* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reconstruction Plan
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Carpetbagger wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
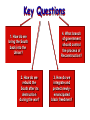
Reconstruction Plans 1. Lincoln’s 2. Johnson’s 3. Radical Republicans Key Questions 1. How do we bring the South back into the Union? 2. How do we rebuild the South after its destruction during the war? 4. What branch of government should control the process of Reconstruction? 3. How do we integrate and protect newlyemancipated black freedmen? Lincoln’s Plan • Pardons to all Southerners (with certain exception) provided they took an oath of allegiance • Restoration of a seceded states to the Union after 10% of qualified voters took the oath • Form a new state government guaranteeing the abolition of slavery • Congress opposed this plan, but Lincoln argued that his presidential powers permitted him to go ahead. President Lincoln’s Plan 10% Plan * Proclamation of Amnesty and Reconstruction (December 8, 1863) * Replace majority rule with “loyal rule” in the South. * He didn’t consult Congress regarding Reconstruction. * Pardon to all but the highest ranking military and civilian Confederate officers. * When 10% of the voting population in the 1860 election had taken an oath of loyalty and established a government, it would be recognized. Johnson’s Plan • Adopted from Lincoln’s plan • Pardoned all Southerners who took the oath (some exceptions, some had to request special pardons) • Recognized the loyal government already established by four of the states • Appointed temporary governors in the other 7 states empowering them to hold elections and form state governments President Johnson’s Plan (10%+) Offered amnesty upon simple oath to all except Confederate civil and military officers and those with property over $20,000 (they could apply directly to Johnson) In new constitutions, they must accept minimum conditions repudiating slavery, secession and state debts. Named provisional governors in Confederate states and called them to oversee elections for constitutional conventions. 1. Disenfranchised certain leading Confederates. EFFECTS? 2. Pardoned planter aristocrats brought them back to political power to control state organizations. 3. Republicans were outraged that planter elite were back in power in the South! Radical Republicans • They held the view that the former CSA were “conquered provinces” and should be punished for disloyalty. • Claimed only the Legislative Br. had the authority to readmit the seceded states • Feared that the southern states would vote Democratic and then regain control of the Federal Government and Congress • Refused to approve the new states governments or seat their representatives in Congress • Radicals took charge of this Reconstruction plan 13th Amendment Ratified in December, 1865. Neither slavery nor involuntary servitude, except as punishment for crime whereof the party shall have been duly convicted, shall exist within the United States or any place subject to their jurisdiction. Congress shall have power to enforce this article by appropriate legislation. th 14 Amendment Ratified in July, 1868. The rights of Citizens may not be abridged by states. * No state shall make or enforce any law which shall abridge the privileges of citizens * Nor shall any state deprive any person of life, liberty, or property without due process of law * Nor deny to any person equal protection of the laws Congress shall have power to enforce, by appropriate legislation, the provisions of this article. Reconstruction Acts of 1867 Military Reconstruction Act * Restart Reconstruction in the 10 Southern states that refused to ratify the 14th Amendment. * Divide the 10 “unreconstructed states” into 5 military districts. 15th Amendment Ratified in 1870. The right of citizens of the United States to vote shall not be denied or abridged by the United States or by any state on account of race, color, or previous condition of servitude. The Congress shall have power to enforce this article by appropriate legislation. Women’s rights groups were furious that they were not granted the vote! Key terms for Chapter 9 • • • • • • • • • • Reconstruction Carpetbaggers Scalawags Sharecropping Tenant farming Freedman Freedman’s Bureau Disenfranchise 13th, 14th and 15th Amendments Henry McNeal Turner