* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Causes of the Civil War!
Second Battle of Corinth wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Port Royal wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Roanoke Island wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Lexington wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Cedar Creek wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
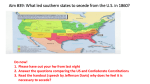
Causes of the Civil War! 1861-1865 What to Do With Slavery? Most Americans were to busy to worry about issues such as slavery. By the 1840s travel was mostly east-west, not north- south, so few Georgians had ever met a New Yorker, and few from Vermont had ever met a Mississippian. Most northerners didn’t care much about slaves and had no desire to either free them or have more blacks moving to the North. As a matter of fact, some northerners wanted to return Africans to Africa and deny American citizenship. It was the frontier expansion that caused Congress and the people to wrestle with the slavery question! American Ideas Manifest Destiny – A belief shared by many Americans in the mid1800s that the United States was meant to expand across the continent to the Pacific Ocean.. (USA= Ocean to Ocean) • State’s Rights- State’s have the right to create their own laws and disregard the federal government, if necessary • Popular Sovereignty-would allow voters in a territory to decided whether they wanted to ban or allow slavery. • Sectionalism – A devotion to the interest of one part of the country rather than the entire country as a whole. Missouri Compromise • • • • Debate: 1819, Missouri wanted to enter the U.S as a slave state. Congress consisted of 11 free, 11 slave states Missouri would throw off the balance of power. Henry Clay’s resolution: – 1. Missouri would enter the U.S as a slave state. – 2. Maine would join the U.S as a free state. – 3. Slavery not allowed in any new territories or states formed north of the 36’ 30’ latitude line(Missouri’s southern border) Slave Codes • According to the Constitution, each slave counted as 3/5 a person. • Slaves escaped to the Northern States, and Canada • In 1850 stricter laws were passed making it mandatory for federal marshals to assist in recapturing runaways. • The Fugitive Slave Act -1850 made it a federal crime to help runaway slaves. • Penalties for helping a slave included fines and imprisonment for up to 6 months. Dred Scott Decision • • • Debate: Dred Scott, a slave of an army surgeon from St. Louis, Missouri, who first sued for his freedom in 1847. His proposal: he became free when he lived in a free territory. Court ruled (1857): – 1. African Americans are not citizens under the U.S. Constitution (3/5) – 2. Missouri Compromise unconstitutional. – 3. Slave status depends on home state. – 4. Slaves were property! – Southerners cheered, Northerners were outraged! – childhood friends of Scott, had helped pay Scott's legal fees through the years. – After the Supreme Court's decision, the former master's sons purchased Scott and his wife and set them free. Dred Scott died nine months later. Abolitionists Abolition – To end slavery Quakers: 1st Abolitionists, challenged slavery (sin) on religious grounds William Lloyd Garrison: published The Liberator, an abolitionist newspaper Harriet Beecher Stowe: wrote a book called “Uncle Tom’s Cabin” John Brown: believed that violence was the only way to end slavery Harriet Tubman: created and maintained the Underground railroad Frederick Douglass: was an escaped slave, and brilliant speaker He published his autobiography and an abolitionist newspaper, The North Star. Compromise of 1850 • Debate- Admission of California to the Union. • Henry Clay’s resolution: • To please the North: California would be a free state, and the slave trade would end in Washington D.C. • To please the South: Congress would not pass laws regarding slavery in the territories won from Mexico, and would pass the Fugitive Slave Act Kansas- Nebraska Act Kansas – Nebraska Act: 1854 law that created Kansas and Nebraska and gave residents the right to vote for for/against Slavery John Brown – and 5 sons killed 5 pro-slavery men. 200 other people killed in the months that followed. “BLEEDING KANSAS!” Stephan Douglas’ Resolution: 1. Divide the land into two territories- Kansas and Nebraska. 