* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Team Sigma
Battle of Malvern Hill wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Appomattox Station wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Sailor's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Arkansas in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Texas in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Red River Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
Kentucky in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Island Number Ten wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Antietam wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
East Tennessee bridge burnings wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Confederate privateer wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
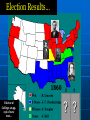
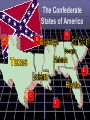
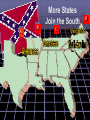
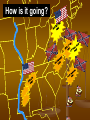
A War Between the States The United States Civil War Waverly-Shell Rock Junior High U.S. History The Election of 1860 Stephen A. Douglas, favored by northern democrats because of his stance on popular sovereignty. John Bell, favored by Constitutional Union Party because of his belief in keeping the country together. John C. Breckenridge, Abraham Lincoln, favored by southern favored by the democrats because Republican Party of his stance on because of his belief in state rights and limiting the spread of protection of slavery in the western slavery. territories. Election results on pp. 403 of old text… A Political Cartoon… Lincoln stands on a No Extension of Slavery platform holds tight with his right hand the rope around Douglas' neck which reads: Squatter sovereignty, and brandishes a rail with his left. John Bell stands on the ground without a platform and has a bell over his head; John C. Breckinridge seated behind him writing New York Ledger; his head is also under the bell. Stephen Douglas with one foot through the Cincinnati Platform and the other on the Mason Dixon Line waves two flags: SOUTH. Dred Scott Decision" and NORTH. Unfriendly Legislation. Another Political Cartoon… John Bell: Bless my soul I give up. John C. Breckinridge: That long legged Abolitionist is getting ahead of us after all. Stephen Douglas: I never run so in my life. John C. Breckinridge dances with President James Buchanan. One more… Lincoln dances with African American woman. Dred Scott seated plays the violin. Stephen Douglas dances with a sovereign in rags. John Bell dances with Native American. Election Results… Electoral College on pp. 196 of new text… ? ? December 20th, 1860 Before Abraham Lincoln was even sworn into office, South Carolina makes true on its threat to leave the Union. South Carolina seceded for much the same reason the 13 colonies separated from Great Britain; they felt their rights were no longer protected under the Constitution. The Confederate States of America D A B E C F How is the Confederate Constitution different from the United States? A Confederate state is “sovereign and independent” Tariffs are now banned on imports A Confederate Congress cannot mess with slavery A president may only serve one six year term. Who will lead this independent nation? Jefferson Davis, of Mississippi Grew up on a plantation with many slaves Strong military background Served in both houses of the US Government Secretary of War for President Pierce What about the US Forts? April 12th, 1861 A War Begins The confederate victory was considered by most historians to be the start of the Civil War. Fort Sumter, South Carolina Visual on pp. 511 of new text… More States Join the South A B C D Why Fight? Put an end to slavery Slavery is an once and for all Preserve the Union U.S. Constitution binds North and South together economic necessity Cotton clashes with manufacturing Fight to live the way they want to live States rights come before federal power Strengths 22 million people Plenty of food & supplies Railroads & Manufacturing Banks & Strong Government Plenty of Weapons Fight will be on home soil Fight on the defensive Outdoor living skills Military leaders among the best (West Point) Volunteers? “Yankees” 75,000 called to serve for 3 months African Americans are turned away “Rebs” 100,000 called to serve for 12 months How will the North Win? Invade the South Control Mississippi River Divide confederate territory in two Blockade southern ports (supplies) Capture capital: Richmond, Virginia How will the South Win? Hold out long enough so North will grow tired Pure Defense Capture Washington D.C. Split the North in two? Secure foreign aid (Britain and France) End Day #1 You’ve seen this before…Notice anything? Our troops are seasoned fighters who have seen war many times before. We have all the money we need to fight this war. We have one of the largest navies in the World. Some of your own people are fighting on our side. Our troops lack experience and training We need more money and equipment. We think we know how to get it. We know the land like the back of our hands. Your enemies want to help us beat you. Who was who? Does it relate to this war? Bull Run, (Manassas Junction) Spring 1861 30 miles from Washington D.C. The first major engagement of the Civil War. 28,450 2,950 32,230 1,750 This battle proved to both sides, the war would not end quickly. The Fight in the West Shiloh, Early 1862 General Ulysses S. Grant attacks in an attempt to capture the Mississippi River. 65,085 13,047 44,968 10,699 How is it going? Lee prevents Union capture of Richmond General Sherman pushes south to control Mississippi. Antietam, Sept. 1862 Lee leads 40,000 troops on Washington D. C. but is pushed back to Virginia. Union forces turn back Lee’s first invasion of the North. The loss discouraged foreign support of the Confederate States. Bloodiest day of fighting. How is it going? Emancipation Proclamation, 1862 “As of January 1st, 1863, all persons held as slaves within any state…in rebellion against the United States, shall be then, henceforth, and forever free.” Five days after the victory at Antietam, President Lincoln makes an announcement that shocks both nations. Lincoln’s proclamation gave the Union soldiers a reason (Video Clip?) to continue fighting and hoped to discourage France and Great Britain from aiding the South. Fredericksburg, Virginia, Dec. 1862 Union 100,007/ CS 72,497 (US 13,353, CSA 4,576) recorded as one of the worst defeats in US Army history. Chancellorsville, May 1862 Lee beat back 120,000 US troops with 60,000. Stonewall Jackson Falls (US 14,000/ CSA 10,000) (Video Clip? X2) Robert E. Lee Discourages North How is it going? General Sherman continues to gain control of Mississippi. July 1st, 1863 “A Turning Point” General George Meade The Battle of Gettysburg to be continued...soon 75,000 97,000 Day 2 Union forces were pushed back through the town the previous day and have taken position in the hills. 15,000 Day 3 Robert E. Lee will order an assault against the Union middle position. (Pickett’s Charge) If the line breaks, Confederate forces will have a clear road on to Washington D.C. Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 The Battle of Gettysburg