* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Civil War - Saddleback College
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Habeas Corpus Suspension Act (1863) wikipedia , lookup
Texas in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
Gettysburg Address wikipedia , lookup
Missouri secession wikipedia , lookup
Ex parte Merryman wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Secession in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Jubal Early wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
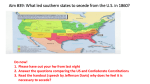
The Civil War (1861-1865) Segment 15 History 16 The Election of Lincoln • Wins Northern, Pacific States Only. No Southern or Border States • Opposition Fragmented into Three Parties: Southern Democrat, Northern Democrat, Constitutional Union • Wins only 39.8% of the Popular Vote. President Lincoln “On the Territorial Question, I am inflexible” Lincoln’s Positions • “House Divided Cannot Stand” • Firm Stand on Territories • Will not touch Slavery in South • Supports USC Amendment Guaranteeing Slavery in South • Slavery will die natural death • Early Believer in “Back to Africa”. Douglas changes him. Electoral College Results of the 1860 Election • Strong Believer in Union. Begs South not to Secede Lincoln Letter to The South Practically Begging For Peace To Alexander H. Stephens For your own eye only. Springfield, Ills. Dec. 22, 1860 Hon. A. H. Stephens-President Lincoln My dear Sir: Your obliging answer to my short note is just received, and for which please accept my thanks. I fully appreciate the present peril the country is in, and the weight of responsibility on me. Do the people of the South really entertain fears that a Republican administration would, directly or indirectly, interfere with their slaves, or with them, about their slaves? If they do, I wish to assure you, as once a friend, and still, I hope, not an enemy, that there is no cause for such fears. The South would be in no more danger in this respect than it was in the days of Washington. I suppose, however, this does not meet the case. You think slavery is right and should be extended; while we think slavery is wrong and ought to be restricted. That I suppose is the rub. It certainly is the only substantial difference between us. Yours very truly A. Lincoln Alexander Stephens Georgia Politician The South Rejects Lincoln • Radical Southerners Use Election as Pretext for Secession • South Carolina votes to Secede: December 20, 1860 • Deep South Votes to Secede in January • Border States in April/May • Lincoln Demonized by Southern Politicians and Press Gov. Francis Pickens South Carolina • Lincoln Overtures Mocked, Ignored, Not Reported in Press “They have thus combined a party exclusively in the Northern States, whose avowed objects, not only endanger the peace, but the very existence of near one-half the States of this Confederacy. And in the recent election for President and Vice-President of these States, they have carried the election upon principles that make it no longer safe for us to rely upon the powers of the Federal Government or the guarantees of the Federal compact” Sequence of Secession: 1860-1861 The Secession Crises Comes to a Head EARLY NORTHERN STRATEGY (Dec 1860-March 1861) • Split Rebellion: Appeal to Border States • Ignore Existing Secession Votes • Search for Compromise • Galvanize Northern Opinion SECESSIONISTS TAKE ACTION • Rebels Seize Federal Land, Property, and Institutions • Border States Vote to Secede • Rebels Surround Federal Military Installations: Demand Surrender • Rebels Meet to form Government • Actions Force Lincoln’s Hand LINCOLN’S ACTIONS • Do Not Surrender Fort Sumter; Resupply • Force Rebels to Fire First: Gain Moral Ground • Holdout, Then Surrender Fort CONSEQUENCES OF SECESSION • War Between the States • West Virginia Secedes from Virginia • Northern Public Opinion Turns on South LINCOLN’S CHOICES • Evacuate Military Installations • Pre-emptive Strike on Rebels • Attempt to Supply Installations • Refuse Surrender, Force Rebels to Fire Rebel Forces Shell Fort Sumter Charleston Harbor – April 12, 1861 The Southern War Strategy The Political Strategy • Form Government • Gain European Recognition • Build Southern Empire • Obtain Independence • Drive Lincoln from office in 1864 Election Rebel Government