the South while contributing to the rapid economic growth of the North and the West. African Americans gained freedom when slavery was abolished, but the way left a legacy of bitterness between North and South that lasted for generations. The Impact Today: Key events during this era still shape our lives today. For example: The institution of slavery was abolished The war established the power of the federal government over the states. Section 1: The Two Sides Main Idea: Both the North and the South had strengths and weaknesses that helped determine their military strategies. Key Terms: Border State Blockade Offensive Rebel Yankee I. Choosing Sides pgs. 460-462 Seven states left the Union and formed the Confederacy in February 1861. Four more states joined in April: Virginia, North Carolina, Tennessee, and Arkansas. The capital was Richmond, Virginia, about 100 miles south from the Union’s capital of Washington, D.C. Border States The border states of Missouri, Kentucky, Maryland, and Delaware stayed in the Union but were divided over which side to support. They played an important part in the war because of their location, and they would seriously damage the North if they seceded. Border States 1. Missouri could control parts of the Mississippi River and major routes West. 2. Kentucky controlled the Ohio River 3. Delaware was close to the North’s important city of Philadelphia. 4. Maryland was very close to Richmond, had important railroad lines, and had the Union’s capital of Washington, D.C., within its borders. Choosing Sides In April a mob in Baltimore attacked Northern troops. Confederate sympathizers burned railroad lines and cut the telegraph line to Washington, isolating it. Lincoln had to be cautious in his response so as not to upset the people of the border states and especially Maryland. He ended up arresting people who supported secession. The border states remained in the Union, but many of the citizens joined Southern armies. Take me home, to the place I belong, West Virginia mountain mama…Take me home! Most white Southerners supported secession, but people in the Appalachian region of Tennessee and Virginia opposed it. In Virginia a movement to secede from the state and rejoin the Union grew. The separate state of West Virginia joined the Union in 1863. Comparing North and South Both sides had advantages and disadvantages. The following were the North’s advantages: 1. a larger population 2. more industry 3. more resources 4. a better banking system to help raise money 5. more ships 6. regular navy members who were mostly loyal to the Union 7. a larger and more efficient railway system 8. Abraham Lincoln’s dedication, intelligence, skill, and humanity Disadvantages The following were the North’s disadvantages: 1. In order to bring the Southern states back in to the Union it would have to invade and hold the South. 2. Many people believed the South had a good chance of winning. Comparing North and South The following were the South’s advantages: 1. strong support for the war from the white population 2. troops fighting on their own land 3. superior military leadership at first (General Robert E. Lee) The following were the South’s disadvantages 1. a smaller population 2. few factories 3. fewer resources, including an inferior railroad system with fewer than half the miles of track and fewer trains than the North 4. belief in states’ rights that limited a strong central gov’t power Comparing North and South War goals were different. The North at first wanted to bring the Southern states back into the Union and wanted to also end slavery. The Union’s plan had three parts. 1. Blockade Southern ports to prevent supplies from entering and cotton from being exported. 2. Gain control of the Mississippi River to cut Southern supply lines and to split the Confederacy. 3. Capture Richmond, the Confederate capital. South’s Plan The South’s goal was to win recognition as an independent nation so the South could preserve their traditional way of life, including slavery. 1. holding on to as much territory as possible until the North tired of fighting 2. having Britain and France pressure the North to end the war 3. sometimes going on the attack by moving north to threaten Washington, D.C., and other Northern cities. American People at War Soldiers came from all walks of life although many came from farms. One difficult aspect of the Civil War was that Americans were fighting other Americans. The average age was 25 years, but about 40% were 21 or younger. A soldier’s term was 90 days at first, but then became longer when the war did not end quickly. The number of soldiers from the North and South differed greatly. By the summer of 1861, the Confederate army, also called the Rebels, had about 112,000 soldiers. The Unions, or Yankee, soldiers numbered about 187,000. By the end of the war, about 850,000 men fought for the Confederacy, and about 2.1 million men fought for the Union. About 200,000 African Americans fought for the Union, and about 10,000 Hispanics fought in the conflict. American People at War Both sides expected the war to end quickly. Some leaders saw the war would be a long one. Northern General William Tecumseh Sherman’s predicted a very long war, and his prediction was accurate.