* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 4 - Civil War Part 1
East Tennessee bridge burnings wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Perryville wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Harpers Ferry wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Appomattox Station wikipedia , lookup
Second Battle of Corinth wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Henry wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Sumter wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Donelson wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fredericksburg wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Big Bethel wikipedia , lookup
Fort Sumter wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Red River Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Hampton Roads wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Roanoke Island wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Hatteras Inlet Batteries wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Malvern Hill wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Island Number Ten wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Union blockade wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Antietam wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Port Royal wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Forts Jackson and St. Philip wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Blockade runners of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
Confederate privateer wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
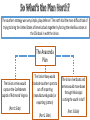
Discuss with the person next to you… What are the 7 basic principles of the U.S. Constitution? (Hint: Unit 2 - #3) 1) Explain with details which side (N or S) was more prepared for war. 2) Describe and detail the North’s “Anaconda Plan”. By February 1861, SEVEN southern states had seceded. My March, only 2 forts in the south remained controlled by the Union (north). One is Fort Sumter in Charleston Harbor. Soldiers at Fort Sumter are in need of supplies. President Lincoln is presented with his first major dilemma… President Lincoln did not want to provoke a full out war, so he decided to send in FOOD supplies only! This forced Jefferson Davis into action. Remember, he is the President of the Confederacy. (the Confederate States of America or CSA) Davis made the first move on April 12, 1861. Davis ordered for the southern troops to begin firing on Fort Sumter, which fell very quickly. Lincoln reacted by calling for volunteers to sign up for war. This caused Virginia to secede. By May of 1861, there were 11 members of the CSA (Confederate States of America). Most citizens (in the north and the south) thought this would be a short war… They were WRONG! Civilian Resources Advantage (N or S) Total Population Industrial Workers Iron Production Food Production Railroads North (2:1) North (4:1) North (15:1) North North Military Resources Advantage (N or S) Eligible for Military Naval Ship Firearm Production Fighting Power North (4:1) North (25:1) North (32:1) North It seemed the north had all the advantages! So what did the south have? 1) Cotton – the south could generate huge revenue from selling cotton on the world market 2) Generals – the south actually had better generals with a stronger military tradition 3) Mindset – the Union was the side interested in getting back together, the south was the side that seceded! The southern strategy was very simple, play defense! The north had the more difficult task of trying to bring the United States of America back together by forcing the rebellious states in the CSA back in with the Union. The Anaconda Plan The Union armies would capture the Confederate capital of Richmond Virginia The Union Navy would blockade southern ports to cut off importing (manufactured goods) or exporting (cotton) (Part 1 Slide) (Part 2 Slide) The Union riverboats and armies would move down through Mississippi cutting the south in half (Part 3 Slide) Discuss with the person next to you… 1) The 3 parts to the Union’s “Anaconda Plan”. 2) Which side (Union or Confederacy) was more prepared for war….give examples! Lincoln ordered his armies to move on Richmond The Confederate armies were camped near Bull Run Creek The battle was back and forth with the North doing well at the start. The 1st Battle of Bull Run Union troops fled & the Southern morale sky-rocketed! The Confederates fought back and held the line (General Johnathan “Stonewall” Jackson) The Union Navy dispatched ships to blockade military and commercial water traffic to & from the south The Union Blockade The Confederate Navy had to develop blockade runners, but was not enough to sustain the war effort in the south March 1862, the Monitor & Merrimack fought in a new style of naval battle IRONCLADS Fort Henry & Fort Donelson Union commander Ulysses S. Grant took 2 strategic forts on the Tennessee and Cumberland Rivers Shiloh Lower Mississippi While gathered near Shiloh, Grant’s forces were attacked. They were able to repel the Confederates but showed many of the flaws for the Union. Commander David Farragut blew through Confederate strong holds to take New Orleans fairly easily. Farragut took the southern end of Mississippi in no time, and the third part of the Anaconda Plan seemed to be working well. Guns and mini-ball Communication The Civil War introduced many new technologies that forced commanders in the field to rethink their military strategies! Naval Improvements Rail Roads The Second and Third parts to the Anaconda Plan (Union’s Plan) were going well, but Part 1 was not (moving on land to capture the southern capital of Richmond). General McClellan was too cautious and refused to move, even though he had an army of 120,000 men! The Union - General McClellan - Cautious commander - Moved slowly - Used only battle tested tactics - After 7 Days Battle, he moved toward the sea - Was able to get ahold of Confederate battle plans - Met Robert E. Lee at ANTIETAM The Confederacy VS - General Robert E. Lee - Very determined - Used unorthodox tactics - Plans included splitting his army from Jackson’s troops - After Lee wins the Second battle of Bull Run, he goes after Washington, D.C. - Met McClellan at ANTIETAM This is the battle that has the single bloodiest day of war during the entire civil war... September 17th = Over 26,000 casualties!! General McClellan does not pursue General Lee’s army as they retreated. This moment represents a chance that the Civil War could have ended. Lincoln fired McClellan as soon as he heard the news.