2. Popular sovereignty would decide the issue of slavery 3. Remove the Missouri Compromise Violence in Congress • In 1856, abolitionist Senator Charles Sumner was beaten in the Senate chamber • He had called S.C. Senator Andrew Butler names during a speech to the Senate • 3 days later, Butler’s nephew, Preston Brooks, beat Sumner with a metal-handled cane • Sumner was beaten unconscious until the cane shattered • Head wounds kept him out of the Senate for 3 years • North outraged, South sent Brooks canes, Senators now armed for work! Preston Brooks Lincoln-Douglas Debates 1858 U.S. Senate Seat not President • • • • 7 Debates on the issue of slavery and its future out West. Lincoln = republican & “slavery shall grow no more” Douglas = democrat and slavery! Douglas won the senate seat BUT the debates established the reputation of Abraham Lincoln for future political interests: The Presidency! 1861-1865 Secession *Lincoln won the presidential election of 1860! Southerners UPSET! *Many Southerners believed that once in power, Lincoln would move to abolish slavery. They feared this would upset their economy and society. *December 17, 1860 South Carolina voted to secede (leave the Union). *They figured that the states voluntarily joined the United States and they could voluntarily leave! Ft. Sumter • Ft. Sumter is located just outside of Charleston, South Carolina, which controlled the entrance to the Charleston Harbor • Before sunrise on April 12, 1861, Confederate soldiers fired the first shots of the Civil War! • Fort is shelled for 34 hours before Union surrenders • No casualties until Union fires a salute as they lower the flag – cannon explodes killing one and wounding three others Ft. Sumter The Fall of Fort Sumter • Crisis at Fort Sumter – Commander Robert Anderson sent the message to Lincoln that Confederate leaders were demanding surrender or would attack. – Low on supplies, Fort Sumter remained in Union hands. The fort was very symbolic to both sides. – Lincoln would not surrender the fort, but would send food and other nonmilitary supplies. – Jefferson Davis would decide whether to attack and go to war or allow the symbol of federal authority to remain. • The attack on the fort – Davis ordered a surprise attack before the supplies could arrive. – On April 12, 1861, the Confederate artillery opened fire on the fort, and an outgunned Fort Sumter surrendered the next day. The Rush to War Response in the North Reaction in the South • Lincoln calls for 75000 volunteers • 90 days’ service to put down the rebellion • Lincoln’s political enemy Stephen Douglas supports the action, “There can be no neutrals in this war, only patriots—or traitors” • Northerners rush to enlist • With call for volunteers, the eight remaining Union slave states now forced to choose a side • Union slave states refused to provide troops to fight against fellow southerners • Confederate states ready to call up men • First Virginia, then Arkansas, Tennessee, and North Carolina secede Goals and Strategies Union Goals • Needed to be carefully defined • War could not center around the dispute over slavery— border states pushed to secede • Fight for patriotic reasons— to save the Union Confederate Goals • South wanted to be left alone with slavery unchanged • Prepared to defend themselves against invasion • Felt northerners would soon tire of war and withdraw http://americanhistory.pppst.com/civilwar.html Choosing Sides • • • Label the States (only the states on the map in folder) Choose 3 light colors and color the North, South, and Border States. Make a key to explain the colors Choosing Sides • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • North California Connecticut Illinois Indiana Iowa Kansas Maine Massachusetts Michigan Minnesota Nevada (became free state in 1864) New Hampshire New Jersey New York Ohio Oregon Pennsylvania Rhode Island Vermont West Virginia (free state in 1863) Wisconsin • South • • • • • • • • • • • Alabama Arkansas Florida Georgia Louisiana Mississippi North Carolina South Carolina Tennessee Texas Virginia • Border States • • • • • Slave states that didn’t secede Delaware Kentucky Maryland Missouri Civil War • North • • • • Yankees, Federals, Union Billy Yanks Blue Battle tune: Battle Hymn of the Republic • South • • • • Rebels, Dixie, Confederacy Johnny Rebs Gray Battle tune: Dixie North Vs. South Assets • • • • • • • • • North Population- 22 million (about 4 million of combat age) About 2,000,000 join the Union Army/Navy (about 46% of eligible men) Economy based on manufacturing 100,000 factories with about one million workers 20,000 miles of railroad and 96% of the nation’s railroad equipment The majority of coalmines and canals (needed for industry) $189,000,000 in bank deposits $56,000,000 in gold Federal income tax started! • North’s Strategy: divide and conquer (preserve the Union) • • • • • • • • South Population- 9 million (5.5 million whites/3.5 million slaves) About 850,000 join Confederate Army/Navy (about 90% of eligible men) Economy based on farming 20,000 factories with about 200,000 workers 9,000 miles of railroad $47,000,000 in bank deposits $37,000,000 in gold South taxed and had to give portion of its crops to fund war • South’s Strategy: survive until North quits (outlast) Making Soldiers • • • • • After the firing at Ft. Sumter, Lincoln calls for 75,000 militiamen After Ft. Sumter, four more states join the Confederacy Northerners were usually “cityboys” Southerners knew the woods, how to shoot and ride Most of the best generals left the Union Army to return to their homeland in the South • Entire towns had their men volunteer together to go to war • They came in their own uniforms with a variety of weapons • Later, both sides use conscription (draft) to get soldiers • Men from ages 18-35 were drafted; some paid people to take their place;Southern planters with many slaves didn’t have to go • Boys volunteered- tricked officials (18 in shoe); some women disguised themselves as men to fight • Blacks not able to fight at first, Lincoln didn’t want problems with border states and others; “White man’s war”; about 200,000 Blacks eventually fight on both sides, some 37,000 die in battle • Frederick Douglass said, “Men of color to arms! Liberty won only by white men would lose half its luster.” • In 1863, Lincoln lets War Dep’t form Bureau of Colored Troops; commanded by whites they fought bravely; 54th Massachusetts Volunteer Infantry Regiment was famous- “Glory” w/Denzell Washington • The average Yank or Reb was a "white, native-born, farmer, Protestant, single, between 18 and 29." He stood about 5 feet 8 inches tall and weighed about 143 pounds. Most soldiers were between the ages of 18 and 39 with an average age just under 26. • Union Army was made up of 1/5 immigrants – they were happy to fight for a country that had given them so much • They included 200,000 Germans; 150,000 Irish; 45,000 English; 15,000 Canadians, and lesser numbers of French, Norwegians, Italians, Mexicans, and Poles • Exact figures for the South are sketchy, but tens of thousands of Irish, Germans, British, French, Canadians, Dutch, and Austrians entered Confederate ranks. • Indians fought on both sides of the battle (Ely Parker) Army Organization • Cavalry- mounted soldiers on horseback; the “eyes and ears” • Artillery- the firepower of the battle; often towed behind horses • Infantry- soldiers on foot fighting in close combat with guns, bayonets, and bare hands if necessary • Quartermasters- provide everything the unit needs to fight- food, supplies, medical equipment, telegraph, etc. About 25 wagons per 1,000 men • Engineers- build roads, bridges, and fortifications; make maps Weapons • Soldiers used breech loaders, muzzle loaders, carbines, shotgun • Pistols were made by Remington, Colt, and others • Ammunition included the Minie ball, gunpowder flasks, caps • Blades included sabers, bayonets, and cutlasses • Guns more powerful, accurate than ever before Big Guns • Three categories: field artillery, guns strapped to carriages, and big guns • The Napoleon howitzer was the most common field artillery • The Rodman was huge; guarded forts • Cannonballs filled with lead slugs or iron balls Specialized Weapons • The Gatling gun was hand cranked and could shoot 600 rounds per minute from six barrels;it saw limited action • The grenade was ceramic and packed with explosives to be thrown at enemies • Balloons were used as observation platforms. One left from a Confederate ship making one of the first aircraft carriers New technology • The portable telegraph was used to transmit troop movement • Photography was used to record gruesome images from the Civil War • Confederacy has few chemicals needed to process photos;North has most photos Anaconda Plan • The Anaconda Plan was proposed in 1861 by Union General Winfield Scott. • He suggested that the Union should blockade Confederate ports and send gunships down the Mississippi river to divide the South in two. • The South would run out of resources and surrender. This would take time, but have the minimal loss of life. • "Anaconda" is taken from the way an anaconda constricts its prey. “Cotton Diplomacy” • South looks for European allies- Britain, France • England decides to stay neutral • South threatens to withhold cotton from England • England