* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Civil War
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Roanoke Island wikipedia , lookup
East Tennessee bridge burnings wikipedia , lookup
Union blockade wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Red River Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Secession in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Blockade runners of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Carpetbagger wikipedia , lookup
Pacific Coast Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Jubal Early wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Texas in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
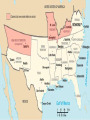
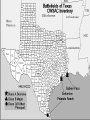
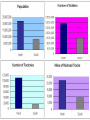
The Civil War Issues that Divide the Country • For years (1850s), the North and South disagreed on issues such as tariffs; distribution of public lands; states’ rights and above all slavery. Issues that Divide the Country • Abolitionists wanted to end slavery. Not all of the Northern whites shared this view and many were prejudice to African Americans: both free and enslaved. Most did not want slavery to spread to new territories. Republican Party vs. Southern Democrats Northerners who were against slavery joined the Republican Party. They also believed that the Southern Democrats were responsible for the economic depression of the late 1850s. The Republican Party thought that prosperity could be brought back by a high tariff, a homestead act, and internal improvement. Republican Party vs. Southern Democrats • Southerners were against the Republican Party because they thought it would end slavery and their way of life. Southern States Vow to Secede • During the 1860 presidential campaign, Southern leaders threatened to secede from the Union if a Republican won the election. They said that sovereign states had entered the Union voluntarily, and they should leave it voluntarily. Southern States Vow to Secede – The Republican candidate Abraham Lincoln won the 1860 presidential election, six states (South Carolina, Miss., Fl., Ala., Geo., and Lou.) withdrew from the Union. The Convention Votes on Secession • Governor Sam Houston opposed seceding and wanted to stay in the Union. A convention was called illegally without his knowledge to see about withdrawing. The Convention Votes on Secession • • Houston found out and called a special session, but the legislature voted for secession. In February 1861, Texas became The Confederacy is Formed • The 7 states met in Montgomery, Alabama. This is known as the Montgomery Convention. The Confederacy is Formed • There they created a new nation, the Confederate States of America. (11 states total) The Confederacy is Formed • They also drew up a new constitution that gave the states much more power than the federal government. • Jefferson Davis was elected President. The Confederacy is Formed • All members of the Confederacy were supposed to take an oath. Sam Houston refused and was removed from office. The Confederacy is Formed – On April 12, 1861, Confederate forces opened fire on U.S. troops at Fort Sumter in Charleston, South Carolina, starting the Civil War. Fort Sumter Texans Become Soldiers • Thousands of Texans joined the army. When there was a shortage of soldiers, the Confederate Congress passed the Conscription Act. This forced enrollment of people into military service between the ages of 18 to 35. Later this number was 17 to 50. • Texans Become Soldiers About 60,000 Texans joined the armed forces of the Confederacy Texans Become Soldiers • Those Texans who were Unionists, meaning favored the Union, left Texas. Some that tried to leave were killed. If they stayed, they ran the risk of being executed. Comparison of Union and CSA[120] Union CSA Total population 22,000,000 (71%) 9,000,000 (29%) Free population 21,567,414 5,500,000 1860 Border state slaves 432,586 NA 1860 Southern slaves NA 3,500,000 Soldiers 2,200,000 (67%) 1,064,000 (33%) Railroad miles 21,788 (71%) 8,838 (29%) Manufactured items 90% 10% Firearm production 97% 3% Bales of cotton in 1860 Negligible 4,500,000 Bales of cotton in 1864 Negligible 300,000 Pre-war U.S. exports 30% 70% Union Strategy Galveston and Brownville • Union ships created a blockade around Texas ports to prevent supplies from getting in or out. Cotton was transported through Mexico and sent to Europe for war materials. Galveston and Brownville • The Union forces took Galveston because it was so weakly defended since all guns had been removed. The Confederates new how important this port was and retook Galveston. Galveston and Brownville The Union also took Brownsville to try to block the trade of cotton through Mexico. The Confederates retook Brownville much like Galveston. Other Battles – – In 1863, the Union tried to invade Texas. The Confederates defeated them at the Battle of Sabine. This battle was important because it ended the North’s campaign to invade Texas. The Confederates also defeated the Union in Louisiana, near the Texas border. The Economy • Farmers and factories made things for the war causing shortages in Texas. This caused women to pick up the slack and do jobs that men had done in the past. The Economy • Prices on goods increased because goods were scarce due to the blockade. The Civil War Ends •In April of 1865, the South surrendered to the more powerful North. The North had more soldiers, more money, and more factories. Civil War Graphs by Wayne by George by Darrielle The Civil War Ends • General Robert E. Lee surrendered to General Ulysses S. Grant in Virginia. The Civil War Ends • The last battle of the Civil War took place in May 1865, at Palmito Ranch, near Brownsville. The Confederate forces defeated the Union forces. The Confederate soldiers then learned that Lee had surrendered a month earlier and the war was over. The Civil War Ends • Nearly 600,000 Northerners and Southerners died. The Civil War Ends • The North’s victory meant the Union was preserved and an end to slavery. President Lincoln had issued the Emancipation Proclamation freeing all the slaves in confederate states. (13th Amendment abolished slavery and was ratified in late 1865) The Civil War Ends • President Lincoln was assassinated by John Wilkes Booth five days after Lee’s surrender. The Civil War Ends • Texas government officials fled to Mexico leaving Texas lawless for some weeks. Eventually, President Andrew Johnson put in a provisional governor. Now Texas faced the problem of rejoining the Union.