* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Goal_3_Civil_War_PPt_2
Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Ulysses S. Grant and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Gettysburg Address wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Lexington wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Port Royal wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Cavalry in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
Blockade runners of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Antietam wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Confederate privateer wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
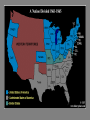
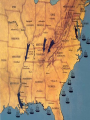
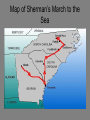
Goal 3 The Civil War 1861-1865 The Union vs. The Confederate States of America The Union (USA) • The North • Blue • President: Abraham Lincoln • Capital: Washington, DC • Commander(s): George McClellan; Ulysses S. Grant * GOAL: preserve the Union The Confederate States of America (The Confederacy) • The South • Grey • President: Jefferson Davis •Capital: Richmond, Va. •Commander: Robert E. Lee •GOAL: preserve states’ rights Advantages Southern Advantages • Profits from “King Cotton” provided money for the war effort. • Great military leaders & a strong military tradition • Soldiers fighting for a “cause” who were highly motivated • • • • • Northern Advantages Larger population so more fighting power More factories to produce war goods More food production Extensive railroad system to transport goods and troops Lincoln was a skilled leader. Anaconda Plan The Union (General Winfield Scott) devised a three part plan to conquer the South: 1. Blockade Southern ports so the South could not export or import; 2. Control the Mississippi River to cut the Confederacy in half; 3. Capture the Confederate capital at Richmond, Va. Major Battles • Ft. Sumter – considered the spark of the Civil War • First Bull Run – considered the first “official” battle of the Civil War • Shiloh- proved the war would be a long one • Antietam – bloodiest single-day battle of the war • Gettysburg – considered the turning point of the war • Vicksburg- effectively cut the Confederacy in two • Appomattox – site of the surrender of Lee to Grant Fort Sumter • The Confederacy fired on Fort Sumter, in the harbor of Charleston, SC on April 12-13, 1861 • These were the first shots fired of the Civil • War It was considered a Southern victory • Lincoln called for volunteers to fight in the war Battle of Bull Run • The Battle of Bull Run was fought on July 21, 1861 in Virginia • Confederacy led by Thomas “Stonewall” Jackson (he stood firm against the Union like a “stone wall”) • The South won! • This was a major morale boost Shiloh • The Battle of Shiloh was fought on April 7, 1862 in Tennessee (considered a “western” battle) • It is significant because it showed the importance of sending out scouts, digging trenches, and building forts • The battle was a draw, but is considered a Confederate loss. Antietam • The Battle of Antietam was fought on September 17, 1862 in Antietam, Maryland. • It was the bloodiest single-day battle in U.S. History. (more than 23,000 men) • Northern victory • Lincoln fired General George McClellan because he was too cautious. Gettysburg • The Battle of Gettysburg was fought July 1-3, 1863 in Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. • This is considered the turning point of the war. After this defeat, the South never attempted a northern invasion again. • The Gettysburg Address was delivered by President Lincoln to honor all those who fought and died on this battlefield. Text of the Gettysburg Address Four score and seven years ago our fathers brought forth on this continent, a new nation, conceived in Liberty, and dedicated to the proposition that all men are created equal. Now we are engaged in a great civil war, testing whether that nation, or any nation so conceived and so dedicated, can long endure. We are met on a great battlefield of that war. We have come to dedicate a portion of that field, as a final resting place for those who here gave their lives that that nation might live. It is altogether fitting and proper that we should do this. But, in a larger sense, we cannot dedicate— we cannot consecrate—we cannot hallow—this ground. The brave men, living and dead, who struggled here, have consecrated it, far above our poor power to add or detract. The world will little note, nor long remember what we say here, but it can never forget what they did here. It is for us the living, rather, to be dedicated here to the unfinished work which they who fought here have thus far so nobly advanced. It is rather for us to be here dedicated to the great task remaining before us—that from these honored dead we take increased devotion to that cause for which they gave the