has cotton supply from India, Egypt • South’s plan backfires Naval blockade • Lincoln decides to blockade (patrol the coast letting nothing through that would help the enemy) the South • Union only had 26 usable ships and 7600 sailors to maintain blockade on entire east coast around Florida to Texas • Blockade runners were ships built to sneak through blockade Battle at Sea • Union controlled sea and blockaded the South, hurting the economy • South made an ironclad called the Virginia, which is a ship heavily armored with iron • The North already had an ironclad called the Monitor • The Monitor forced the Virginia to withdraw after a minor fight at sea and kept the blockade strong Who is Wilmer McLean? • The Civil War began on Wilmer McLean’s farm in Manassas Junction, Virginia, with the First Battle of Bull Run. A Union shell exploded in his kitchen. Wilmer McLean moved his family to get away from the conflict. • Almost four years later his new home, near Appomattox Court House, Virginia, was the agreed location for General Robert E. Lee to surrender to General Ulysses S. Grant on APRIL 9, 1865. • The war began in Wilmer McLean’s front yard and ended in his front parlor (living room). • The Civil War resulted in approximately 258,000 Confederate deaths and 360,000 Union deaths. General Lee took off his sword and handed it to General Grant, and Grant handed it back. Wilmer McLean Journal Entries (5 or more sentences for each entry) • Journal Entry #1 – July 21, 1861 Write about McLean's experience and why he is moving. • Journal Entry #2 – April 9, 1865 Write about McLean’s feeling about the war ending, and people plundering his house after • • • • • • Battle of Bull Run 1st real battle of the war is south of Washington D.C. Union troops inexperienced – pick berries on way to fight! Washington socialites pack picnic lunch to watch the battle Union holds early advantage, take break, Rebels reinforce Stonewall Jackson stands firm, Union defeated Yankees run home, Rebels don’t take advantage and follow Antietam • Confederates hoped for victory in North to gain European aid • Unknown to the South, the North found plans of attack and planned a counterattack • The bloodiest single-day battle in the war and a victory for the Union Shiloh • • • • • Confederates initiated this battle Pushed Grant’s army back Union soldiers arrived/Grant began counterattack Confederates retreat Union won greater control of Mississippi River Valley Emancipation Proclamation • In September of 1862, the Union army won a major battle, defeating Confederate forces at Antietam in Maryland. • Five days later President Lincoln first discussed freeing enslaved peoples in the Confederate states. • On January 1, 1863 Lincoln issued an order that has come to be called the Emancipation Proclamation. • The Proclamation allowed Americans who had been enslaved to serve in the Army and Navy. • About 200,000 African Americans eventually served. Emancipation Proclamation • • • • • Lincoln called for all slaves in Confederate States to be freed This encouraged southern slaves to escape This hurt the southern economy African Americans and Abolitionists praised this Changed the focus of the war from preserve Union to include freeing the slaves The Emancipation Proclamation applied only to states that had seceded from the Union. •Slavery remained untouched and still legal in the loyal Border States (Missouri, Kentucky, Maryland, and Delaware). Emancipation Proclamation Find the Evidence Read the second paragraph of the Emancipation Proclamation: • “That on the first day of January, in the year of our Lord one thousand eight hundred and sixty-three, all persons held as slaves within any State or designated part of a State, the people whereof shall then be in rebellion against the United States, shall be then, thence forward, and forever free; and the Executive Government of the United States, including the military and naval authority thereof, will recognize and maintain the freedom of such persons, and will do no act or acts to repress such persons, or any of them, in any efforts they may make for their actual freedom.” Explanation: • The Emancipation Proclamation applied only to states that had seceded from the Union, leaving slavery untouched and still legal in the loyal Border States (Missouri, Kentucky, Maryland, and Delaware). The Road to Gettysburg: 1863 Gettysburg • • July 1-3, 1863 - Gettysburg, PA Gen. George G. Meade [US]; Gen. Robert E. Lee [CS] • Lee took offensive and led an attack in the north • The South pushed the North lines back