Forms in Alabama State House, 1861 • Turn Northern Public against the War The Military Strategy • Fight Defensive War • Avoid Major Engagements if possible. Simply Survive Federal Assault Against Fixed Rebel Fortifications – Fredericksburg, VA 1862 • Inflict Casualties on North Make them sue for peace • Invade North 2x to Increase Alarm, Insecurity • Use Small Size as Advantage The Northern War Strategy The Political Strategy • Woo Pro Unionists in the South • Exhaust Southerners; Make them Renunciate Secession • Isolate Southern States from Each Other • Isolate Southern States from Europe General George B. McClellan Federal Army Union Flag 1861 • Emancipate Slaves: Keep Europe Out • Do not use the word “Confederacy” The Military Strategy • Take the Offensive • Besiege Southern Cities – McClellan • NO! Destroy the Rebel Army – Lincoln • Emancipate Slaves – Open Second Front • Control Mississippi River – Split South • Naval Blockade of Southern Ports: Starve South of Supplies, Trade, Food • Use Numerical Superiority to Advantage Richmond, Virginia Lay in Ruin - 1865 Northern Strengths, Southern Weaknesses Northern Strengths • 7 to 1 Population Advantage • Industry: Iron, Steel, Textiles, Goods • Self Sufficient Economy: Enough Farms • Massive Production of War Material • Large Navy – To Blockade the South • Could claim moral high-ground in Europe Charles Frierson, 15th MS Infantry Rebel Army Dwight Woodbury 4th MI Infantry Federal Army • New Immigrants: New Soldiers + Workers • Excellent Equipment, Supplies for Troops • Extensive Transportation Links - Rail • Extensive Communication Links - Telegraph Southern Weaknesses • Trade Dependent Economy • Economy in Ruins: Overprinted Money, Can’t Get Credit, Can’t Sell Goods • Poorly Equipped Troops • Weak, Bickering, Ineffectual Government Northern Industry + War Production - 1861 Lincoln Expands The War Aims WAR AIM -OUTSET OF WAR - 1861 • War to Preserve the Union • Most Northerners cared not about Slavery Gettysburg Address • Most Northerners believed blacks inferior • Northerners Felt Southerners were Traitors WAR AIM AFTER 1862 • Emancipates the Slaves in Union Controlled Parts of South • Begins Talking about War as Moral Crusade to end Slavery • “Dedicated to the Proposition that All Men Are Created Equal” MOTIVES FOR THE CHANGE The Emancipation Proclamation • Open Second Front by Releasing Slaves • Increase Recruitment Efforts for Blacks • Keep Europeans from Recognizing South • Lincoln Becomes a Changed Man RISKS OF STRATEGY • Risk Alienating Northern Whites who fight only to restore The Union The South Surrenders Ground Down by War of Attrition • Army Destroyed • Economy Ruined • Cities and Infrastructure Destroyed The Appomattox Courthouse - Virginia • Slave and Plantation Life Destroyed • Secession Fever Evaporates • Political Will to Fight Disintegrates 1864-65 Southern Politicians Approach North about Re-Entering The Union 1865 The Army Surrounded and Exhausted General Lee Surrenders to General Grant Overprinting Causes Hyper-Inflation 1865 Lee’s Army of Northern Virginia Surrenders The Effects of the War THE HIGH PRICE • 558,052 Dead (Mostly From Disease) • 412,475 Wounded – Many Amputees and Invalids • $5.2 Billion Cost (in 1865 Dollars) • The South Lay in Total Ruin Rebel Dead at Antietam, Maryland, October 1862 WHAT WAS GAINED • The South is Defeated and would re-enter the Union • 13th Amendment to USC Ends Slavery in 1865 • The Secession Question is Resolved in the “Negative” Federal Dead at Cold Harbor, Virginia - 1865 Atlanta in Ruins - 1865 Discussion Topic 1: The South and The Civil War • How did the South Miscalculate by attempting secession from the Union? • Despite the risks and odds against success, why did the South proceed with secession? Discussion Topic 2: Suspending Habeas Corpus Was the Civil War justifiable cause for Lincoln to suspend the Writ of Habeas Corpus? What does the Constitution say about suspending Habeas Corpus? Discussion Topic 3: The War after 1864 Was there any point in the South prolonging the war after Lincoln's 1864 reelection? Having failed in their goal of making a war-weary North vote out Lincoln, should Jefferson Davis have ordered Lee to surrender? Discussion Topic 4: The Civil War and The U.S. Economy In what ways did the Civil War damage the U.S. economy for years after the war?