last full measure of devotion—that we here highly resolve that these dead shall not have died in vain—that this nation, under God, shall have a new birth of freedom— and that government of the people, by the people, for the people, shall not perish from the earth. Vicksburg • The Battle of Vicksburg was fought on July 4, 1863. It was actually a siege of Vicksburg, Mississippi. • Union victory • The Union successfully carved the Confederacy in two as a result of this victory. (Anaconda Plan) Map of Siege of Vicksburg Appomattox Courthouse • On April 9, 1865, Southern General Robert E. Lee surrendered to Union General Ulysses S. Grant at Appomattox Courthouse, Virginia. Slavery as a War Aim • Slavery did not become a war aim until 1863. • The Union feared that Britain would join on the side of the South if they did not include abolition as a war aim. • The Emancipation Proclamation was issued as a military decree freeing all slaves in rebelling territories. No slave was emancipated, however, until the end of the war with the passage of the 13th Amendment. 54th Massachusetts Regiment • An all-African American regiment that was formed in Massachusetts • This regiment is famous for its attack on Fort Wagner during the war. The commander Robert Gould Shaw led his men into battle in Charleston harbor. • Many were killed, however, the 54th earned respect for its discipline and courage in battle. • This battle was the subject of the movie Glory. William T. Sherman • March to the Sea • Union commander that believed in total war • Marched through the South burning everything in his path in an effort to break the will of the South Map of Sherman’s March to the Sea Effects of the Civil War • Established the supremacy of federal authority over the states. • Eventually, slavery was abolished, through legislation (13th Amendment). • No state would ever try to secede from the Union again. Civil War: Important Points • Causes of the Civil War (the expansion of slavery was a KEY issue) • Uncle Tom’s Cabin significance • Underground RR & Harriet Tubman • Dred Scott case significance • Significance of KansasNebraska Act • Southern reaction to Lincoln’s election • Southern advantages/Northern advantages • Robert’s E. Lee’s choice to lead the South • Anaconda Plan • Why McClellan was fired • Significance of ALL the battles • Goal of Lincoln in the Civil War • Purpose of the Gettysburg Address • Purpose of the Emancipation Proclamation • General William T. Sherman • Effects of the Civil War Life During the Civil War: North • To help meet the costs of war, the Union government added an income tax of 3% on all income per $800 per year. • The tax was increased over time. • The Union also raised tariffs. • The largest source of funds for the war came from government bonds. • Legal Tender Act of 1862 (government could print greenbacks-paper money)’ • Homestead Act, 1862- encouraged settlement of western lands by granting land at a very low cost to those who would farm it. Life During the Civil War: North • To raise an army, the North passed a conscription law (draft). • Rioting broke out in protest. The New York Draft Riot of 1863 lasted for 4 days. • To avoid the draft, a man could pay $300 and hire a replacement. This led to the phrase, “a rich man’s war, but a poor man’s fight”. Life During the Civil War: North • Copperheads, or Peace Democrats, formed opposing Lincoln’s handling of the war and demanding an end to fighting. • President Lincoln suspended the constitutional right of habeas corpus (can’t be held in jail without a formal charge). Lincoln gave the military the right to arrest people suspected of disloyalty to the Union. Lincoln and the Copperheads Life During the Civil War: South • South lacked the resources to meet the demands of war • Blockade Runners tried to break the blockade of the southern coast in an effort to survive. • President Jefferson Davis authorized the printing of paper money with nothing backing it except the government’s promise to pay. • Inflation and a shortage of food led to rioting in the South. Life During the Civil War: South • Mary Boykin Chestnut of South Carolina kept a diary that has become a famous record of one experience of the war in the South. • The Confederate government enacted conscription laws to help raise troops. Women in the War • Many took over family businesses, farms, or plantations. • Clara Barton worked as a nurse in the war. This led to the formation of the Red Cross. Clara Barton Election of 1864 Impact of the War • 13th, 14th, 15th Amendments • The assassination of Abraham Lincoln by John Wilkes Booth • Mathew Brady- war photographer • Land Grant College Act- gave money from the sale of public lands to states for the establishment of universities that taught agriculture • Tariff passed to protect industrialization • Southern landscape was shattered. • Migration west • Freedmen’s Bureau Mathew Brady’s Photographs