until Union stands firm at Cemetery Ridge • Pickett’s Charge (day 3): Gen. George Pickett saw more than half of his 15,000 men die in failed attempt at Cemetery Ridge…”General Lee, I have no division.” • On July 4, Lee began withdrawing his army. His train of wounded stretched more than fourteen miles! • Grant captures Vicksburg, MS on same day July 4th – Union now controls entire Mississippi River! • Gettysburg was TURNING POINT in war – South never led another attack in the North •South never in North again • South is on the defensive with North in pursuit •South never has the same troop strength •South loses great officers at Gettysburg •Lee loses his invincibility Gettysburg Casualties Gettysburg Address • Lincoln gives short, moving speech after battle • Reminds crowd of ideals of liberty, equality, and democracy • Dedicates himself and North to winning war and preserving the Union African-American Recruiting Poster • African Americans were not able to fight at first, Lincoln didn’t want problems with border states and others; “White man’s war”; about 200,000 African Americans eventually fight on both sides, some 37,000 die in battle • Frederick Douglass said, “Men of color to arms! Liberty won only by white men would lose half its luster.” • In 1863, Lincoln lets War Dep’t form Bureau of Colored Troops; commanded by whites they fought bravely; 54th Massachusetts Volunteer Infantry Regiment was famous- “Glory” w/Denzell Washington The Famous 54th Massachusetts Black Troops Freeing Slaves Sherman’s March to the Sea • Sherman took Atlanta in Sept. 1864, Sherman’s success helps Lincoln win reelection • In Nov. 1864 Sherman burned Atlanta, and started the march • Sherman’s March to the sea – Union army cut a path of destruction 60 miles wide and 300 miles long! • 60,000 troops, 25,000 horses, 2,500 wagons, 600 ambulance carts • His troops burned crops, tore up train tracks (Sherman neckties), burned/looted homes and towns. • He led his troops over 650 miles in less than 100 marching days, losing only 600 men • 19,000 former slaves followed the Union army to freedom! TOTAL WAR! • SHERMAN WAGED TOTAL WAR – war against the enemy troops, and everything that supported the Confederates - all military and civilian resources Sherman’s March to the Sea Map • Label States • Draw the Union Advance (Sherman’ March) Blue or purple • Draw the Confederate retreat: orange or red • Add explosions and dates of battles • Color Confederate States (any light color) • Don’t forget to add the symbols to the key or legend! Sherman’s “March to the Sea” through Georgia, 1864 Appomattox Courthouse • Lee’s army trapped between Sherman and Grant • Facing starvation he decides situation is hopeless and surrenders to Grant on April 9, 1865 at Appomattox Courthouse • Grant’s terms were easy – Rebels must not turn against country again, can keep horse and sidearms (swords) • After 4 years of battle and 620,000 deaths, war is over • Bitterness between North and South would linger Surrender at Appomattox April 9, 1865 Civil War Casualties in Comparison to Other Wars Ford’s Theater (April 14, 1865) Lincoln’s Assassination • On evening of April 14, 1865 President Lincoln goes to Ford’s Theater with his wife to see a play • John Wilkes Booth, an unemployed actor and southerner sneaks into Lincoln’s theater box and shoots him in head • Booth escapes, but is later caught and shot • Lincoln dies next day, and VP Andrew Johnson is sworn in The Assassination The Assassin John Wilkes Booth WANTED! Reconstruction • Reconstruction was the plan for reuniting the nation and rebuilding the South without slavery (planned by Lincoln) • Once 10% of a state’s voters pledged loyalty and a ban on slavery, they could form gov’t/be readmitted to statehood • 13th Amendment of Dec. 18, 1865 made slavery illegal in US • Freedmen’s Bureau provided relief to poor blacks and whites in South; distributed food, built schools, provided teachers Black Codes • Southern states began to pass laws to limit the freedom of African Americans – Black Codes • Blacks without jobs could be arrested and sentenced to forced labor without pay (sounds like slavery!) • President Johnson vetoes bills that gave rights to Blacks – was impeached by Congress; not convicted by one vote • Ku Klux Klan was a secret organization to spread terror to newly freed slaves • Jim Crow Laws were designed to segregate, or separate, blacks and whites in the South • Poll Tax was designed to deny Blacks the vote by making them pay, some places made African Americans pass a literacy test to vote!